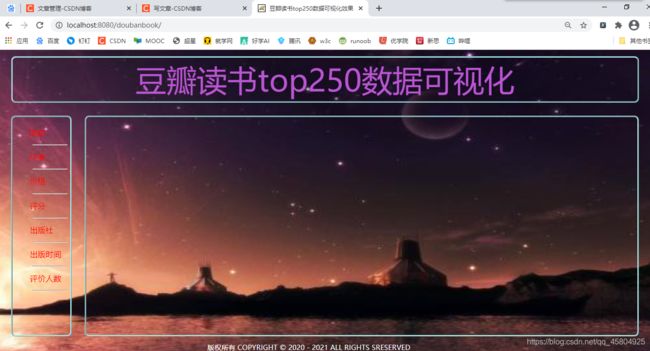
python爬虫豆瓣读书top250+数据清洗+数据库+Java后端开发+Echarts数据可视化(四)
之前的博客已经写了python爬取豆瓣读书top250的相关信息和清洗数据、将数据导入数据库并创建相应的数据表,以及进行项目准备工作,接下来开始正式编写后台代码。
如果有没看懂的或是不了解上一部分说的是什么内容的,请看
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45804925/article/details/112848887
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45804925/article/details/112898570
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45804925/article/details/112989112
创建本项目采用的是JavaEE经典三层架构,依次实现对实体类、持久层、业务层、web层、前端页面的开发。
不太了解的话,可以看看我下面的图: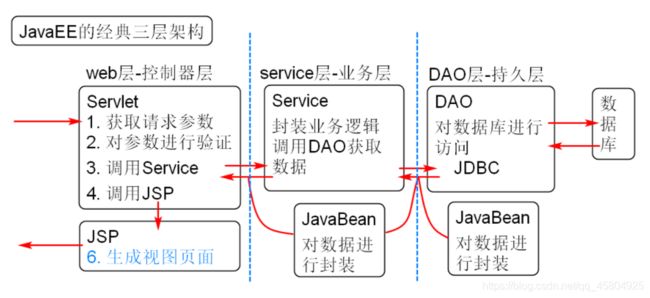
接下来先看一下都需要新建哪些package和相应文件。接下来一步步实现这些。
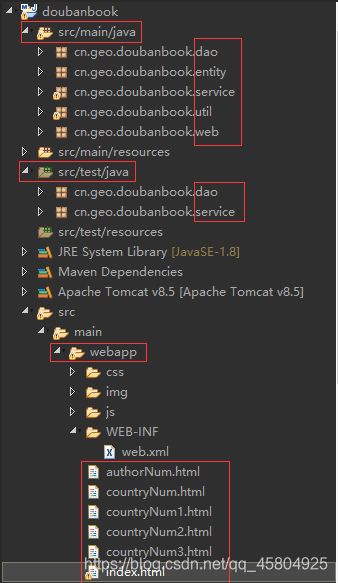
依次要实现的分别是关于国家、作者、价格、评分、出版社、出版时间、评价人数的相关数据可视化。
1. 主页面实现效果
2 各个国家出版图书数量
2.1 在cn.geo.doubanbook.entity包下创建Country.java类
package cn.geo.doubanbook.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* 各个国家出版的图书数量
* @author SGG
*
*/
public class Country implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3474471822110684432L;
private String country;
private Integer num;
public Country() {
}
public Country(String country, Integer num) {
super();
this.country = country;
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Country [country=" + country + ", num=" + num + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((country == null) ? 0 : country.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((num == null) ? 0 : num.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Country other = (Country) obj;
if (country == null) {
if (other.country != null)
return false;
} else if (!country.equals(other.country))
return false;
if (num == null) {
if (other.num != null)
return false;
} else if (!num.equals(other.num))
return false;
return true;
}
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public Integer getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(Integer num) {
this.num = num;
}
}
在这个代码中主要有三步:
- 定义两个私有变量
private String country; private Integer num; - 右键——>source——>无参构造器、带参构造器、get/set方法、hashCode和equals方法、toString方法
如下图所示:

- 实现Serializable接口
PS: 如果单独的实现Serializable接口不会报错,但是会有警报,如下图所示:

选择上图所框出来的即可。
2.2 在cn.geo.doubanbook.dao包下创建CountryDAO.java类
package cn.geo.doubanbook.dao;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
import cn.geo.doubanbook.entity.Country;
import cn.geo.doubanbook.util.DBUtils;
/**
* 各个国家出版的图书数量的持久层类
* @author SGG
*
*/
public class CountryDAO {
/**
* 查询各个国家出版的图书数量
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public List<Country> listCountry() throws SQLException {
List<Country> list = new ArrayList<Country>(248);
// 从数据库连接池获取连接
Connection conn = DBUtils.getConn();
// 声明SQL的执行器
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
// 执行SQL语句
String sql = "select * from book_country_num";
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
// 对结果集进行操作
while(rs.next()) {
// 获取该行数据中的指定字段
String country = rs.getString("country");
int num = rs.getInt("num");
// 创建Country对象,封装一行数据
Country cn= new Country(country, num);
// 将Country对象 保存到集合中
list.add(cn);
}
// 关闭连接释放资源
st.close();
conn.close();
return list;
}
}
2.3 持久层测试用例开发
- 首先,在项目中可以使用JUnit来构建测试用例的运行环境。在项目的pom.xml中添加对junit的依赖:
<!-- junit依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
- 然后,在项目的src/test/java下的cn.geo.doubanbook.dao包下创建CountryDAOTest.java类,作为CountryDAO的测试类。
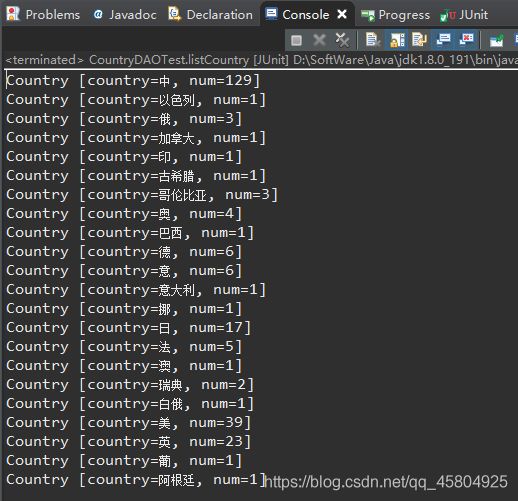
接下来,在CountryDAOTest.java类中,开发对应的测试方法,测试方法一般与被测试方法同名,在测试方法中,调用被测试类的目标方法,并输出查询到的数据,查看数据是否正常输出。
在该方法前添加@Test注解,代表该方法是Junit的一个测试方法。
package cn.geo.doubanbook.dao;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import cn.geo.doubanbook.dao.CountryDAO;
import cn.geo.doubanbook.entity.Country;
public class CountryDAOTest {
CountryDAO dao = new CountryDAO();
/**
* 测试CountryDAO中的listCountry方法中的方法
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Test
public void listCountry() throws SQLException{
List<Country> list = dao.listCountry();
list.forEach(item->System.out.println(item));
}
}
- 进行测试
将鼠标定位在方法名上,右键——>Run as——>JUnit Test
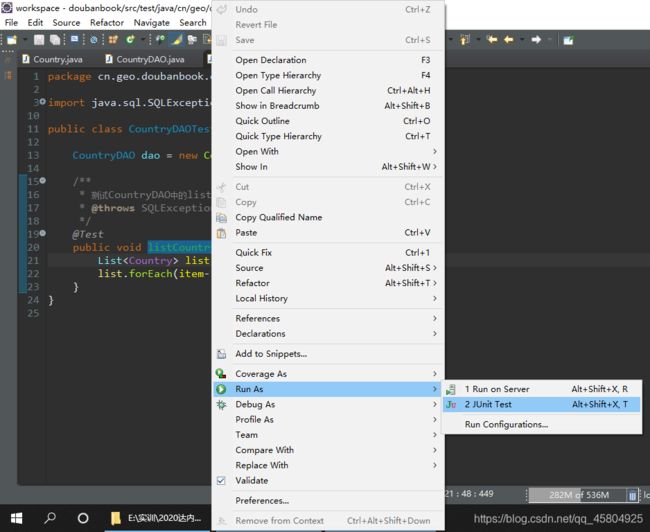
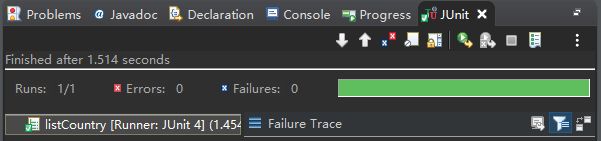
在下方的视图工具栏中,会多出一个junit的视图,如果方法正常运行,会显示绿色进度条。如果方法运行出现异常,会显示红色进度条。测试结果如下:
2.4 在cn.geo.doubanbook.entity包下创建CountryVO.java类
创建cn.geo.doubanbook.service包下的CountryService.java类,作为国家书籍数量数据的业务层类,该类中负责封装具体的业务处理逻辑,负责调用持久层方法获取数据。
在本用例中,持久层查询到的数据以Country.java的集合的形式进行封装,与前端ECharts所需的数据格式不符。
在业务层中,需要将持久层查询到的数据转变成ECharts所需的数据格式。 新的数据格式使用CountryVO.java进行封装。
package cn.geo.doubanbook.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 封装页面所需数据的JavaBean
*/
public class CountryVO implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7471693957674857938L;
private List<String> xData;
private List<Integer>yData;
public CountryVO() {
}
public CountryVO(List<String> xData, List<Integer> yData) {
super();
this.xData = xData;
this.yData = yData;
}
public List<String> getxData() {
return xData;
}
public void setxData(List<String> xData) {
this.xData = xData;
}
public List<Integer> getyData() {
return yData;
}
public void setyData(List<Integer> yData) {
this.yData = yData;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((xData == null) ? 0 : xData.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((yData == null) ? 0 : yData.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
CountryVO other = (CountryVO) obj;
if (xData == null) {
if (other.xData != null)
return false;
} else if (!xData.equals(other.xData))
return false;
if (yData == null) {
if (other.yData != null)
return false;
} else if (!yData.equals(other.yData))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CountryVO [xData=" + xData + ", yData=" + yData + "]";
}
}
方法也是三步——同创建实体类2.1所示。
2.5 在cn.geo.doubanbook.service包下创建CountryService.java类
package cn.geo.doubanbook.service;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import cn.geo.doubanbook.dao.CountryDAO;
import cn.geo.doubanbook.entity.Country;
import cn.geo.doubanbook.entity.CountryVO;
public class CountryService {
private CountryDAO dao = new CountryDAO();
public CountryVO findCountry() {
// 调用持久层方法,查询所需数据
List<Country> list = null;
try {
list = dao.listCountry();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
// 创建xData,保存x轴数据
List<String> xData = new ArrayList<String>(list.size());
// 创建yData,保存y轴数据
List<Integer> yData = new ArrayList<Integer>(list.size());
// 遍历持久层查询到的数据
for(Country cn: list) {
xData.add(cn.getCountry());
yData.add(cn.getNum());
}
// 创建CountryVO对象,封装xData和yData
CountryVO vo = new CountryVO(xData, yData);
return vo;
}
}
2.6 业务层测试用例开发
在src/test/java下cn.geo.doubanbook.service包下开发CountryServiceTest.java类,并在其中开发相应的测试方法,具体代码如下:
package cn.geo.doubanbook.service;
import org.junit.Test;
import cn.geo.doubanbook.entity.CountryVO;
public class CountryServiceTest {
CountryService service = new CountryService();
@Test
public void findCountry() {
CountryVO vo = service.findCountry();
System.out.println(vo);
}
}
2.7 Web层开发
基于JavaEE的设计,Web层需要开发Servlet来响应用户的请求。开发者开发的类,必须继承javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet,才能被Tomcat作为一个Servlet来使用。
javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet没有包含在JDK的library中,因此需要在当前项目中额外引入对应的jar包,引入的方式有2种:
- 通过Maven添加servlet的依赖
- 在项目中引入Tomcat的library
本项目中采用第二种方式:右键项目 -> Build Path -> Configure Build Path->选择Libraries标签 -> 点击右侧的 Add Library… -> 在列表中选择 Server Runtime -> 选择Tomcat8.5 -> OK -> Apply -> Apply and Close,配置完成。
根据业务需求,Servlet需要将vo对象转变成JSON字符串,这里使用阿里巴巴的fastjson插件来实现。
首先,在pom.xml中添加对fastjson的依赖:
<!-- json解析jar包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.7</version>
</dependency>
然后,在cn.geo.doubanbook.web包下的CCountryServlet.java中开发响应用户请求的代码:
package cn.geo.doubanbook.web;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import cn.geo.doubanbook.entity.CountryVO;
import cn.geo.doubanbook.service.CountryService;
public class CountryServlet extends HttpServlet{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4869015457920074899L;
private CountryService service = new CountryService();
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 调动业务层方法,获取CountryVO
CountryVO vo = service.findCountry();
// 判断CountryVO是否不为null
if(vo != null) {
// 将vo对象转变成JSON字符串-基于JSON插件实现
String jsonStr = JSON.toJSONString(vo);
// 通知浏览器,本次返回的数据是JSON格式
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
// 将JSON字符串添加到response对象中
resp.getWriter().write(jsonStr);
} else {
// 返回空的json字符串
// 通知浏览器,本次返回的数据是JSON格式
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
// 将JSON字符串添加到response对象中
resp.getWriter().write("{}");
}
}
}
2.8 在webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml文件中对Servlet进行配置:
<!-- 配置Servlet的名称和所在位置 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>CountryServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>cn.geo.doubanbook.web.CountryServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<!-- 配置Servlet映射的路径 -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>CountryServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/country</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
2.9 启动项目
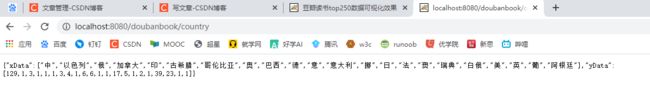
在浏览器地址栏直接访问http://localhost:8080/nybikeT/tripDayCount,查看是否可以正确返回JSON数据。
展示结果如下:
2.10 前端页面开发
在这里用到了Echart,可以查看Echarts官网进行学习。
在webapp根目录下,创建countryNum.html文件。
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>各个国家出版图书数量title>
<script src="js/echarts.min.js">script>
<script src="js/jquery-1.11.0.min.js">script>
head>
<body>
<div id="country" style="width: 1350px;height:400px;">div>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 声明服务器数据的url
var url = "http://localhost:8080/doubanbook/country";
// 发送Ajax请求,从服务器获取数据
$.get(url, function(result) {
// x轴数据: 国家
var xData = result.xData;
// y轴数据: 数量
var yData = result.yData;
// 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例
var myChart = echarts.init(document.getElementById('country'));
// 指定图表的配置项和数据
var option = {
// 图表标题
title: {
text: '各个国家出版图书数量--折线图+柱状图'
},
// 提示框
tooltip: {
show: true,
// trigger: 'item'
trigger: 'axis',
axisPointer: {
type: 'cross',
label: {
backgroundColor: '#6a7985'
}
}
},
// 图例
legend: {
data: ['出版量']
},
//工具栏组件
toolbox:{
show:true,
feature:{
//需要的功能
saveAsImage:{
show: true //保存为图片
},
dataView:{
show: true //数据视图
},
dataZoom:{
show: true //区域缩放与区域缩放还原
},
magicType:{
type: ['line', 'bar'] //动态类型转换
}
}
},
// x轴
xAxis: {
data: xData,
type: 'category',
axisTick:{
alignWithLabel: true,//竖线对准文字
interval: 0,
//坐标轴刻度标签的显示间隔(在类目轴中有效),默认会采用标签不重叠的方式显示标签(也就是默认会将部分文字显示不全)
//可以设置为0强制显示所有标签,如果设置为1,表示隔一个标签显示一个标签,如果为3,表示隔3个标签显示一个标签,以此类推
},
axisLabel:{
interval: 0 //显示全部信息
}
},
// y轴
yAxis:[{
type:'value'
}],
// 系列列表
series: [{
name: '出版量',
type: 'line',
data: yData
}, {
name: '出版量',
type: 'bar',
data: yData,
color: new echarts.graphic.LinearGradient(1, 0, 0, 1, [{
offset: 0,
color: '#00FF00'
}, {
offset: 0.5,
color: '#3A8EE6'
}, {
offset: 0.8,
color: '#ddd'
}])
}]
};
// 使用刚指定的配置项和数据显示图表
myChart.setOption(option);
});
script>
body>
html>
重启项目,在浏览器地址栏输入http://localhost:8080/doubanbook/countryNum.html,查看是否可以正确显示各个国家出版图书数量数据可视化效果。
3 总结
这是其中的一个关于书籍国家的相关代码,接下来复习的其他的代码没有那么详细了。