Fast RCNN 正负样本划分及采样
class RoIHeads(torch.nn.Module):
__annotations__ = {
'box_coder': det_utils.BoxCoder,
'proposal_matcher': det_utils.Matcher,
'fg_bg_sampler': det_utils.BalancedPositiveNegativeSampler,
}
def __init__(self,
box_roi_pool, # Multi-scale RoIAlign pooling
box_head, # TwoMLPHead
box_predictor, # FastRCNNPredictor
# Faster R-CNN training
fg_iou_thresh, bg_iou_thresh, # default: 0.5, 0.5
batch_size_per_image, positive_fraction, # default: 512, 0.25
bbox_reg_weights, # None
# Faster R-CNN inference
score_thresh, # default: 0.05
nms_thresh, # default: 0.5
detection_per_img): # default: 100
super(RoIHeads, self).__init__()
self.box_similarity = box_ops.box_iou
# assign ground-truth boxes for each proposal
self.proposal_matcher = det_utils.Matcher(
fg_iou_thresh, # default: 0.5
bg_iou_thresh, # default: 0.5
allow_low_quality_matches=False)
self.fg_bg_sampler = det_utils.BalancedPositiveNegativeSampler(
batch_size_per_image, # default: 512
positive_fraction) # default: 0.25
'''...'''
def forward(self,
features, # type: Dict[str, Tensor]
proposals, # type: List[Tensor]
image_shapes, # type: List[Tuple[int, int]]
targets=None # type: Optional[List[Dict[str, Tensor]]]
):
# type: (...) -> Tuple[List[Dict[str, Tensor]], Dict[str, Tensor]]
"""
Arguments:
features (List[Tensor])
proposals (List[Tensor[N, 4]])
image_shapes (List[Tuple[H, W]])
targets (List[Dict])
"""
if self.training:
# 划分正负样本,统计对应gt的标签以及边界框回归信息
proposals, labels, regression_targets = self.select_training_samples(proposals, targets)
else:
labels = None
regression_targets = None
# 将采集样本通过Multi-scale RoIAlign pooling层
# box_features_shape: [num_proposals, channel, height, width]
box_features = self.box_roi_pool(features, proposals, image_shapes)
# 通过roi_pooling后的两层全连接层
# box_features_shape: [num_proposals, representation_size]
box_features = self.box_head(box_features)
# 接着分别预测目标类别和边界框回归参数
class_logits, box_regression = self.box_predictor(box_features)
result = torch.jit.annotate(List[Dict[str, torch.Tensor]], [])
losses = {
}
if self.training:
assert labels is not None and regression_targets is not None
loss_classifier, loss_box_reg = fastrcnn_loss(
class_logits, box_regression, labels, regression_targets)
losses = {
"loss_classifier": loss_classifier,
"loss_box_reg": loss_box_reg
}
else:
boxes, scores, labels = self.postprocess_detections(class_logits, box_regression, proposals, image_shapes)
num_images = len(boxes)
for i in range(num_images):
result.append(
{
"boxes": boxes[i],
"labels": labels[i],
"scores": scores[i],
}
)
return result, losses
self.select_training_samples函数
如果是训练模式,self.select_training_samples函数划分正负样本,统计对应gt的标签以及边界框回归信息
def select_training_samples(self,
proposals, # type: List[Tensor]
targets # type: Optional[List[Dict[str, Tensor]]]
):
# type: (...) -> Tuple[List[Tensor], List[Tensor], List[Tensor]]
"""
划分正负样本,统计对应gt的标签以及边界框回归信息
list元素个数为batch_size
Args:
proposals: rpn预测的boxes
targets:
Returns:
"""
# 检查target数据是否为空
self.check_targets(targets)
dtype = proposals[0].dtype
device = proposals[0].device
# 获取标注好的boxes以及labels信息
gt_boxes = [t["boxes"] for t in targets]
gt_labels = [t["labels"] for t in targets]
# append ground-truth bboxes to proposal
# 将gt_boxes拼接到proposal后面
proposals = self.add_gt_proposals(proposals, gt_boxes)
# get matching gt indices for each proposal
# 为每个proposal匹配对应的gt_box,并划分到正负样本中
matched_idxs, labels = self.assign_targets_to_proposals(proposals, gt_boxes, gt_labels)
# sample a fixed proportion of positive-negative proposals
# 按给定数量和比例采样正负样本
sampled_inds = self.subsample(labels)
matched_gt_boxes = []
num_images = len(proposals)
# 遍历每张图像
for img_id in range(num_images):
# 获取每张图像的正负样本索引
img_sampled_inds = sampled_inds[img_id]
# 获取对应正负样本的proposals信息
proposals[img_id] = proposals[img_id][img_sampled_inds]
# 获取对应正负样本的真实类别信息
labels[img_id] = labels[img_id][img_sampled_inds]
# 获取对应正负样本的gt索引信息
matched_idxs[img_id] = matched_idxs[img_id][img_sampled_inds]
gt_boxes_in_image = gt_boxes[img_id]
if gt_boxes_in_image.numel() == 0:
gt_boxes_in_image = torch.zeros((1, 4), dtype=dtype, device=device)
# 获取对应正负样本的gt box信息
matched_gt_boxes.append(gt_boxes_in_image[matched_idxs[img_id]])
# 根据gt和proposal计算边框回归参数(针对gt的)
regression_targets = self.box_coder.encode(matched_gt_boxes, proposals)
return proposals, labels, regression_targets
self.check_targets函数用于检查target数据是否为空:
def check_targets(self, targets):
# type: (Optional[List[Dict[str, Tensor]]]) -> None
assert targets is not None
assert all(["boxes" in t for t in targets])
assert all(["labels" in t for t in targets])
self.add_gt_proposals将gt_boxes拼接到proposal后面:
def add_gt_proposals(self, proposals, gt_boxes):
# type: (List[Tensor], List[Tensor]) -> List[Tensor]
"""
将gt_boxes拼接到proposal后面
Args:
proposals: 一个batch中每张图像rpn预测的boxes
gt_boxes: 一个batch中每张图像对应的真实目标边界框
Returns:
"""
proposals = [
torch.cat((proposal, gt_box))
for proposal, gt_box in zip(proposals, gt_boxes)
]
return proposals
assign_targets_to_proposals为每个proposal匹配对应的gt_box,并划分到正负样本中
def assign_targets_to_proposals(self, proposals, gt_boxes, gt_labels):
# type: (List[Tensor], List[Tensor], List[Tensor]) -> Tuple[List[Tensor], List[Tensor]]
"""
为每个proposal匹配对应的gt_box,并划分到正负样本中
Args:
proposals:
gt_boxes:
gt_labels:
Returns:
"""
matched_idxs = []
labels = []
# 遍历每张图像的proposals, gt_boxes, gt_labels信息
for proposals_in_image, gt_boxes_in_image, gt_labels_in_image in zip(proposals, gt_boxes, gt_labels):
if gt_boxes_in_image.numel() == 0: # 该张图像中没有gt框,为背景
# background image
device = proposals_in_image.device
clamped_matched_idxs_in_image = torch.zeros(
(proposals_in_image.shape[0],), dtype=torch.int64, device=device
)
labels_in_image = torch.zeros(
(proposals_in_image.shape[0],), dtype=torch.int64, device=device
)
else:
# set to self.box_similarity when https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/27495 lands
# 计算proposal与每个gt_box的iou重合度
match_quality_matrix = box_ops.box_iou(gt_boxes_in_image, proposals_in_image)
# 计算proposal与每个gt_box匹配的iou最大值,并记录索引,
# iou < low_threshold索引值为 -1, low_threshold <= iou < high_threshold索引值为 -2
matched_idxs_in_image = self.proposal_matcher(match_quality_matrix)
# 限制最小值,防止匹配标签时出现越界的情况
# 注意-1, -2对应的gt索引会调整到0,获取的标签类别为第0个gt的类别(实际上并不是),后续会进一步处理
clamped_matched_idxs_in_image = matched_idxs_in_image.clamp(min=0)
# 获取proposal匹配到的gt对应标签
labels_in_image = gt_labels_in_image[clamped_matched_idxs_in_image]
labels_in_image = labels_in_image.to(dtype=torch.int64)
# label background (below the low threshold)
# 将gt索引为-1的类别设置为0,即背景,负样本
bg_inds = matched_idxs_in_image == self.proposal_matcher.BELOW_LOW_THRESHOLD # -1
labels_in_image[bg_inds] = 0
# label ignore proposals (between low and high threshold)
# 将gt索引为-2的类别设置为-1, 即废弃样本
ignore_inds = matched_idxs_in_image == self.proposal_matcher.BETWEEN_THRESHOLDS # -2
labels_in_image[ignore_inds] = -1 # -1 is ignored by sampler
matched_idxs.append(clamped_matched_idxs_in_image)
labels.append(labels_in_image)
return matched_idxs, labels
图示assign_targets_to_proposals函数功能
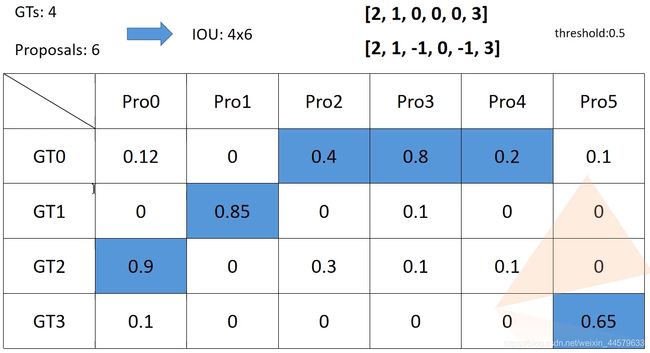
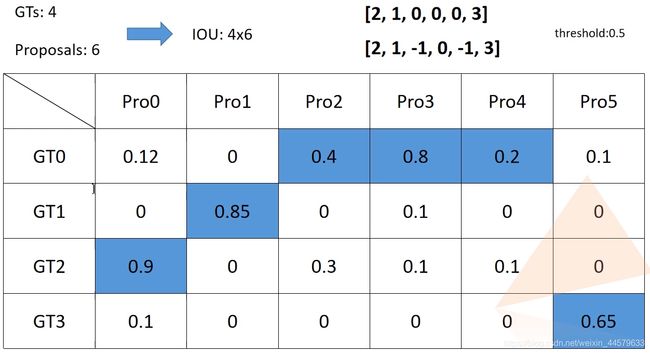
其中用到的proposal_matcher在Matcher类,与之前RPN部分类似
subsample函数按给定数量和比例采样正负样本
def subsample(self, labels):
# type: (List[Tensor]) -> List[Tensor]
# BalancedPositiveNegativeSampler
sampled_pos_inds, sampled_neg_inds = self.fg_bg_sampler(labels)
sampled_inds = []
# 遍历每张图片的正负样本索引
for img_idx, (pos_inds_img, neg_inds_img) in enumerate(zip(sampled_pos_inds, sampled_neg_inds)):
# 记录所有采集样本索引(包括正样本和负样本)
# img_sampled_inds = torch.nonzero(pos_inds_img | neg_inds_img).squeeze(1)
img_sampled_inds = torch.where(pos_inds_img | neg_inds_img)[0]
sampled_inds.append(img_sampled_inds)
return sampled_inds
其中用到的fg_bg_sampler也与之前RPN部分类似
self.box_coder.encoder函数与之前RPN部分类似
