黑马程序员—网络编程和用户图形界面
——Java培训、Android培训、iOS培训、.Net培训、期待与您交流! ——-
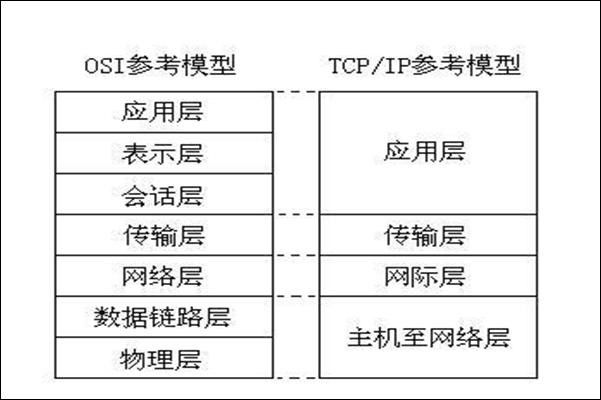
开发处于传输层和网际层:
应用层为:FTP和HTTP协议等。
传输层为:UDP和TCP等。
网际层为:IP。
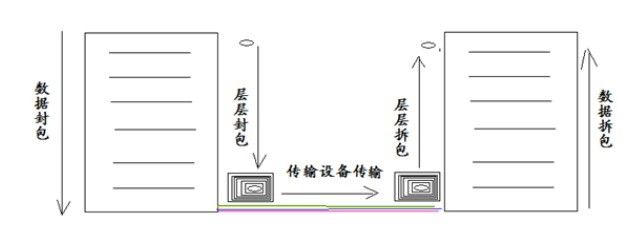
通常用户操作的是应用层,而编程人员需要做的是传输层和网际层,用户在应用层操作的数据,经过逐层封包,最后到物理层发送到另一个模型中,再进行逐层解包。
2.传输协议:
2.1UDP:
udp传输:
DatagramSocket 和 DatagramPacket
1.建立发送端,接收端。
2.建立数据包。
3.调用Socket的发送接收方法。
4.关闭资源。
发送端和接收端是两个独立的运行程序。
演示代码:
需求1:
通过Udp传输方式,将一段文字数据发送出去。
class UdpSend
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//思路:
//1.创建DatagramSocket对象,建立UdpSocket服务。
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
//2.提供数据,并将数据封装到数据包中。
byte[] buf = "shuju".getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp =
new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length,InetAddress.getByName("192.168.100.103"),10000);
//3.通过socket服务的发送功能,将数据包发送出去。
ds.send(dp);
//4.关闭资源。
ds.close();
}
}需求2:
定义一个应用程序,用于接收Udp协议传输的数据并处理。
class UdpReceive
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
//思路:
//1.定义一个Udpscoket服务,通常会监听一个端口,其实就是给这个接收
//网络应用程序定义数字标识,方便于明确哪些数据过来该应用程序可以处理。
//定义udpsocket服务,创建端点。
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10000);
//2.定义一个数据包,因为要存储接收到的字节数据,
//因为数据包对象中有更多功能可以提取字节数据中的不同数据信息。
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp =
new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
//3.通过socket服务的receive方法将收到的数据存入已定义好的数据包中。
ds.receive(dp);
//4.通过数据包对象的特有功能,将这些不同的数据取出,打印在控制台上。
String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
String data = new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength());
int port = dp.getPort();
System.out.println(ip+".."+data+".."+port);
//5.关闭资源。
ds.close();
}
}需求3:
需求:上传图片。
分析:
客户端:
1.建立服务端点。
2.读取客户端已有的图片数据。
3.通过socket输出流将数据发给服务端。
4.读取服务端的反馈信息。
5.关闭。
演示代码:
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class PicClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.100.103",10007);
BufferedInputStream bufi =
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("c:\\myjava\\红色的枫叶.jpg"));
BufferedOutputStream bufOut = new BufferedOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len =0;
while ((len=bufi.read(buf))!=-1)
{
bufOut.write(buf,0,len);
}
//告诉服务端数据已写完。
s.shutdownOutput();
BufferedReader bufIn =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String str = bufIn.readLine();
System.out.println("server:"+str);
bufi.close();
s.close();
}
}
class PicServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10007);
Socket s = ss.accept();
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip+"...connected");
BufferedInputStream bufIn =
new BufferedInputStream(s.getInputStream());
BufferedOutputStream bufo =
new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("醉枫林.jpg"));
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while ((len =bufIn.read(buf))!=-1)
{
bufo.write(buf,0,len);
}
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
out.println("图片上传成功");
bufo.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}服务端:
这个服务端有个局限性,当A客户端连接上以后,被服务端获取到。
服务端执行具体流程,这时B客户端连接,只能等待。
因为服务端还没有处理完A客户端的请求,还没有循环回来执行下次accept方法,
所以暂时获取不到B客户端对象。
那么为了可以让多个客户端同时并发访问服务端。
服务端最好就是将每个客户端封装到一个单独的线程中去,这样,就可以同时处理
多个客户端请求。
如何定义线程呢?
只要明确了每一个客户端要在服务端执行的代码即可,将该代码存入run方法中。
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class PicThread implements Runnable
{
private Socket s;
PicThread(Socket s)
{
this.s = s;
}
public void run()
{
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
try
{
int count = 1;
System.out.println(ip+"...connected");
File file = new File(ip+"("+count+")"+".jpg");
while(file.exists())
file = new File(ip+"("+(count++)+")"+".jpg");
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
int len = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while ((len=in.read(buf))!=-1)
{
fos.write(buf,0,len);
}
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
out.write("上传图片成功".getBytes());
fos.close();
s.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new RuntimeException(ip+"上传图片失败");
}
}
}
class PicClient
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
if (args.length!=1)
{
System.out.println("请选择一个jpg格式图片");
return ;
}
File file = new File(args[0]);
if(!(file.exists() && file.isFile()))
{
System.out.println("文件有问题,要么文件不存在,要么不是文件");
return ;
}
if (!file.getName().endsWith(".jpg"))
{
System.out.println("图片格式错误,请重新上传");
return ;
}
if (file.length()>1024*1024*5)
{
System.out.println("文件太大,请重新上传");
return ;
}
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.100.103",10007);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
int len = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while ((len=fis.read(buf))!=-1)
{
out.write(buf,0,len);
}
s.shutdownOutput();
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bt = new byte[1024];
int num = in.read(bt);
System.out.println(new String(bt,0,num));
fis.close();
s.close();
}
}
class PicServer
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10007);
while (true)
{
Socket s = ss.accept();
new Thread(new PicThread(s)).start();
}
}
}练习:
需求:客户端通过键盘录入用户名,服务端对这个用户名进行校验。
如果用户存在,在服务端显示xxx,已登陆。
并在客户端显示xxx,欢迎光临。
如果用户不存在,在服务端显示xxx,尝试登陆,
并在客户端显示xxx,该用户不存在。
最多尝试登陆三次。
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class LoginClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.100.103",10008);
BufferedReader bufr =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
BufferedReader bufIn =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
for (int x=0; x<3; x++)
{
String line = bufr.readLine();
if (line==null)
break;
out.println(line);
String info = bufIn.readLine();
System.out.println("info:"+info);
if (info.contains("欢迎"))
break;
}
bufr.close();
s.close();
}
}
class UserThread implements Runnable
{
private Socket s;
public UserThread(Socket s)
{
this.s = s;
}
public void run()
{
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip+"...connected");
try
{
for (int x=0; x<3; x++)
{
BufferedReader bufIn =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String name = bufIn.readLine();
if(name==null)
break;
BufferedReader bufr =
new BufferedReader(new FileReader("user.txt"));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
String line =null;
boolean flag =false;
while ((line=bufr.readLine())!=null)
{
if (line.equals(name))
{
flag =true;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
{
System.out.println(name+",已登陆。");
out.println(name+",欢迎光临。");
break;
}
else
{
System.out.println(name+",尝试登陆。");
out.println(name+",用户不存在。");
}
}
s.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new RuntimeException(ip+"校验失败");
}
}
}
class LoginServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10008);
while (true)
{
Socket s = ss.accept();
new Thread(new UserThread(s)).start();
}
}
}2.2 TCP:
TCP传输:
1.Socket(客户端)和ServerSocket(服务端)
客户端:
通过查阅socket对象,发现在该对象建立时,就可以去连接指定主机。
因为tcp是面向连接的,所以在建立socket服务时,就要有服务端存在,
并连接成功,形成通路后,在该通道进行数据的传输。
步骤:
1)创建Socket服务,并指定要连接的主机和端口。
2)获取客户端对象的输出流来写需要发送出去的数据。
3)关闭客户端。
服务端:
步骤:
1)建立服务端的socket服务,ServerSocket();
并监听一个端口。
2.获取连接过来的客户端对象。
通过ServerSocket的accept方法,没有连接就会等,所以这个方法是阻塞式的。
3.客户端如果发过来数据,那么服务端要使用对应的客户端对象,并获取到该
客户端对象的读取流来读取发送过来的数据并打印在控制台上。
4.关闭服务端。(可选操作,一般不关闭。)
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class TcpClient
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
//创建客户端的socket服务,指定目的主机和端口。
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.100.103",10003);
//为了发送数据,应该获取socket流中的输出流。
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
out.write("day day up !".getBytes());
s.close();
}
}
class TcpServer
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
//建立服务端socket服务,并监听一个端口。
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10003);
//通过accept方法获取连接过来的客户端对象。
Socket s = ss.accept();
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip+"....connected");
//获取到该客户端对象的读取流来读取发送过来的数据。
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = in.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}演示tcp传输的客户端和服务端互访。
需求:客户端给服务端发送数据,服务端收到后,给客户端反馈信息。
客户端:
1.建立socket服务,指定要连接的主机和端口。
2.获取socket流中的输出流,将数据写到该流中,通过网络发送给服务端。
3.获取socket流中的输入流,将服务端反馈的数据获取,并打印。
4.关闭客户端资源。
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class TcpClient2
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.100.103",10004);
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
out.write("服务端,你好".getBytes());
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
byte[] buf =new byte[1024];
int len =in.read(buf);//阻塞式方法,没收到信息会停留在那等待。
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
s.close();
}
}
class TcpServer2
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10004);
Socket s = ss.accept();
String ip =s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip+"...连接上了");
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = in.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
Thread.sleep(10000);//(休眠十秒,客户端会延迟十秒收到服务端信息)。
out.write("客户端,我已收到你信息".getBytes());
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}
需求:建立一个文本转换服务器。
客户端给服务端发送文本,服务端会将文本转化成大写返回给客户端。
而且客户端可以不断的进行文本转化,当客户端输入over时,转换结束。
分析:
客户端:
既然是操作设备上的数据,那么就可以使用io技术,并按照io的操作规律来思考。
源:键盘录入。
目的:网络设备,网络输出流。
而且操作的是文本数据,可以选择字符流。
步骤:
1.建立服务。
2.获取键盘录入。
3.将数据发送给服务端。
4.获取服务端返回的大写数据。
5.结束,关闭客户端。
因为都是文本数据,可以使用字符流来进行操作,同时提高效率,加入缓冲技术。
服务端:
源:socket读取流。
目的:socket输出流。
都是文本,装饰。
该例出现的问题:
现象:客户端和服务端都在莫名的等待,这是为什么呢?
因为客户端和服务端都有阻塞式的方法,这些方法没有读到结束标记,
那么就会一直等待,导致两端都在等待。
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class TransClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.100.103",10005);
//定义读取键盘数据的流对象。
BufferedReader bufr =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
//定义目的,将数据写入到socket输出流,发送给服务端。
/*BufferedWriter bufout =
new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));*/
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);//既可以接收字符流也可以接收字节流。
//定义一个socket读取流,读取服务端返回的大写信息。
BufferedReader bufin =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line=bufr.readLine())!=null)
{
if("over".equals(line))
break;
out.println(line);
/*
bufout.write(line);
bufout.newLine();
bufout.flush();
*/
String str = bufin.readLine();
System.out.println("server:"+str);
}
bufr.close();
s.close();
}
}
class TransServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10005);
Socket s = ss.accept();
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip+"...connected");
//读取socket读取流中的数据。
BufferedReader bufin =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
//目的:socket输出流,将大写数据写入到socket输出流,并发送给客户端。
/*BufferedWriter bufout =
new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));*/
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);//带自动刷新,println带自动换行。
String line = null;
while ((line=bufin.readLine())!=null)
{
System.out.println(line);
out.println(line.toUpperCase());
/*
bufout.write(line.toUpperCase());
bufout.newLine();
bufout.flush();
*/
}
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}3.GUI(用户图形界面):
3.1概述:
1、GUI:GraphicalUser Interface,即图形用户界面,用于计算机与用户交互的一种方式。
2、计算机与用户交互的两种方式:GUI和CLI
GUI: Graphical User Interface,图形用户接口,用图形方式,来显示计算机操作界面,方便直观。
CLI: Command LineUser Interface,命令行用户接口,即常见的Dos命令行操作,须记住一些命令,操作不直观。
3、java也将这种界面封装为对象,其中的对象都放在了两个包中:java.Awt包和javax.Swing包。
java.Awt包:Abstract Window Toolkit,即抽象窗口工具包。要调用本地系统方法实现功能,属重量级控件。
javax.Swing包:在AWT的基础上建立的一套图形界面系统,其中提供了更多的组件,且完全由java实现,增强了移植性,属轻量级控件。
3.2布局管理器:
1、布局:容器中的组件排列方式
2、常见的布局管理器:
1)FlowLayout:流式布局管理器。从左向右排列,是Panel默认的布局管理器
2)BorderLayout:边界式布局管理器,东南西北中的排列方式,是Frame的默认布局管理器。如果窗体中只有一个组件,将会覆盖整个窗体。
3)GridLayout:网格式布局管理器,规则的矩阵
4)CardLayout:卡片式布局管理器,即选项卡
5)GridBayLayout:网格包布局管理器,非规则矩阵
3、如果存在多种布局方式,如何创建窗体界面呢?步骤:
1)先将窗体Frame进行大区域的划分,设置其布局管理器,加入面板Panel
2)将组件加入Panel,设置面板的布局管理器。
3.3 GUI应用:
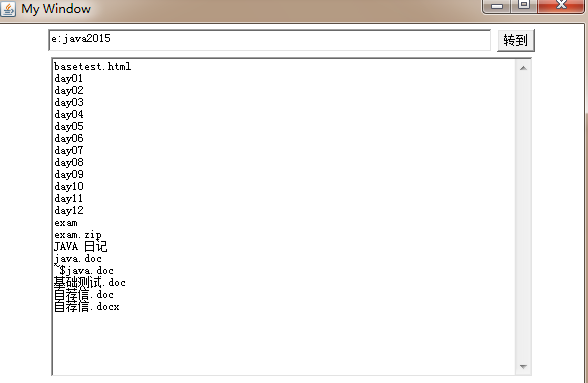
需求1:创建一个窗口,可以实现查询电脑里目录文件的功能:
package mywindow;
import java.io.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class MyWindowDemo2
{
private Frame f;
private TextField tf;
private Button bt;
private TextArea ta;
private Dialog d;
private Label lab;
private Button okButton;
MyWindowDemo2()
{
init();
}
public void init()
{
f = new Frame("My Window");
f.setBounds(200,300,600,400);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
tf = new TextField(60);
bt = new Button("转到");
ta = new TextArea(20,66);
f.add(tf);
f.add(bt);
f.add(ta);
d = new Dialog(f,"Microsoft Internet Explorer",true);
d.setBounds(300,100,400,100);
d.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
lab = new Label();
okButton = new Button("确定");
d.add(lab);
d.add(okButton);
myEvent();
f.setVisible(true);
}
public void myEvent()
{
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
bt.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
showDir();
}
});
tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter()
{
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e)
{
if(e.getKeyCode()==KeyEvent.VK_ENTER)
{
showDir();
}
}
});
d.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
d.setVisible(false);
}
});
okButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
d.setVisible(false);
}
});
}
public void showDir()
{
String dirPath = tf.getText();
File dir = new File(dirPath);
if(dir.exists() && dir.isDirectory())
{
ta.setText("");
String[] names = dir.list();
for(String name : names)
{
ta.append(name+"\r\n");
}
}
else
{
String info = "找不到'"+dirPath+"'.请确认路径或者Internet地址正确.";
lab.setText(info);
d.setVisible(true);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new MyWindowDemo2();
}
}
需求:模仿记事本,创建一个简单的文本编辑器。
package mytxt;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
public class MyTxt
{
private Frame f;
private MenuBar bar;
private Menu fileMenu1,fileMenu2;
private MenuItem createItem,openItem,saveItem,closeItem,helpItem;
private FileDialog openDia,saveDia;
private TextArea ta;
private File file;
private Dialog d;
private Label lab;
private Button b;
MyTxt()
{
init();
}
public void init()
{
f = new Frame("记事本");
bar = new MenuBar();
fileMenu1 = new Menu("文件");
fileMenu2 = new Menu("帮助");
createItem = new MenuItem("新建");
openItem = new MenuItem("打开");
saveItem = new MenuItem("保存");
closeItem = new MenuItem("退出");
helpItem = new MenuItem("查看帮助");
openDia = new FileDialog(f,"打开",FileDialog.LOAD);
saveDia = new FileDialog(f,"保存",FileDialog.SAVE);
ta = new TextArea();
d = new Dialog(f,"windows 帮助和支持",true);
d.setBounds(300,100,700,100);
d.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
lab = new Label();
b=new Button("确定");
f.setBounds(300,100,700,500);
f.setMenuBar(bar);
f.add(ta);
bar.add(fileMenu1);
bar.add(fileMenu2);
fileMenu1.add(createItem);
fileMenu1.add(openItem);
fileMenu1.add(saveItem);
fileMenu1.add(closeItem);
fileMenu2.add(helpItem);
d.add(lab);
d.add(b);
myEvent();
f.setVisible(true);
}
public void myEvent()
{
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
createItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
ta.setText("");
}
});
openItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
openDia.setVisible(true);
String dirPath = openDia.getDirectory();
String fileName = openDia.getFile();
if(dirPath==null || fileName==null)
return ;
try
{
ta.setText("");
file = new File(dirPath,fileName);
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String line = null;
while ((line=bufr.readLine())!=null)
{
ta.append(line+"\r\n");
}
bufr.close();
}
catch (IOException e1)
{
throw new RuntimeException("打开文件失败");
}
}
});
saveItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
if(file==null)
{
saveDia.setVisible(true);
String dirPath = saveDia.getDirectory();
String fileName = saveDia.getFile();
if (dirPath == null || fileName == null)
return ;
file = new File(dirPath,fileName);
}
try
{
BufferedWriter burw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
String text = ta.getText();
burw.write(text);
burw.close();
}
catch (IOException e2)
{
throw new RuntimeException("保存文件失败");
}
}
});
closeItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
helpItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
String info = "欢迎使用本人编写的txt文档,如有任何不明白的问题,请联系本人QQ:258960039,祝您生活愉快。";
lab.setText(info);
d.setVisible(true);
}
});
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
d.setVisible(false);
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new MyTxt();
}
}
——Java培训、Android培训、iOS培训、.Net培训、期待与您交流! ——-