Faster R-CNN预测结果后处理
bilibili
roi_head.py
class RoIHeads(torch.nn.Module):
'''...'''
def forward(self,
features, # type: Dict[str, Tensor]
proposals, # type: List[Tensor]
image_shapes, # type: List[Tuple[int, int]]
targets=None # type: Optional[List[Dict[str, Tensor]]]
):
# type: (...) -> Tuple[List[Dict[str, Tensor]], Dict[str, Tensor]]
if self.training:
# 划分正负样本,统计对应gt的标签以及边界框回归信息
proposals, labels, regression_targets = self.select_training_samples(proposals, targets)
else:
labels = None
regression_targets = None
# 将采集样本通过Multi-scale RoIAlign pooling层
# box_features_shape: [num_proposals, channel, height, width]
box_features = self.box_roi_pool(features, proposals, image_shapes)
# 通过roi_pooling后的两层全连接层
# box_features_shape: [num_proposals, representation_size]
box_features = self.box_head(box_features)
# 接着分别预测目标类别和边界框回归参数
class_logits, box_regression = self.box_predictor(box_features)
result = torch.jit.annotate(List[Dict[str, torch.Tensor]], [])
losses = {
}
if self.training:
assert labels is not None and regression_targets is not None
loss_classifier, loss_box_reg = fastrcnn_loss(
class_logits, box_regression, labels, regression_targets)
losses = {
"loss_classifier": loss_classifier,
"loss_box_reg": loss_box_reg
}
else:
boxes, scores, labels = self.postprocess_detections(class_logits, box_regression, proposals, image_shapes)
num_images = len(boxes)
for i in range(num_images):
result.append(
{
"boxes": boxes[i],
"labels": labels[i],
"scores": scores[i],
}
)
return result, losses
self.postprocess_detections函数
def postprocess_detections(self,
class_logits, # type: Tensor
box_regression, # type: Tensor
proposals, # type: List[Tensor]
image_shapes # type: List[Tuple[int, int]]
):
# type: (...) -> Tuple[List[Tensor], List[Tensor], List[Tensor]]
"""
对网络的预测数据进行后处理,包括
(1)根据proposal以及预测的回归参数计算出最终bbox坐标
(2)对预测类别结果进行softmax处理
(3)裁剪预测的boxes信息,将越界的坐标调整到图片边界上
(4)移除所有背景信息
(5)移除低概率目标
(6)移除小尺寸目标
(7)执行nms处理,并按scores进行排序
(8)根据scores排序返回前topk个目标
Args:
class_logits: 网络预测类别概率信息
box_regression: 网络预测的边界框回归参数
proposals: rpn输出的proposal
image_shapes: 打包成batch前每张图像的宽高
Returns:
"""
device = class_logits.device
# 预测目标类别数
num_classes = class_logits.shape[-1]
# 获取每张图像的预测bbox数量
boxes_per_image = [boxes_in_image.shape[0] for boxes_in_image in proposals]
# 根据proposal以及预测的回归参数计算出最终bbox坐标
pred_boxes = self.box_coder.decode(box_regression, proposals)
# 对预测类别结果进行softmax处理
pred_scores = F.softmax(class_logits, -1)
# split boxes and scores per image
# 根据每张图像的预测bbox数量分割结果
pred_boxes_list = pred_boxes.split(boxes_per_image, 0)
pred_scores_list = pred_scores.split(boxes_per_image, 0)
all_boxes = []
all_scores = []
all_labels = []
# 遍历每张图像预测信息
for boxes, scores, image_shape in zip(pred_boxes_list, pred_scores_list, image_shapes):
# 裁剪预测的boxes信息,将越界的坐标调整到图片边界上
boxes = box_ops.clip_boxes_to_image(boxes, image_shape)
# create labels for each prediction
labels = torch.arange(num_classes, device=device)
labels = labels.view(1, -1).expand_as(scores)
# remove prediction with the background label
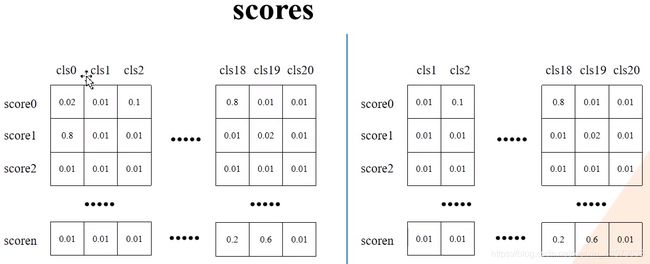
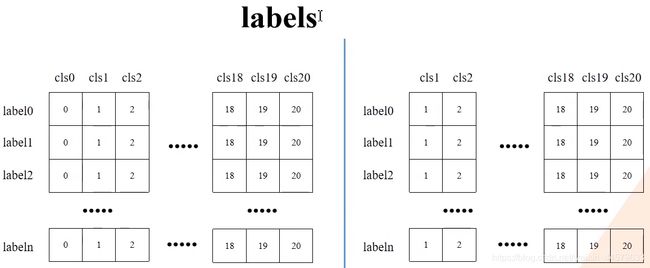
# 移除索引为0的所有信息(0代表背景)
boxes = boxes[:, 1:]
scores = scores[:, 1:]
labels = labels[:, 1:]
移除索引为0的所有信息(0代表背景)前后的boxes,scores,labels对比

继续回到代码postprocess_detections函数中
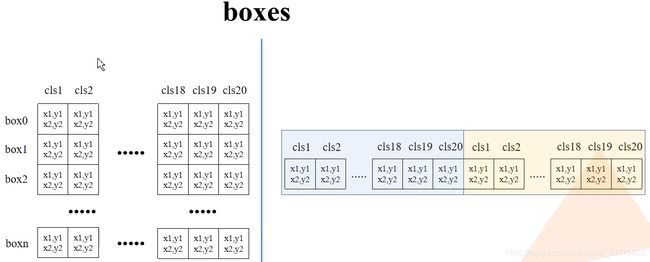
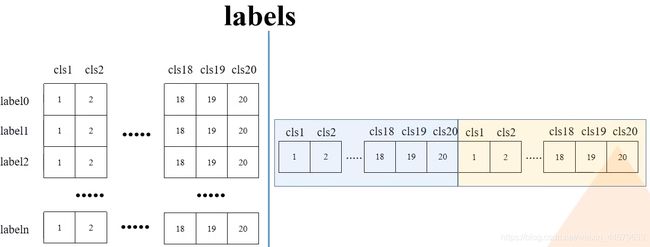
# batch everything, by making every class prediction be a separate instance
boxes = boxes.reshape(-1, 4)
scores = scores.reshape(-1)
labels = labels.reshape(-1)
reshape前后的boxes,scores,labels对比

继续回到代码postprocess_detections函数中
# remove low scoring boxes
# 移除低概率目标,self.scores_thresh=0.05
# gt: Computes input > other element-wise.
# inds = torch.nonzero(torch.gt(scores, self.score_thresh)).squeeze(1)
inds = torch.where(torch.gt(scores, self.score_thresh))[0]
boxes, scores, labels = boxes[inds], scores[inds], labels[inds]
# remove empty boxes
# 移除小目标
keep = box_ops.remove_small_boxes(boxes, min_size=1.)
boxes, scores, labels = boxes[keep], scores[keep], labels[keep]
# non-maximun suppression, independently done per class
# 执行nms处理,执行后的结果会按照scores从大到小进行排序返回
keep = box_ops.batched_nms(boxes, scores, labels, self.nms_thresh)
# keep only topk scoring predictions
# 获取scores排在前topk个预测目标
keep = keep[:self.detection_per_img]
boxes, scores, labels = boxes[keep], scores[keep], labels[keep]
all_boxes.append(boxes)
all_scores.append(scores)
all_labels.append(labels)
return all_boxes, all_scores, all_labels
self.box_coder.decode函数在BoxCoder类中
class BoxCoder(object):
def decode(self, rel_codes, boxes):
# type: (Tensor, List[Tensor]) -> Tensor
"""
Args:
rel_codes: bbox regression parameters
boxes: anchors/proposals
Returns:
"""
assert isinstance(boxes, (list, tuple))
assert isinstance(rel_codes, torch.Tensor)
boxes_per_image = [b.size(0) for b in boxes]
concat_boxes = torch.cat(boxes, dim=0)
box_sum = 0
for val in boxes_per_image:
box_sum += val
# 将预测的bbox回归参数应用到对应anchors上得到预测bbox的坐标
pred_boxes = self.decode_single(
rel_codes.reshape(box_sum, -1), concat_boxes
)
return pred_boxes.reshape(box_sum, -1, 4)
def decode_single(self, rel_codes, boxes):
"""
From a set of original boxes and encoded relative box offsets,
get the decoded boxes.
Arguments:
rel_codes (Tensor): encoded boxes (bbox regression parameters)
boxes (Tensor): reference boxes (anchors/proposals)
"""
boxes = boxes.to(rel_codes.dtype)
# xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax
widths = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0] # anchor/proposal宽度
heights = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1] # anchor/proposal高度
ctr_x = boxes[:, 0] + 0.5 * widths # anchor/proposal中心x坐标
ctr_y = boxes[:, 1] + 0.5 * heights # anchor/proposal中心y坐标
wx, wy, ww, wh = self.weights # RPN中为[1,1,1,1], fastrcnn中为[10,10,5,5]
dx = rel_codes[:, 0::4] / wx # 预测anchors/proposals的中心坐标x回归参数
dy = rel_codes[:, 1::4] / wy # 预测anchors/proposals的中心坐标y回归参数
dw = rel_codes[:, 2::4] / ww # 预测anchors/proposals的宽度回归参数
dh = rel_codes[:, 3::4] / wh # 预测anchors/proposals的高度回归参数
# limit max value, prevent sending too large values into torch.exp()
# self.bbox_xform_clip=math.log(1000. / 16) 4.135
dw = torch.clamp(dw, max=self.bbox_xform_clip)
dh = torch.clamp(dh, max=self.bbox_xform_clip)
pred_ctr_x = dx * widths[:, None] + ctr_x[:, None]
pred_ctr_y = dy * heights[:, None] + ctr_y[:, None]
pred_w = torch.exp(dw) * widths[:, None]
pred_h = torch.exp(dh) * heights[:, None]
# xmin
pred_boxes1 = pred_ctr_x - torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=pred_ctr_x.dtype, device=pred_w.device) * pred_w
# ymin
pred_boxes2 = pred_ctr_y - torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=pred_ctr_y.dtype, device=pred_h.device) * pred_h
# xmax
pred_boxes3 = pred_ctr_x + torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=pred_ctr_x.dtype, device=pred_w.device) * pred_w
# ymax
pred_boxes4 = pred_ctr_y + torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=pred_ctr_y.dtype, device=pred_h.device) * pred_h
pred_boxes = torch.stack((pred_boxes1, pred_boxes2, pred_boxes3, pred_boxes4), dim=2).flatten(1)
return pred_boxes
clip_boxes_to_image裁剪预测的boxes信息,将越界的坐标调整到图片边界上
def clip_boxes_to_image(boxes, size):
# type: (Tensor, Tuple[int, int]) -> Tensor
"""
Clip boxes so that they lie inside an image of size `size`.
裁剪预测的boxes信息,将越界的坐标调整到图片边界上
Arguments:
boxes (Tensor[N, 4]): boxes in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format
size (Tuple[height, width]): size of the image
Returns:
clipped_boxes (Tensor[N, 4])
"""
dim = boxes.dim()
boxes_x = boxes[..., 0::2] # x1, x2
boxes_y = boxes[..., 1::2] # y1, y2
height, width = size
if torchvision._is_tracing():
boxes_x = torch.max(boxes_x, torch.tensor(0, dtype=boxes.dtype, device=boxes.device))
boxes_x = torch.min(boxes_x, torch.tensor(width, dtype=boxes.dtype, device=boxes.device))
boxes_y = torch.max(boxes_y, torch.tensor(0, dtype=boxes.dtype, device=boxes.device))
boxes_y = torch.min(boxes_y, torch.tensor(height, dtype=boxes.dtype, device=boxes.device))
else:
boxes_x = boxes_x.clamp(min=0, max=width) # 限制x坐标范围在[0,width]之间
boxes_y = boxes_y.clamp(min=0, max=height) # 限制y坐标范围在[0,height]之间
clipped_boxes = torch.stack((boxes_x, boxes_y), dim=dim)
return clipped_boxes.reshape(boxes.shape)
remove_small_boxes函数移除宽高小于指定阈值的索引
def remove_small_boxes(boxes, min_size):
# type: (Tensor, float) -> Tensor
"""
Remove boxes which contains at least one side smaller than min_size.
移除宽高小于指定阈值的索引
Arguments:
boxes (Tensor[N, 4]): boxes in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format
min_size (float): minimum size
Returns:
keep (Tensor[K]): indices of the boxes that have both sides
larger than min_size
"""
ws, hs = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1] # 预测boxes的宽和高
# keep = (ws >= min_size) & (hs >= min_size) # 当满足宽,高都大于给定阈值时为True
keep = torch.logical_and(torch.ge(ws, min_size), torch.ge(hs, min_size))
# nonzero(): Returns a tensor containing the indices of all non-zero elements of input
# keep = keep.nonzero().squeeze(1)
keep = torch.where(keep)[0]
return keep
batched_nms执行nms处理,执行后的结果会按照scores从大到小进行排序返回
def batched_nms(boxes, scores, idxs, iou_threshold):
# type: (Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, float) -> Tensor
"""
Performs non-maximum suppression in a batched fashion.
Each index value correspond to a category, and NMS
will not be applied between elements of different categories.
"""
if boxes.numel() == 0:
return torch.empty((0,), dtype=torch.int64, device=boxes.device)
# strategy: in order to perform NMS independently per class.
# we add an offset to all the boxes. The offset is dependent
# only on the class idx, and is large enough so that boxes
# from different classes do not overlap
# 获取所有boxes中最大的坐标值(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
max_coordinate = boxes.max()
# to(): Performs Tensor dtype and/or device conversion
# 为每一个类别/每一层生成一个很大的偏移量
# 这里的to只是让生成tensor的dytpe和device与boxes保持一致
offsets = idxs.to(boxes) * (max_coordinate + 1)
# boxes加上对应层的偏移量后,保证不同类别/层之间boxes不会有重合的现象
boxes_for_nms = boxes + offsets[:, None]
keep = nms(boxes_for_nms, scores, iou_threshold)
return keep
利用offsets = idxs* (max_coordinate + 1)将不同类别的边界框分开,以便于可以一次性对所有的边界框进行nms处理,非常高效
原本的边界框:
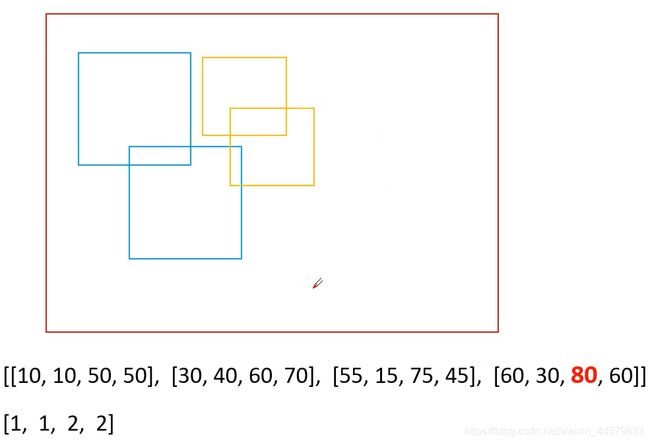
处理后的边界框:
