MyBatis源码分析之数据库连接池
Mybatis源码分析之数据库连接池DataSource
0、简介
本篇文章主要记录下学习Mybatis数据库连接池的理解,本打算先写解析mapper的源码分析文章,随后想想mapper等元素解析相关的文章单独放一个系列记录。此篇文章主要介绍Mybatis大的模块分析。
此文章主要记录以下几个点:
1、为什么需要数据库连接池
2、Mybatis数据库连接池的分类
3、Mybatis数据库连接池源码分析
1、为什么需要数据库连接池
一般提到池,大家第一印象就是池化后降低资源创建的消耗,获取速度快等等。没错,就是需要达到这些效果。
首先演示下没有池的情况下,每次查询数据库创建新的连接的耗时情况。
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Connection connection = testOpenConn();
Long afterGetConn = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 我测试程序在testOpenConn()中获取了10次连接,这里将耗时除10
System.out.println("Get Conn consume time :"+(afterGetConn - beginTime)/10);
String statement = "select * from user";
PreparedStatement statement2 = connection.prepareStatement(statement);
statement2.executeQuery();
System.out.println("after execute consume time:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-afterGetConn));
}
public static Connection testOpenConn() throws SQLException{
Connection connection = null;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
connection = (Connection) DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://192.168.65.129:3306/test", "root", "root");
}
return connection;
}
}
程序在我电脑上执行的结果如下图:
从上面的执行结果可以看出创建一个新的连接平均耗时 47 ms,那么假设串行获取10000个连接,光获取连接耗时470000ms,7分多钟,不敢想象呀。
下面我将Connection作为成员变量缓存起来,然后执行10次查询看看效果。
public class MainTest {
public static Connection connection;
static{
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
connection = (Connection) DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://192.168.65.129:3306/test", "root", "root");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
Connection connection = getConnection();
String statement = "select * from user";
PreparedStatement statement2 = connection.prepareStatement(statement);
statement2.executeQuery();
}
Long after = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("consume time :"+(after - beginTime)/10);
}
public static Connection getConnection() {
return connection;
}
}
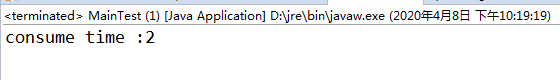
执行结果如下图:
不多说了,一切尽在结果中。由此可知,合理利用系统资源可以大大降低系统耗时,Mybatis的数据库连接池的目的就是降低获取资源耗时,提高资源利用率。
2、Mybatis数据库连接池分类
首先看下配置文件中一般如何配置数据源的
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="..." value="..."/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
再说下Mybatis什么时候使用到数据库连接?
来看下面一段熟悉的代码
public class UserDaoTest {
@Test
public void findUsers(){
SqlSession sqlSession = getSessionFactory().openSession();
sqlSession.selectList("select * from user"); // 调用这一行代码时候获取数据库连接
}
private static SqlSessionFactory getSessionFactory(){
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
String resource = "configuration.xml";
try {
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
}
在上面代码调用selectList()方法执行实际查询时候会去获取数据库连接,我截取源码中的部分代码如下所示
// 其中会调用如下代码获取数据库连接
Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog());
// BaseExecutor中的代码
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
// 调用transaction.getConnection()获取数据库连接
Connection connection = transaction.getConnection();
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return connection;
}
}
// JdbcTransaction中实现的代码
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return connection;
}
// JdbcTransaction中实际调用dataSource.getConnection()方法获取数据库连接
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
// 这段代码到了实际的dataSource调用方法获取数据库连接对象了
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
if (level != null) {
connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
}
setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);
}
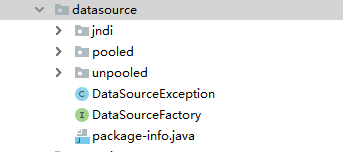
下面我们就要介绍到核心点了,在Mybatis项目源码下我们可以看到有如下一个包,里面就是Mybatis获取数据源相关类
从图中可以看出Mybatis的datasource包中主要有三个分类:① jndi ② pooled ③ unpooled。这三个包分别代表使用jndi获取数据源相关、池化获取数据源相关、非池化获取数据源相关。
平常我们说的Mybaits的数据库连接池一般都是和pooled包下 的类相关。下面我们就分别分析下pooled包和unpooled包下的相关类。
先看一张类的关系图
2.1 UNPOOLED
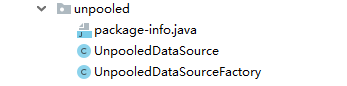
unpooled包下的类如图所示
下面先概要介绍下各个类的用处:
- UnpooledDataSource:普通的DataSource实现类,里面实现了Mybatis相关的数据源逻辑。
- UnpooledDataSourceFactory : 非池化数据源工厂。
源码的其他部分相对来说比较简单,我们直接分析跟主题相关的代码。下面就直接看UnpooledDataSource的getConnection()方法
// 下面就是UnpooledDataSource的getConnection()方法
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 内部调用doGetConnection()方法
return doGetConnection(username, password);
}
private Connection doGetConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
Properties props = new Properties();
if (driverProperties != null) {
props.putAll(driverProperties);
}
if (username != null) {
props.setProperty("user", username);
}
if (password != null) {
props.setProperty("password", password);
}
// 继续调用doGetConnection()方法
return doGetConnection(props);
}
// 这段代码想必大家非常熟悉吧
private Connection doGetConnection(Properties properties) throws SQLException {
// 加载驱动类
initializeDriver();
// 获取数据库连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
// 配置连接(设置隔离级别、是否自动提交等)
configureConnection(connection);
return connection;
}
到这里就基本上讲完了UnpooledDataSource的主要功能了,和我们平常手动做实验获取数据库连接基本差不多。
2.2 POOLED
pooled的包下的类如下图所示,下面主要讲下PooledDataSource相关源码
下面先概要介绍下各个类的用处:
- PooledConnection : 对普通Connection的一个包装,实现了InvocationHandler,方便后面通过代理来做一些操作。
- PooledDataSource : DataSource的实现类,组合了非池化数据源类。
- PooledDataSourceFactory : 数据源工厂类,继承自非池化数据源工厂类。
- PooledState : 记录数据库连接池的一些状态,比如空闲连接列表、活跃连接列表。
在分析实际源码之前我先记录下预备知识,从上面可以看出来pooled包下面比unpooled包明显多出来两个类:PooledConnection和PooledState
下面我们简要介绍下相关类
① PooledConnection
介绍下PooledConnection类的要点和重要属性
// 首先此类实现了InvacationHandler,不必多说,想要实现jdk动态代理
class PooledConnection implements InvocationHandler {
// 常量字符串,要对connection的close方法做特殊处理
private static final String CLOSE = "close";
// Connection接口类对象
private static final Class<?>[] IFACES = new Class<?>[] {
Connection.class };
// 组合了PooledDataSource引用,方便一些操作
private final PooledDataSource dataSource;
// 真实数据库连接对象
private final Connection realConnection;
// 代理数据库连接对象
private final Connection proxyConnection;
// 构造函数
public PooledConnection(Connection connection, PooledDataSource dataSource) {
this.hashCode = connection.hashCode();
this.realConnection = connection;
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.createdTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.lastUsedTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.valid = true;
// 直接使用此类生成一个Connection代理类
this.proxyConnection =(Connection)Proxy.newProxyInstance(Connection.class.getClassLoader(), IFACES, this);
}
// 代理方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
// 这里可以看出,当调用PooledConnection生成的Connection的代理类的close方法时候
// 不是直接关闭连接,而是调用了dataSource.pushConnection(this)方法
// 这个方法我们后面分析
if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode() && CLOSE.equals(methodName)) {
dataSource.pushConnection(this);
return null;
}
try {
if (!Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// issue #579 toString() should never fail
// throw an SQLException instead of a Runtime
checkConnection();
}
return method.invoke(realConnection, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
② PoolState
PoolState类主要管理数据库连接池的相关状态,比如空闲列表、活跃列表等等。在这里有个疑问就是这个类有点感觉没必要,个人觉得完全可以将PoolState所有属性和功能放入PooledDataSource类。后面再悟下。
public class PoolState {
// 有一个PooledDataSource的引用
protected PooledDataSource dataSource;
// 这个列表代表空闲连接列表
protected final List<PooledConnection> idleConnections = new ArrayList<>();
// 这个列表是活跃连接列表
protected final List<PooledConnection> activeConnections = new ArrayList<>();
// 构造方法
public PoolState(PooledDataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
}
③ PooledDataSource
public class PooledDataSource implements DataSource {
// 组合了一个PoolState对象
private final PoolState state = new PoolState(this);
// 组合了一个UnpooledDataSource对象,复用公共属性和方法。
private final UnpooledDataSource dataSource;
// OPTIONAL CONFIGURATION FIELDS
// 下面是一些可以配置的属性,见名知意
protected int poolMaximumActiveConnections = 10;
protected int poolMaximumIdleConnections = 5;
protected int poolMaximumCheckoutTime = 20000;
protected int poolTimeToWait = 20000;
protected int poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance = 3;
public PooledDataSource(String driver, String url, String username, String password) {
dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource(driver, url, username, password);
expectedConnectionTypeCode = assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword());
}
}
好了,以上就是相关类的简要介绍,下面我们进入正题,开始分析PooledDataSource的getConnection()方法,方法稍长,注释一步一步解释,先上一张流程图,对照流程图看代码更清晰,流程图中省略了中断响应的步骤。
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 内部调用popConnection方法
// dataSource是PooledDataSource内部组合的UnpooledDataSource类来存放数据库用户名等数据
return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection();
}
// 核心方法
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
boolean countedWait = false;
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;
// 当conn为null时候循环获取conn
while (conn == null) {
// 对state加锁
// state是PooledDataSource内部组合的PoolState对象
synchronized (state) {
// 如果空闲连接列表不为空,那么久直接从空闲列表里面获取一个连接
if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) {
// Pool has available connection
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checked out connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " from pool.");
}
} else {
// 若空闲列表为空,但是活跃连接数量小于连接池配置的最大活跃连接数
// 那么创建一个新的PooledConnection赋值给conn
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {
// Can create new connection
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Created connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// 空闲列表为空,活跃连接数也不小于最大活跃数限制
// 那么将活跃列表中最先加入的连接拿出来
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0);
// 获取其检查时间(也可以理解为加入活跃列表时候的时间)
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime();
// 如果检查时间大于连接池最大检查时间,那么尝试将其从活跃列表移除
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {
// 变更状态相关属性
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime;
// 从活跃连接列表移除加入列表时间超时的PooledConnection
state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection);
// 被移除的连接的真实数据库连接若不是设置了自动提交
// 那么将其回滚
if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
try {
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
/*
Just log a message for debug and continue to execute the following
statement like nothing happened.
Wrap the bad connection with a new PooledConnection, this will help
to not interrupt current executing thread and give current thread a
chance to join the next competition for another valid/good database
connection. At the end of this loop, bad {@link @conn} will be set as null.
*/
log.debug("Bad connection. Could not roll back");
}
}
// 使用在活跃列表超时的连接的真实数据库连接重新创建一个PooledConnection
// 将其赋值给conn
conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this); // 设置新连接的相关属性
conn.setCreatedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getCreatedTimestamp());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getLastUsedTimestamp());
// 置超时连接为无效
oldestActiveConnection.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Claimed overdue connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// 如果活跃列表中最先进入的连接的检查时间都不大于最大检查时间
// 那么调用Object.wait(time)等待,等待期间可以响应中断
// 等待结束后进行下一次while循环继续获取连接
try {
if (!countedWait) {
state.hadToWaitCount++;
countedWait = true;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection.");
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
// 如果上面代码执行完以后conn不为空,就说明拿到了一个连接
if (conn != null) {
// 判断连接是否有效
if (conn.isValid()) {
// 如果PooledConnection的真实数据库连接不是自动提交的
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
// 那么使用之前必须先执行回滚操作
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
// 更新检查时间为当前时间
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
// 将连接加入活跃列表
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
state.requestCount++;
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
} else {
// 若连接是失效的
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection.");
}
// 将state的坏连接点计数+1
state.badConnectionCount++;
// 本地坏连接计数+1
localBadConnectionCount++;
// 将conn置空等待下次循环
conn = null;
// 如果本地坏连接数大于连接池最大空闲节点数和连接池最大本地坏连接容忍数之和
// 那么就抛出异常
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
if (conn == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
return conn;
}
最后讲解下当PooledConnection连接使用完之后释放相关的源码分析,从上面PooledConnection类的简要分析时候可知,PooledConnection内部组合了两个Connection对象,一个是真实的数据库连接对象,一个是Connection的代理对象。连接池对外使用的是Connection的代理对象,在代理内部除close()方法外的其他方法都会调用真实数据库连接对象的相应方法method.invoke(realConnection, args),只有代理对象的close()方法调用时候逻辑如下
// 回想PooledConnection内部invoke方法中的判断,当方法名是close的时候
if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode() && CLOSE.equals(methodName)) {
// 调用dataSource的pushConnection方法
// 此处的dataSource就是PooledDataSource对象
dataSource.pushConnection(this);
return null;
}
下面再来分析下pushConnection方法源码,首先先看一张流程图,对照流程图看源码逻辑更清晰。
protected void pushConnection(PooledConnection conn) throws SQLException {
// 先对state加锁
synchronized (state) {
// 将conn从活跃列表中移除
state.activeConnections.remove(conn);
// 如果conn是有效的,那么还要将conn本身"清除干净"
if (conn.isValid()) {
// 如果空闲列表小于最大空闲数量限制,且conn和数据库连接池的其他连接是同型的
if (state.idleConnections.size() < poolMaximumIdleConnections && conn.getConnectionTypeCode() == expectedConnectionTypeCode) {
// 将累计检查时间+要放入空闲列表连接的检查时间
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
// conn若是非自动提交,那么放入空闲列表之前将conn中数据"清理"(回滚)
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 创建一个新的PooledConnection,将conn的真实数据库连接放入
PooledConnection newConn = new PooledConnection(conn.getRealConnection(), this);
// 将newConn放入空闲列表
state.idleConnections.add(newConn);
newConn.setCreatedTimestamp(conn.getCreatedTimestamp());
newConn.setLastUsedTimestamp(conn.getLastUsedTimestamp());
// 将conn设置为非法
conn.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Returned connection " + newConn.getRealHashCode() + " to pool.");
}
// 唤醒在popConnection中wait的线程
state.notifyAll();
} else {
// 如果空闲列表满了或者此连接和数据库连接池中其他连接不同型
// 将state累积检查时间加上conn的检查时间
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
// 对conn进行"清理"
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 将conn的真实数据库连接关闭
conn.getRealConnection().close();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closed connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
// 设置conn非法标志
conn.invalidate();
}
} else {
// 如果连接是无效的
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") attempted to return to the pool, discarding connection.");
}
// 将state的坏连接计数+1
state.badConnectionCount++;
}
}
}
以上就是对本次看Mybatis数据库连接池源码的理解。若有不正确的地方,欢迎指正。