用数组或链表实现栈及栈的应用(中缀表达式转后缀表达式)
package com.whb.stack;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayStackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试一下ArrayStack 是否正确
//先创建一个ArrayStack对象->表示栈
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(4);
String key = "";
boolean loop = true; //控制是否退出菜单
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(loop) {
System.out.println("show: 表示显示栈");
System.out.println("exit: 退出程序");
System.out.println("push: 表示添加数据到栈(入栈)");
System.out.println("pop: 表示从栈取出数据(出栈)");
System.out.println("请输入你的选择");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key) {
case "show":
stack.list();
break;
case "push":
System.out.println("请输入一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
stack.push(value);
break;
case "pop":
try {
int res = stack.pop();
System.out.printf("出栈的数据是 %d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出~~~");
}
}
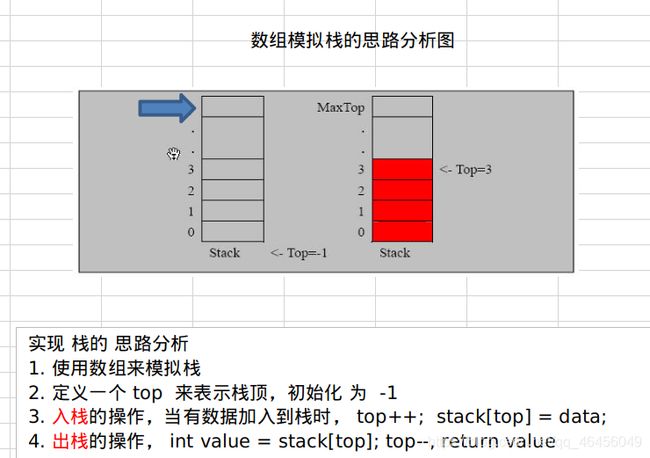
class ArrayStack{
private int maxSize;
private int[] stack;
private int top = -1; // 栈顶
public ArrayStack(int maxSize){
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[this.maxSize];
}
public boolean isFull(){
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return top == -1;
}
public void push(int value){
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
stack[top] = value;
}
public int pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("栈空, 没有数据");
}
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
}
public void list(){
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("栈空, 没有数据");
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
}
链表模拟栈
将新节点放到链表最前端
package com.whb.stack;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LinkListStackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkListStack stack = new LinkListStack(4);
String key = "";
boolean loop = true; //控制是否退出菜单
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(loop) {
System.out.println("show: 表示显示栈");
System.out.println("exit: 退出程序");
System.out.println("push: 表示添加数据到栈(入栈)");
System.out.println("pop: 表示从栈取出数据(出栈)");
System.out.println("请输入你的选择");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key) {
case "show":
stack.show();
break;
case "push":
System.out.println("请输入一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
stack.push(value);
break;
case "pop":
try {
int res = stack.pop();
System.out.printf("出栈的数据是 %d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出~~~");
}
}
class LinkListStack{
public Node top = null;
public int maxSize;
public int size;
public LinkListStack(int maxSize){
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
public boolean isFull(){
if(size==maxSize){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
if(top==null){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void push(int value){
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
Node newNode = new Node(value);
if(top==null){
top = newNode;
}else{
newNode.next = top;
top = newNode;
}
size++;
}
public int pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("----栈空-----");
}
size--;
int value = top.value;
top = top.next;
return value;
}
public void show(){
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("---栈空----");
return;
}
Node temp = top;
while (temp!=null){
System.out.println(temp.value);
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
}
package com.whb.stack;
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
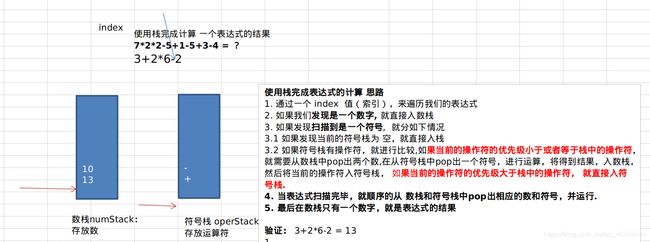
String expression = "7*2/2-5+1-5+3-4";
ArrayStack2 numStack = new ArrayStack2(10);
ArrayStack2 operStack = new ArrayStack2(10);
int index = 0;
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int oper = 0;
int res = 0;
char ch = ' ';
String keepNum = "";
while (true){
ch = expression.charAt(index);
if(operStack.isOper(ch)){
// 如果是运算符
if(!operStack.isEmpty()){
// 如果符号栈有操作符,就进行比较,如果当前的操作符的优先级小于或者等于栈中的操作符,就需要从数栈中pop出两个数,
// 再从符号栈中pop出一个符号,进行运算,将得到结果,入数栈,然后将当前的操作符入符号栈
if(operStack.priority(ch) <= operStack.priority(operStack.peek())){
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);
numStack.push(res);
operStack.push(ch);
}else{
operStack.push(ch);
}
}else{
// 如果为空直接入符号栈..
operStack.push(ch);
}
}else {
// 1. 当处理多位数时,不能发现是一个数就立即入栈,因为他可能是多位数
// 2. 在处理数,需要向expression的表达式的index 后再看一位,如果是数就进行扫描,如果是符号才入栈
// 3. 因此我们需要定义一个变量 字符串,用于拼接
keepNum += ch;
if(index == expression.length() - 1){
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
}else{
if(operStack.isOper(expression.charAt(index+1))){
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
keepNum = "";
}
}
}
index++;
if(index >= expression.length()){
break;
}
}
while (true){
if(operStack.isEmpty()){
break;
}
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);
numStack.push(res);
}
res = numStack.pop();
System.out.printf("表达式 %s = %d", expression, res);
}
}
class ArrayStack2{
private int maxSize;
private int[] stack;
private int top = -1; // 栈顶
public ArrayStack2(int maxSize){
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[this.maxSize];
}
public boolean isFull(){
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return top == -1;
}
public void push(int value){
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
stack[top] = value;
}
// 查看栈顶的值
public int peek(){
return stack[top];
}
public int pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("栈空, 没有数据");
}
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
}
public void list(){
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("栈空, 没有数据");
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
public int priority(int oper){
if(oper == '*' || oper == '/'){
return 1;
}else if(oper == '+' || oper == '-'){
return 0;
}else {
return -1;
}
}
public boolean isOper(char val){
return !('0'<=val&&val<='9');
}
public int cal(int num1, int num2, int oper){
int res = 0;
switch (oper) {
case '+':
res = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
res = num2 - num1;// 注意顺序
break;
case '*':
res = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
res = num2 / num1;
break;
default:
break;
}
return res;
}
}
中缀表达式转后缀表达式
思路分析
/** 中缀表达式转后缀表达式思路:
* 1. 创建两个栈s1和s2
* 2. 遍历中缀表达式,当是数字时,直接压入s1中
* 3. 当是操作符号,如果s2栈顶当前为空或者s2栈顶为"(",则将此操作符直接压入s2
* 4. 当此操作符的优先级小于等于s2栈顶的操作符时,则弹出s2栈顶操作符压入s1中,再次从第3步判断
* 5. 当此操作符号是"("时,直接压入s2栈中
* 6. 当此操作符是")"时,则依次弹出s2中的操作符并压入s1中,直到遇到"(",然后把"("弹出后结束
* 7. 遍历结束后将s2中的剩余操作符依次弹出并放入s1中
* 8. 将s1栈逆序后逐个弹出 */
代码实现
package com.whb.stack;
import java.util.*;
public class PolandNotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/** 中缀表达式转后缀表达式思路:
* 1. 创建两个栈s1和s2
* 2. 遍历中缀表达式,当是数字时,直接压入s1中
* 3. 当是操作符号,如果s2栈顶当前为空或者s2栈顶为"(",则将此操作符直接压入s2
* 4. 当此操作符的优先级小于等于s2栈顶的操作符时,则弹出s2栈顶操作符压入s1中,再次从第3步判断
* 5. 当此操作符号是"("时,直接压入s2栈中
* 6. 当此操作符是")"时,则依次弹出s2中的操作符并压入s1中,直到遇到"(",然后把"("弹出后结束
* 7. 遍历结束后将s2中的剩余操作符依次弹出并放入s1中
* 8. 将s1栈逆序后逐个弹出
*/
//String suffixExpression = "30 4 + 5 * 6 -";
// String suffixExpression = "4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / +"; // 76
// List list = getListString(suffixExpression);
// System.out.println("rpnList = " + list);int res = calculate(list);
// System.out.println("计算的结果是 = " + res);
String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5";//注意表达式
List<String> infixExpressionList = toInfixExpressionList(expression);
System.out.println("中缀表达式对应的List=" + infixExpressionList); // ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5]
List<String> suffixExpreesionList = parseSuffixExpreesionList(infixExpressionList);
System.out.println("后缀表达式对应的List" + suffixExpreesionList); //ArrayList [1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,–]
System.out.printf("expression=%d", calculate(suffixExpreesionList)); // ?
}
// ArrayList [1,+,(,(,2,+,3,),*,4,),-,5] =》 ArrayList [1,2,3,+,4,*,+,5,–]
public static List<String> parseSuffixExpreesionList(List<String> ls) {
List<String> s1 = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<String> s2 = new Stack<>();
System.out.println(ls);
for (String str:ls){
if (str.matches("\\d+")){
s1.add(str);
}else {
if(str.equals("(")){
s2.push(str);
}else if(str.equals(")")){
while (!s2.peek().equals("(")){
s1.add(s2.pop());
}
s2.pop();
}else {
if(s2.empty()){
s2.push(str);
}else {
while (Operation.getValue(str)<=Operation.getValue(s2.peek())){
s1.add(s2.pop());
if(s2.empty()){
break;
}
}
s2.push(str);
}
}
}
}
while (!s2.empty()){
s1.add(s2.pop());
}
return s1;
}
// 将中缀表达式转成对应的List
public static List<String> toInfixExpressionList(String s){
List<String> ls = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;
String str;
char c;
while (i<s.length()){
// 非数字时
if((c=s.charAt(i))<'0' || (c=s.charAt(i))>'9'){
ls.add("" + c);
i++;
}else {
str = "";
while (i < s.length()){
c = s.charAt(i);
if(c>='0' && c<='9'){
str += c;
i++;
}else {
break;
}
}
ls.add(str);
}
}
return ls;
}
public static List<String> getListString(String exp){
String[] strs = exp.split(" ");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s:strs){
list.add(s);
}
return list;
}
public static int calculate(List<String> ls){
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
for (String item:ls){
// 正则匹配到是数的话压入栈中
if(item.matches("\\d+")){
stack.push(item);
}else{
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int res = 0;
if(item.equals("+")){
res = num1 + num2;
} else if (item.equals("-")) {
res = num1 - num2;
} else if (item.equals("*")) {
res = num1 * num2;
} else if (item.equals("/")) {
res = num1 / num2;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误");
}
stack.push("" + res);
}
}
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
}
class Operation{
private static Map<String, Integer> valmap = new HashMap<>();
static {
valmap.put("+",0);
valmap.put("-",0);
valmap.put("*",1);
valmap.put("/",1);
valmap.put("(",-1);
}
public static int getValue(String operation) {
int a = valmap.get(operation);
return a;
}
}