数据结构学习_03_线性表
数据结构中常用的线性表
- 1 线性表的概念
- 2 线性表的分类
- 3 各种线性表的概念和实现
-
- 3.1 顺序表
-
- 3.1.2 概念
- 3.1.2 实现
- 3.2 链表
-
- 3.1.2 概念
- 3.1.2 实现
- 3.3 栈
-
- 3.1.2 概念
- 3.1.2 实现
- 3.4 队列
-
- 3.1.2 概念
- 3.1.2 实现
1 线性表的概念
线性表(Linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列,逻辑形式是线性,实际使用比较广泛。
2 线性表的分类
常见的线性表有:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串等。
3 各种线性表的概念和实现
3.1 顺序表
3.1.2 概念
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元一次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储,在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
1、静态顺序表:使用定长数据存储(不常用)
2、动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储
3.1.2 实现
声明:
#ifndef _SEQLIST_H_
#define _SEQLIST_H_
#include定义:
#include "SeqList.h"
//初始化动态顺序表
void SLInit(SL* psl){
psl->array = (SLDataType*)(malloc(sizeof(SLDataType)* 4));
if (psl->array == NULL){
printf("malloc error!");
exit(-1);
}
psl->capacity = 4;
psl->size = 0;
}
//扩容
void SLExpandCapacity(SL* psl){
if (psl->size >= psl->capacity){
psl->capacity *= 2;
psl->array = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->array, sizeof(SLDataType)*psl->capacity);
if (psl->array == NULL){
printf("扩容失败!\n");//一般不会扩容失败
exit(-1);
}
}
}
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* psl){
assert(psl);
psl->size--;
}
//打印动态顺序表中的数据
void SLPrint(SL* psl){
assert(psl);
for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++){
printf("%d ", psl->array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
//如果满了就要增容,2倍
/*SLExpandCapacity(psl);
psl->array[psl->size] = x;
psl->size++;*/
//复用接口
SLInsert(psl, psl->size, x);
}
/*无论在头部插入数据还是在尾部插入数据,都要考虑当容量够不够,去扩容*/
//头插
void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDataType x){
assert(psl);
//如果满了就要增容,2倍
SLExpandCapacity(psl);
int end = psl->size - 1;
//从尾部向右移动数据
while (end >= 0){
psl->array[end + 1] = psl->array[end];
end--;
}
psl->array[0] = x;
psl->size++;
}
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* psl){
assert(psl);
/*int start = 0;
while (start < psl->size - 1)
{
psl->array[start] = psl->array[start + 1];
start++;
}
psl->size--;*/
SLErase(psl, 0);
}
//任意位置插入
void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, SLDataType x){
assert(psl);
assert(pos <= psl->size && pos >= 0);
//扩容
SLExpandCapacity(psl);
int end = psl->size - 1;
while (end >= pos){
psl->array[end + 1] = psl->array[end];
end--;
}
psl->array[pos] = x;
psl->size++;
}
//任意位置删除
void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos){
assert(psl);
assert(pos < psl->size && pos >= 0);
while (pos < psl->size - 1){
psl->array[pos] = psl->array[pos + 1];
pos++;
}
psl->size--;
}
//销毁循序表--->free动态开辟的空间,指针置空,避免野指针
void SLDestory(SL* psl){
assert(psl);
free(psl->array);//动态开辟的内存用完需要释放掉
psl->array = NULL;
psl->capacity = psl->size = 0;
}
//在循序表中找到x元素的下标_二分查找
int SLFind(SL* psl, SLDataType x){
assert(psl);
int start = 0;
int end = psl->size - 1;
int mid = 0;
while (start <= end){
mid = start + ((end - start) >> 1);
if (x > psl->array[mid]){
start = mid + 1;
}
else if (x < psl->array[mid]){
end = mid - 1;
}
else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
//顺序表排序_冒泡排序
void SLSort(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
for (int i = 0; i < psl->size - 1; i++)
{
int flag = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < psl->size - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (psl->array[j]>psl->array[j + 1])
{
SLDataType temp = psl->array[j];
psl->array[j] = psl->array[j + 1];
psl->array[j + 1] = temp;
flag = 0;
}
}
if (flag == 1)
{
break;
}
}
}
3.2 链表
3.1.2 概念
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。

链表的结构非常多样
1、单向、双向
2、带头、不带头
3、循环、非循环
虽然有这么多的链表结构,但是我们在实际中最常用还是两种结构:
1、无头单向非循环链表:
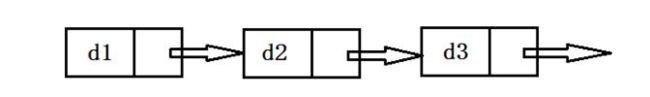
结构简单一般不会单独用来存储数据。实际中更多作为其他数据结构的子结构,如:队列,哈希桶、图的邻接表等。
2、带头双向循环链表

结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然有些小复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现这个结构结构带来了很多优势,实现起来反而简单很多。
3.1.2 实现
无头单向非循环链表:
声明:
#ifndef _SINGLELIST_H_
#define _SINGLELIST_H_
#include定义:
#include "SingleList.h"
//打印链表
void SListPrint(SLNode* phead)
{
SLNode* cur = phead;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
//新增结点
SLNode* BuySListNode(SingleListNodeDataType x){
SLNode* newNode = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("申请失败!\n");//一般不会申请失败
exit(-1);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
//在链表的尾部插入结点
void SListPushBack(SLNode** pphead, SingleListNodeDataType x)
{
SLNode* newNode = BuySListNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newNode;
}
else{
//首先遍历链表找到尾结点
SLNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newNode;
}
}
//在链表的尾部删除节点
void SListPopBack(SLNode** pphead)
{
//1、没有节点的空链表
//2、一个节点
//3、一个以上节点
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
else if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);//释放掉指针*pphead所指向的堆空间
*pphead = NULL;
//可以置为NULL,也可以不这样做,
//因为函数调用完后,函数栈帧里的局部变量也就被销毁了
}
else{
SLNode* tail = *pphead;
SLNode* pre = NULL;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
pre = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
pre->next = NULL;
}
}
//单链表删除pos位置后的节点
void SListEraseAfter(SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
if (pos->next != NULL)
{
SLNode* next = pos->next;
SLNode* nextNext = next->next;
pos->next = nextNext;
free(next);
}
}
//单链表在pos之后的位置插入x
void SListInsertAfter(SLNode* pos, SingleListNodeDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SLNode* newNode = BuySListNode(x);
newNode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newNode;
}
//查找节点,在此基础上你可以修改节点
SLNode* SListFind(SLNode* phead, SingleListNodeDataType x)
{
SLNode* cur = phead;
while (cur!=NULL)
{
if (cur->data==x)
{
return cur;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
return NULL;//程序要是走到这里说明链表中没有这个值或者链表为空
}
//在单链表的头部插入节点
void SListPushFront(SLNode** pphead, SingleListNodeDataType x)
{
//方法一:
*pphead这个指针指向的是第一个节点。
不管3721先获取一个新节点再说
//SLNode* newNode = BuySListNode(x);
1、链表为空
//if (*pphead == NULL)
//{
// *pphead = newNode;
// (*pphead)->next = NULL;
//}
//else
//{
// SLNode* next = *pphead;//临时保存后面要用,否则直接断开就找不到它了
// *pphead = newNode;
// (*pphead)->next = next;
//}
//方法二:
SLNode* newNode = BuySListNode(x);
newNode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newNode;
}
//在单链表的头部删除节点
void SListPopFront(SLNode** pphead)
{
//空链表
//一个节点
//一个以上的节点
//方法一:
/*if (*pphead == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空\n");
return;
}
else if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
else{
SLNode* head = *pphead;
*pphead = (*pphead)->next;
free(head);
}*/
//内存泄漏是指向内存的指针丢了
//方法二:
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SLNode* next = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = next;//要是next为空其实就是一个节点的情况
}
}
带头双向循环链表:
声明:
#pragma once
#include 定义:
#include "List.h"
//C语言中除了静态变量和全局变量不初始化会有初始值,其他的是随机值,随机值会带来
//问题
ListNode* BuyListNode(ListDataType x)
{
ListNode* newNode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newNode->val = x;
newNode->prev = NULL;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
if (cur != pHead)
{
while (cur != pHead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
else
{
printf("NULL");
printf("\n");
}
}
void ListInit0(ListNode** ppHead)
{
*ppHead = BuyListNode(0);
(*ppHead)->next = *ppHead;
(*ppHead)->prev = *ppHead;
}
ListNode* ListInit1()
{
ListNode* phead = BuyListNode(0);
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
return phead;
}
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, ListDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
//ListNode* tail = pHead->prev;
//ListNode* newNode = BuyListNode(x);
pHead tail newNode
//tail->next = newNode;
//newNode->prev = tail;
//newNode->next = pHead;
//pHead->prev = newNode;
ListInsert(pHead, x);
}
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
assert(pHead->next != pHead);
//ListNode* tail = pHead->prev;
//ListNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;
pHead tail tailPrev
//pHead->prev = tailPrev;
//tailPrev->next = pHead;
//free(tail);
//tail = NULL;//置空tail防止野指针,因为tail是局部变量,不置空也不会有影响
当时要养成好的习惯
ListErase(pHead->prev);
}
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, ListDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* newNode = BuyListNode(x);
//ListNode* first = pHead->next;
phead newNode first
//pHead->next = newNode;
//newNode->prev = pHead;
//newNode->next = first;
//first->prev = newNode;
ListInsert(pHead->next, x);//代码复用
}
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
assert(pHead->next != pHead);
//ListNode* first = pHead->next;
//ListNode* second = first->next;
pHead first second
//pHead->next = second;
//second->prev = pHead;
//free(first);
//first = NULL;
ListErase(pHead->next);
}
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, ListDataType x)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
if (cur->val == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, ListDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* newNode = BuyListNode(x);
ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
//posPrev newNode pos
posPrev->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = posPrev;
newNode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newNode;
}
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
ListNode* posNext = pos->next;
posPrev->next = posNext;
posNext->prev = posPrev;
free(pos);
}
void ListClear(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
ListNode* cur = pHead->next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pHead->next = pHead;
pHead->prev = pHead;
}
void ListDestory(ListNode** ppHead)
{
assert(*ppHead);
ListClear(*ppHead);
free(*ppHead);
*ppHead = NULL;
}
测试:
#include "List.h"
void TestList01()
{
/*ListNode* pHead = NULL;
ListInit0(&pHead);*/
ListNode* pHead = ListInit1();
ListPushBack(pHead, 1);
ListPushBack(pHead, 2);
ListPushBack(pHead, 3);
ListPushBack(pHead, 4);
ListPrint(pHead);
ListPopFront(pHead);
ListPrint(pHead);
ListDestory(&pHead);
}
int main()
{
TestList01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.3 栈
3.1.2 概念
栈是一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一段进行插入和删除操作。进行数据的插入和删除的一段称为栈顶,另一端称为栈顶。栈中的数据遵循的规则是先进后出或者后进先出。

压栈:栈的插入操作叫做压栈/进栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈,出数据也在栈顶。
3.1.2 实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表来实现,相对而言,用数组的结构实现起来更优一些,因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。实际中使用较多的是支持动态增长的栈。如果你使用链表来实现也是可以的,使用双向链表完全可以,单向链表要注意哪边当栈顶。
声明:
#pragma once
#include 定义:
#include "Stack.h"
//初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->_a = (StackDataType*)malloc(sizeof(StackDataType)* 4);
pst->_top = 0;
pst->_capacity = 4;
}
//销毁栈
void StackDestory(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->_a);
pst->_a = NULL;//防止野指针
pst->_top = pst->_capacity = 0;
}
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, StackDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
//判断是否需要扩容
if (pst->_capacity == pst->_top)
{
pst->_capacity *= 2;
StackDataType* tmp = (StackDataType*)realloc(pst->_a, sizeof(StackDataType)*pst->_capacity);
if (tmp)
{
pst->_a = tmp;
}
else
{
printf("内存申请失败!");
exit(-1);
}
}
pst->_a[pst->_top] = x;
pst->_top++;
}
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->_top > 0);//栈里没有数据是不能出栈的
pst->_top--;
}
//获取栈的数据个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->_top;
}
//判断栈是否为空,空返回1,非空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
//return !pst->_top;
return pst->_top == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
//获取栈顶数据
StackDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
//空帧栈顶没有数据,不能获取
assert(pst->_top > 0);
return pst->_a[pst->_top - 1];
}
3.4 队列
3.1.2 概念
队列:在一端进行插入数据的操作,在另一端进行删除数据的操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先入先出的特性。进行插入操作的一端称为队尾,进行删除操作的一端称为队头。
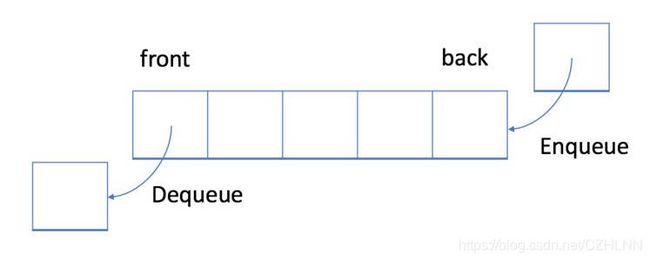
3.1.2 实现
队列可以用数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列是在数组头上删除数据,这时候涉及移动数据,效率很低。
声明:
#pragma once
#include 定义:
#include "Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->_head = pq->_tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->_head;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->_head = pq->_tail = NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QueueDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* newNode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("内存申请失败!");
exit(-1);
}
newNode->data = x;
newNode->_next = NULL;
if (pq->_head == NULL)
{
pq->_head = pq->_tail=newNode;//一个节点都没有,别忘记tail,否则
//tail一直为空,程序崩了
}
else
{
pq->_tail->_next = newNode;
pq->_tail = newNode;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->_head);
QueueNode* next = pq->_head->_next;
free(pq->_head);
pq->_head = next;
//头删,要注意队列只有一个节点的情况,tail会成野指针
if (pq->_head == NULL)
{
pq->_tail = NULL;
}
}
QueueDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->_head);
return pq->_head->data;
}
QueueDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->_tail);
return pq->_tail->data;
}
//1是空队列,0不是
int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->_head == NULL ? 1 : 0;
//return !pq->_head;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
//这是一个O(n)的接口
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QueueNode* cur = pq->_head;
while (cur)
{
++size;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return size;
}