Python KMeans聚类分析
今天用python实现了一下简单的聚类分析,顺便熟悉了numpy数组操作和绘图的一些技巧,在这里做个记录。
from pylab import *
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
## 利用numpy.append()函数实现matlab多维数组合并的效果,axis 参数值为 0 时是 y 轴方向合并,参数值为 1 时是 x 轴方向合并,分别对应matlab [A ; B] 和 [A , B]的效果
#创建5个随机的数据集
x1=append(randn(500,1)+5,randn(500,1)+5,axis=1)
x2=append(randn(500,1)+5,randn(500,1)-5,axis=1)
x3=append(randn(500,1)-5,randn(500,1)+5,axis=1)
x4=append(randn(500,1)-5,randn(500,1)-5,axis=1)
x5=append(randn(500,1),randn(500,1),axis=1)
# 下面用较笨的方法把5个数据集合并成 (2500,2)大小的数组data
data=append(x1,x2,axis=0)
data=append(data,x3,axis=0)
data=append(data,x4,axis=0)
data=append(data,x5,axis=0)
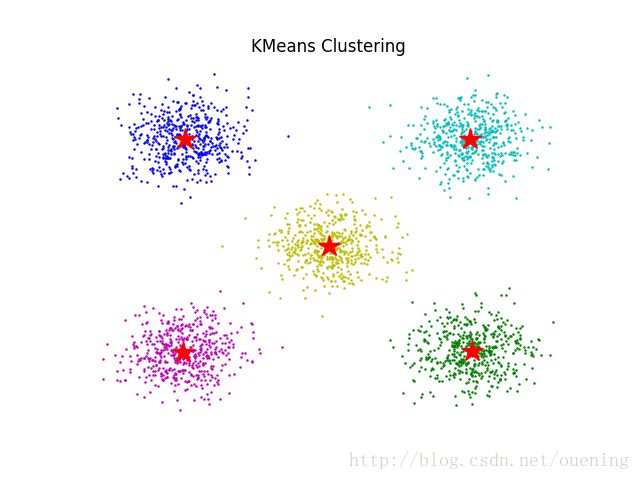
plot(x1[:,0],x1[:,1],'oc',markersize=0.8)
plot(x2[:,0],x2[:,1],'og',markersize=0.8)
plot(x3[:,0],x3[:,1],'ob',markersize=0.8)
plot(x4[:,0],x4[:,1],'om',markersize=0.8)
plot(x5[:,0],x5[:,1],'oy',markersize=0.8)
k=KMeans(n_clusters=5,random_state=0).fit(data)
t=k.cluster_centers_ # 获取数据中心点
plot(t[:,0],t[:,1],'r*',markersize=16) # 显示这5个中心点,五角星标记~
title('KMeans Clustering')
box(False)
xticks([]) # 去掉坐标轴的标记
yticks([])
show()2017/01/11更新
今天重新试运行程序的出现报错了,提示导入NUMPY_MKL失败,因为之前用命令pip install -U numpy手动更新了numpy,最初的是在http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#numpy 里下载的numpy-1.11.2+mkl-cp27-cp27m-win_amd64.whl 文件安装的,只要重新安装回去就可以了
2017/1/18
python中还有一个叫plotly 的package,可以通过pip install plotly 或 pip3 install plotly(Python3.X) ,使用这个package可以绘制精美的图像,官网中有很多例子介绍,同时plotly 还支持matlab,R等,但是个人觉得plotly 的绘图语法相比matplotlib 的繁琐,需要照着例程来修改才比较方便,不过如果只是要想数据可视化更好看的话参考官网例程并做修改也无妨,下面是来自官网的一段示例代码:
import plotly.plotly as py
import plotly.graph_objs as go
import plotly
import numpy as np
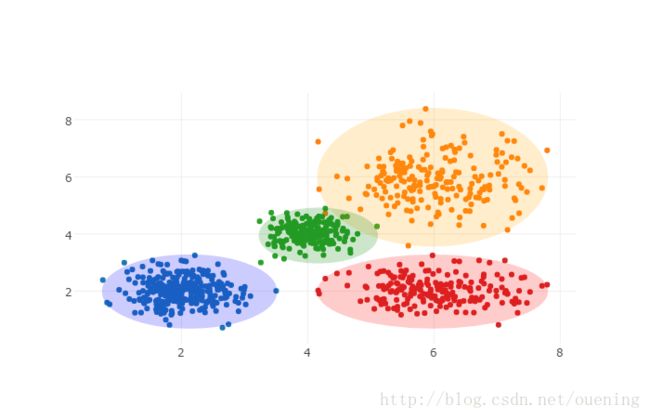
#生成三组高斯分布(Gaussian Distribution)点集
x0 = np.random.normal(2, 0.45, 300)
y0 = np.random.normal(2, 0.45, 300)
x1 = np.random.normal(6, 0.8, 200)
y1 = np.random.normal(6, 0.8, 200)
x2 = np.random.normal(4, 0.3, 200)
y2 = np.random.normal(4, 0.3, 200)
#创建图形对象 graph object
trace0 = go.Scatter(
x=x0,
y=y0,
mode='markers',
)
trace1 = go.Scatter(
x=x1,
y=y1,
mode='markers'
)
trace2 = go.Scatter(
x=x2,
y=y2,
mode='markers'
)
trace3 = go.Scatter(
x=x1,
y=y0,
mode='markers'
)
#布局是一个字典,字典关键字keys包括:'shapes', 'showlegend'
layout = {
'shapes': [
{
'type': 'circle',
'xref': 'x',
'yref': 'y',
'x0': min(x0),
'y0': min(y0),
'x1': max(x0),
'y1': max(y0),
'opacity': 0.2,
'fillcolor': 'blue',
'line': {
'color': 'blue',
},
},
{
'type': 'circle',
'xref': 'x',
'yref': 'y',
'x0': min(x1),
'y0': min(y1),
'x1': max(x1),
'y1': max(y1),
'opacity': 0.2,
'fillcolor': 'orange',
'line': {
'color': 'orange',
},
},
{
'type': 'circle',
'xref': 'x',
'yref': 'y',
'x0': min(x2),
'y0': min(y2),
'x1': max(x2),
'y1': max(y2),
'opacity': 0.2,
'fillcolor': 'green',
'line': {
'color': 'green',
},
},
{
'type': 'circle',
'xref': 'x',
'yref': 'y',
'x0': min(x1),
'y0': min(y0),
'x1': max(x1),
'y1': max(y0),
'opacity': 0.2,
'fillcolor': 'red',
'line': {
'color': 'red',
},
},
],
'showlegend': False,
}
data = [trace0, trace1, trace2, trace3]
#图像包括数据部分和布局部分
fig = {
'data': data,
'layout': layout,
}
#使用离线的方式绘制图像,因为没有注册官方的网站,而且那个网站不容易进去,所以用离线绘制
plotly.offline.plot(fig, filename='clusters')
总结:plotly 这个库虽然语法比较繁琐,但是对数据显示要求较高的情况下可以充分利用,一般绘图的话使用matplotlib比较方便,特别是ipython模式下先执行from pylab import * 可以获得和MATLAB 类似的工作环境。