python决策树及规则解析
上一篇博文用随机森林实现了发欺诈模型的构建,但随机森林隶属于集成学习的一种,属于黑箱算法,为了增强模型的解释性,本篇博文采用同样的数据适用决策树算法再次构建模型,并输出可视化二叉树形图以及规则文本,并对决策树输出规则文本进行解析,形成sql语句。这样的话决策树每个分支下的客户群规则画像就变得一目了然,并可以使用解析后的sql语句直接运行在数据库。
具体的数据加载、数据清洗及预处理、特征工程、数据抽样及拆分等过程见博主上一篇博文:
python随机森林算法实现反欺诈案例完整建模流程
……(续)
接上一篇博文模型验证及之前程序…
决策树分类–未剪枝
模型训练
from sklearn import tree
def Model_Train(x_train,y_train):
model = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier() #model = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy') 使用信息熵作为划分标准,对决策树进行训练
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
return model
model_tree = Model_Train(X_train,y_train)
输出各指标影响力
系数反映每个特征的影响力。越大表示该特征在分类中起到的作用越大
print(model_tree.feature_importances_)
模型评估
#进行模型评估,计算出相应的准确率、召回率和F值
y_pred_rf = model_tree.predict(X_test)
# Compute confusion matrix
cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred_rf)
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
print(cnf_matrix)
print("Precision metric in the testing dataset: ", (cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[0,1] + cnf_matrix[1,1])).round(4))
print("Recall metric in the testing dataset: ", (cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[1,0] + cnf_matrix[1,1])).round(4))
决策树可视化二叉树
import pydotplus
play_feature_E = 'TOTOL_7_ZJ_CNT', 'H_MAX_CIRCLE', 'CHG_CELLS', 'ZJ_CNT_RATE', 'TOTOL_7_ZJ_DUR', 'ZHANBI', 'CORP_USER_NAME_家庭客户', 'TERM_PRICE_未识别', 'WEEK_CNT', 'DIS_OPP_HOME_NUM', 'MIX_CDSC_FLG_0.0', 'ALL_LL_DUR', 'TOTAL_DIS_BJ_NUM_RATE', 'ALL_LL_USE', 'MIX_CDSC_FLG_1.0', 'TOTOL_7_BJ_D_DUR', 'BJ_LOCAL_CNT', 'ACT_DAY_RATE', 'ZJ_TOTAL_DURATION', 'CUST_ASSET_CNT', 'ZJ_DURATION_RATIO_0_15', 'AMT', 'ZJ_AVG_DURATION', 'GENDER_未识别', 'ZJ_DURATION_30_60_CNT', 'DURATION_RATIO_0_15', 'ZJ_DURATION_RATIO_15_30'
play_class = 'no','yes'
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(model_tree,
out_file = None,
feature_names = play_feature_E,
class_names = play_class,
filled = True,
rounded = True,
special_characters = True)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
graph.write_pdf('tree_model_fsr_output101.pdf')
决策树分类–预剪枝
模型训练
from sklearn import tree
def Model_Train(x_train,y_train):
model = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(min_samples_split = 30,min_samples_leaf = 30)
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
return model
model_tree = Model_Train(X_train,y_train)
其中:
- min_samples_split:当对一个内部结点划分时,要求该结点上的最小样本数,默认为2。
- min_samples_leaf:设置叶子结点上的最小样本数,默认为1。当尝试划分一个结点时,只有划分后其左右分支上的样本个数不小于该参数指定的值时,才考虑将该结点划分,换句话说,当叶子结点上的样本数小于该参数指定的值时,则该叶子节点及其兄弟节点将被剪枝。在样本数据量较大时,可以考虑增大该值,提前结束树的生长。
本次案例主要采用min_samples_split、min_samples_leaf两个参数来对决策树进行剪枝。
模型评估
#进行模型评估,计算出相应的准确率、召回率和F值
y_pred_rf = model_tree.predict(X_test)
# 生成混淆矩阵
# Compute confusion matrix
cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred_rf)
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
print(cnf_matrix)
print("Precision metric in the testing dataset: ", (cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[0,1] + cnf_matrix[1,1])).round(4))
print("Recall metric in the testing dataset: ", (cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[1,0] + cnf_matrix[1,1])).round(4))

对比预剪枝决策树模型和未剪枝决策树模型评估结果可以看出,预剪枝后,模型查准率有所提升,但查全率有所下降,说明决策树剪枝后,对新数据的预测泛性更好,不易过拟合。
输出规则文本及可视化图
tree.export_graphviz(model_tree,out_file = 'tree_rule102.txt',
feature_names = play_feature_E,
class_names=['0', '1'],
filled=True,
node_ids=True,
rounded=True,
special_characters=True)
import pydotplus
play_feature_E = 'TOTOL_7_ZJ_CNT', 'H_MAX_CIRCLE', 'CHG_CELLS', 'ZJ_CNT_RATE', 'TOTOL_7_ZJ_DUR', 'ZHANBI', 'CORP_USER_NAME_家庭客户', 'TERM_PRICE_未识别', 'WEEK_CNT', 'DIS_OPP_HOME_NUM', 'MIX_CDSC_FLG_0.0', 'ALL_LL_DUR', 'TOTAL_DIS_BJ_NUM_RATE', 'ALL_LL_USE', 'MIX_CDSC_FLG_1.0', 'TOTOL_7_BJ_D_DUR', 'BJ_LOCAL_CNT', 'ACT_DAY_RATE', 'ZJ_TOTAL_DURATION', 'CUST_ASSET_CNT', 'ZJ_DURATION_RATIO_0_15', 'AMT', 'ZJ_AVG_DURATION', 'GENDER_未识别', 'ZJ_DURATION_30_60_CNT', 'DURATION_RATIO_0_15', 'ZJ_DURATION_RATIO_15_30'
play_class = 'no','yes'
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(model_tree,
out_file = None,
feature_names = play_feature_E,
class_names = play_class,
filled = True,
rounded = True,
special_characters = True)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data)
graph.write_pdf('tree_model_fsr_output102.pdf')
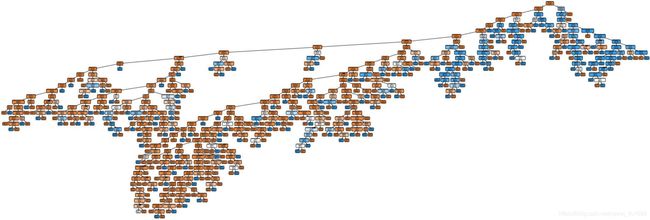
完整树:

完整树局部:

预剪枝决策树二叉树相比未剪枝决策树二叉树,可以看出二叉树包括树深和分叉都要单薄很多,还可以继续调节min_samples_split、min_samples_leaf两个参数来对决策树进行剪枝程度的控制。
决策树输出规则解析
不管是决策时输出二叉树还是文本规则都是原始规则,不够直观,下面以预剪枝决策树输出规则为例进行解析,生成我们通常容易理解的语言,比如sql语句。
第一步:读取文件,写入对应中间结果表
filepath="tree_rule102.txt"
dict_node = {
}
label = []
value_pool = []
#list_node = []
list_direction = []
dict_direction = {
}
f_w = open(filepath,'r',encoding='UTF-8')
line = f_w.readline()
while line:
if line.startswith('digraph'):
line = f_w.readline()
continue
if line.startswith('node'):
line = f_w.readline()
continue
if line.startswith('edge'):
line = f_w.readline()
continue
if line.startswith('}'):
line = f_w.readline()
continue
if line.find('label=)>-1:
#list_node.append(line)
pos = line.index('[')
key = line[0:pos].strip()
content = line[pos:].strip()
dict_node[key] = content
if line.find('->') > -1:
if line.find('[labeldistance') > -1:
pos = line.index('[')
line = line[0:pos]
temp = line.split('->')
else:
temp = line.replace(";","").split('->')
key = int(temp[0].strip())
value = temp[1].strip()
list_direction.append(str(key)+","+str(value))
if key in dict_direction:
temp_value = dict_direction[key]
value = temp_value+","+value
dict_direction[key] = value
line = f_w.readline()
try:
if '&le' in line:
continue
else:
lb = line[line.index('class =')+8: line.index('>, fillcolor')]
label.append(lb)
except ValueError:
continue
try:
if '&le' in line:
continue
else:
value_tmp = line[line.index('value =')+8: line.index('
class')]
value_tmp = eval(value_tmp)
value_pool.append(value_tmp)
except ValueError:
continue
f_w.close()
第二步:装入全路径树字典
按照事先已知的节点方向列表(顺序),定义树路径字典,根据顺序动态拼装装入到全路径树字典
dict_tree ={
}
for j in list_direction:
dict_tree[j] = j
temp = j.split(',')
#print("j="+j)
for key in dict_tree.keys(): # 01 02 23
key_temp = key.split(',')
if key_temp[0] != temp[0] :
if key_temp[1] == temp[0]:
#print("key="+key)
temp_node = dict_tree.get(key)+","+temp[1]
dict_tree[j] = temp_node
else:
pass
list_result = [] #取全路径树字典value, 放入list_result
for value in dict_tree.values():
list_result.append(value)
#根据生成的全路径列表,去掉路径包含关系子项
list_del = [] #确定要删除的子项
for v in range(len(list_result)):
for x in range(len(list_result)):
if list_result[v]==list_result[x]:
continue
#print("list_result[x]="+list_result[x])
#print("list_result[v]="+list_result[v])
if list_result[x].find(list_result[v])>-1:
list_del.append(list_result[v])
x=v
break
#定义中间结果,过滤list_result中的需求删除的子项,写入到list_response
list_response=[] #最终树路径结果表
for item in list_result:
#print(item)
#print(item in list_del)
if item not in list_del:
list_response.append(item)
#解析dict_node节点字典,确定节点编号对应的内容
node_dict = {
}#节点编号-内容表
for keys,values in dict_node.items():
key =keys
value = values.split('
')
if len(value)>0:
if value[1].find('gini')==-1: #非叶子结点
#print(value[1])
node_dict[keys] = value[1]
else:
#print("values is null")
pass
#根据树路径结果表 和 节点关系字典dict_direction ,确定节点的左右
result = []
for item in list_response:
#print("item="+item)
temp = item.split(',')
end = len(temp)
start_pos = 0
result_end = [] #按照树路径结果表定义字典,进行输出
while start_pos+1 < end:
str_sub = temp[start_pos:start_pos+2] #将节点顺序二二组合,根据字典确认符号关系(需要多次遍历节点关系字典,考虑那里可以优化)
start_pos += 1
node = int(str_sub[0])
next_node = int(str_sub[1])
if node in dict_direction:
values = dict_direction.get(node).split(',')
node_value = node_dict.get(str(node))
if next_node == int(values[0]): #根据节点关系字典dict_direction,因为是二叉树,所以关系表中对应的关系为左[0]右[1],
#print(str(node)+"<="+values[0])
node_value = node_value.replace("≤","<=")
if next_node == int(values[1]):
#print(str(node)+">"+values[1])
node_value = node_value.replace("≤",">")
result_end.append(node_value)
else:
pass
result.append(result_end)
第三步:union处理
a = [[i, j] for i, j in zip(label, result) if i == '1']
b = [' and '.join(i[1]) for i in a]
c = ' and '.join(b)
for i in range(len(b)):
temp = b[i].split('and')
remove_dup_col_dict = {
}
for item in temp:
#print(item.strip())
if item.find('<=')>0:
temp_str = item.split('<=')
col_str = temp_str[0].strip()
temp_key = col_str+" <="
if temp_key in remove_dup_col_dict.keys():
temp_value = remove_dup_col_dict[temp_key]
if temp_value > temp_str[1].strip():
remove_dup_col_dict[temp_key] = temp_str[1].strip()
else:
remove_dup_col_dict[temp_key] = temp_str[1].strip()
if item.find('>')>0:
temp_str = item.split('>')
col_str = temp_str[0].strip()
temp_key = col_str+" >"
if temp_key in remove_dup_col_dict.keys():
temp_value = remove_dup_col_dict[temp_key]
if temp_value < temp_str[1].strip():
remove_dup_col_dict[temp_key] = temp_str[1].strip()
else:
remove_dup_col_dict[temp_key] = temp_str[1].strip()
if len(remove_dup_col_dict)>0:
temp_str=""
for key,value in remove_dup_col_dict.items():
temp = key +" "+value
temp_str = temp_str +temp + ' and '
temp_str=temp_str[:-4]
第四步:拼接SQL
# -----------------------最后把结果放在了temp_str当中---------------------
end = '0'
sql_start = 'select case '
sql_end = 'else ' + end + ' end;'
result_sql = []
result_sql.append(sql_start)
for i in range(len(result)):
sql_ste = 'when ' + ' and '.join(result[i]) + ' then ' + label[i] + '\n'
result_sql.append(sql_ste)
result_sql.append(sql_end)
第五步:将规则读取出来并读入txt
with open('out_sql102.txt', 'w') as f:
f.writelines(result_sql)