VS2019创建RealSense2.0 SDK新项目--使用深度数据测量物理世界中两点间的距离
项目:
硬件平台:
win10 x64
Visual Studio 2019
Intel Realsense SDK 2.0
这是在官网上下载的例程,默认安装在C盘,include是头文件,samples是例子
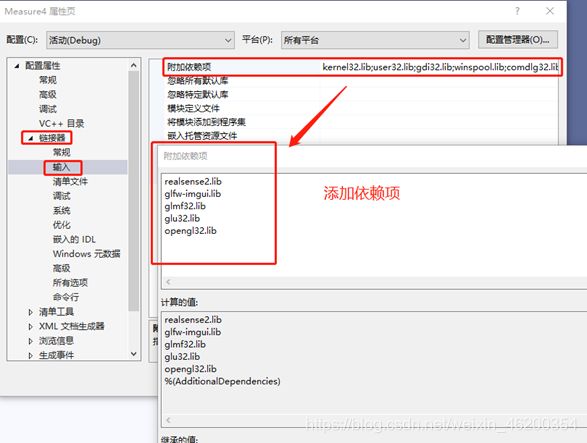
先说明:Hello第一个例子添加的依赖项只需要realsense2.lib就行,其他的例程则需要添加更多的依赖项,否则会报错
问题描述:
在VS新建工程这里坑比较多,以下是手把手教建工程,如果已经配置成功的可略过不看哦~
1.环境变量配置(设置完之后,建议电脑重启一下,不过问题不大,看实际情况)
电脑——属性——高级系统设置——环境变量——系统变量——Path——如下图:

2.打开vs,新建一个工程,我把这个工程放在E盘,然后在解决方案资源管理器,右键打开属性
引入头文件和库目录+添加依赖项,完成一切后,连上相机就可以啦~
原因分析:
大量的头文件和依赖项,没有的话,靠一个main函数跑不了,路径什么的一定要设置好才行,不过每次新建都得引入一次是真的烦人,可以试下在其他的环境下跑吧。
关于用深度测两点间的距离:
本教程介绍了使用深度数据测量现实距离的简单方法。
注意:测量真实对象的尺寸是深度相机的明显应用之一。
该示例并不是要成为合适的度量工具,而是要展示关键概念。
使用更好的算法,可以大大提高测量结果。
在本教程中,您将学习如何:
在空间上使颜色流与深度对齐(与rs-align中的深度与颜色对齐相反)
利用后处理来处理丢失或嘈杂的深度数据
在2D像素和3D空间中的点之间转换
利用多核来并行化数据流
使用OpenGL在深度上方叠加颜色
#include //该头文件包含M_PI的定义
#include我们使用glBlendFunc颜色Alpha通道在深度上叠加对齐颜色(流必须具有一定格式RGBA才能正常工作)。
此示例说明了一个简短而复杂的处理流程。每个线程的速率略有不同,它们都需要同步但彼此之间不必阻塞。
这是通过使用线程安全frame_queue的作为同步原语和rs2::frame引用计数来跨线程进行对象生存期管理来实现的。
注释可能表达的不太准确,可去官网下载源码,自己翻译~
第一次写,主要是想让大家遇见这么没有什么技术性可言的坑时能顺利跳过~