MLP分类——MNIST(手写数字识别)
MLP分类——MNIST(手写数字识别)
目录
- MLP分类——MNIST(手写数字识别)
- 数据集
- model+predicted
数据集
#导入数据
X_train = load_data("train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz") / 255.0
X_test = load_data("t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz") / 255.0
y_train = load_data("train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz",True).reshape(-1)
y_test = load_data("t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz",True).reshape(-1)
print(X_train.shape, y_train.shape, X_test.shape, y_test.shape, sep = '\n')
#60000个训练数据+10000个测试数据
count = 0
sample_size = 30
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 6))
for i in np.random.permutation(X_train.shape[0])[:sample_size]:
count = count + 1
plt.subplot(1, sample_size, count)
plt.axhline('')
plt.axvline('')
plt.text(x=10, y=-10, s=y_train[i], fontsize=18)
plt.imshow(X_train[i].reshape(28, 28), cmap=plt.cm.Greys)
plt.show()
model+predicted
实验用到MLPClassifier
#拟牛顿法,需要较多的迭代次数,所以max_iter默认200,两个100个节点的隐藏层
lbfgs = MLPClassifier(solver = 'lbfgs', hidden_layer_sizes = [100,100], activation = 'relu',
alpha = 1e-4, random_state = 100, verbose = 1)
#基于梯度下降的自适应优化算法,分批训练数据
sgd = MLPClassifier(solver = 'sgd', hidden_layer_sizes = [100,100], activation = 'relu',
alpha = 1e-4, random_state = 100, verbose = 1, learning_rate_init = 0.1)
#训练模型
lbfgs.fit(X_train, y_train)
sgd.fit(X_train, y_train)
#预测
lbfgs_predict = lbfgs.predict(X_test)
sgd_predict = sgd.predict(X_test)
print("lbfgs在训练集准确度: %f" % lbfgs.score(X_train, y_train))
print("lbfgs在测试集准确度: %f" % lbfgs.score(X_test, y_test))
print("sgd在训练集准确度: %f" % sgd.score(X_train, y_train))
print("sgd在测试集准确度: %f" % sgd.score(X_test, y_test))
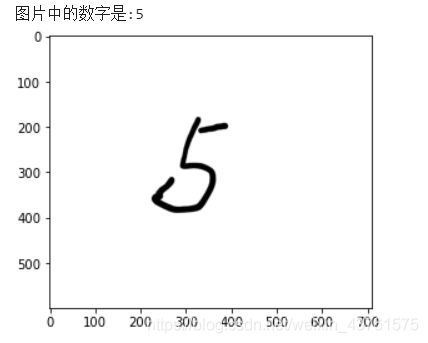
#导入图像处理工具
from PIL import Image
#打开图像
image = Image.open("write_5.png").convert('F')
plt.imshow(image)
#调整图像的大小
image = image.resize((28,28))
arr = []
#将图像中的像素作为预测数据点的特征
for i in range(28):
for j in range(28):
pixel = 1.0 - float(image.getpixel((j,i)))/255.
arr.append(pixel)
#由于只有一个样本,所以需要进行reshape操作
arr1 = np.array(arr).reshape(1,-1)
#进行图像识别
print('图片中的数字是:{:.0f}'.format(sgd.predict(arr1)[0]))