JAVA-高频面试题汇总:链表
前言
为了让小伙伴们更好地刷题,我将所有leetcode常考题按照知识点进行了归纳。
高频题汇总:
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:动态规划
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:字符串
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:二叉树(上)
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:二叉树(下)
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:回溯
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:链表
接下来还会进行其他模块的总结,有一起在准备暑期实习的JAVA后端的伙伴可以一起交流!
小编微信: Apollo___quan
目录
- 反转链表(剑指)
- 反转链表 II
- 两个链表的第一个公共节点(剑指)
- 两个链表的第一个公共节点(剑指)
- 合并两个排序的链表
- 合并K个升序链表
- 从尾到头打印链表
- 链表中倒数第k个节点
- 删除链表的节点(剑指)
- 删除排序链表中的重复元素
- 删除链表中重复的结点(剑指)
- 复杂链表的复制(剑指)
1.反转链表(剑指)
思路
双指针,pre和cur
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode pre = null, cur = head, next; //注意pre初始化null
while(cur != null){
next = cur.next; //暂存后继节点
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
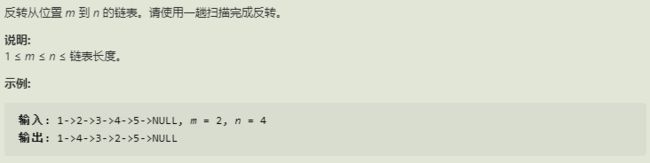
2.反转链表 II
思路

1.con定位到m前一个,tail第m个。m~n就当作普通的链表反转,然后更改con和tail的指针即可。
2.需要注意con可能为null,当m=1时
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
// Empty list
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// Move the two pointers until they reach the proper starting point
// in the list.
ListNode cur = head, prev = null;
while (m > 1) {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
m--;
n--;
}
ListNode con = prev, tail = cur; //con和tail为了之后连接
ListNode third = null;
while (n > 0) {
//对m~n中间的进行反转
third = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = third;
n--;
}
//根据con和tail调整连接
if (con != null) {
//注意con可能为null,当m=1时
con.next = prev;
} else {
head = prev;
}
tail.next = cur;
return head;
}
}
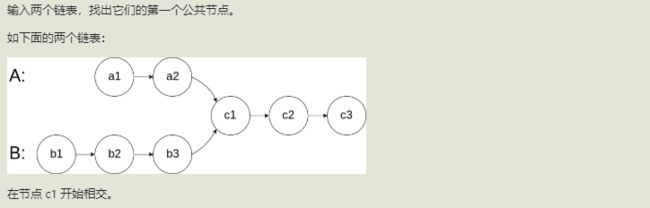
3.两个链表的第一个公共节点(剑指)
思路
双指针,在第一个交点必相遇(走过的路径都等于A+B+公共)
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode cur1=headA;
ListNode cur2=headB;
while(cur1!=cur2){
if(cur1==null) //cur1从A走完从B起点
cur1=headB;
else{
cur1=cur1.next;}
if(cur2==null) cur2=headA; //cur2从B走完从A起点
else
cur2=cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
}
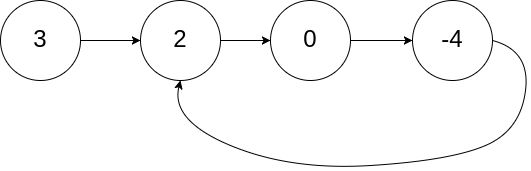
4. 两个链表的第一个公共节点(剑指)
思路
设置快慢指针,都从链表头出发,快指针每次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,假如有环,一定相遇于环中某点(结论1)。接着让两个指针分别从相遇点和链表头出发,两者都改为每次走一步,最终相遇于环入口(结论2)。以下是两个结论证明:
1、设置快慢指针,假如有环,他们最后一定相遇。
2、两个指针分别从链表头和相遇点继续出发,每次走一步,最后一定相遇与环入口。
证明结论1:设置快慢指针fast和low,fast每次走两步,low每次走一步。假如有环,两者一定会相遇(因为low一旦进环,可看作fast在后面追赶low的过程,每次两者都接近一步,最后一定能追上)。
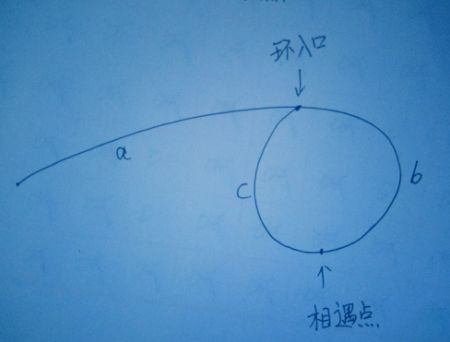
证明结论2:
设:
链表头到环入口长度为–a
环入口到相遇点长度为–b
相遇点到环入口长度为–c
则:相遇时
快指针路程=a+(b+c)k+b ,k>=1 其中b+c为环的长度,k为绕环的圈数(k>=1,即最少一圈,不能是0圈,不然和慢指针走的一样长,矛盾)。
慢指针路程=a+b
快指针走的路程是慢指针的两倍,所以:
(a+b)*2=a+(b+c)k+b
化简可得:
a=(k-1)(b+c)+c 这个式子的意思是: 链表头到环入口的距离=相遇点到环入口的距离+(k-1)圈环长度。其中k>=1,所以k-1>=0圈。所以两个指针分别从链表头和相遇点出发,最后一定相遇于环入口。
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead)
{
ListNode fast=pHead;
ListNode slow=pHead;
while(true){
if(fast == null || fast.next == null|| fast.next.next == null) return null;
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow) break; //第一次相遇时跳出
}
fast=pHead; //快指针从头开始走
while(true){
if(fast==slow) return fast; //快指针必定在入口处与慢指针再相遇
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
}
5.合并两个排序的链表
思路
引入伪头节点list,节点tar指向list
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode list=new ListNode();
ListNode tar=list;
while(l1!=null&&l2!=null){
if(l1.val<=l2.val) {
tar.next=l1;
l1=l1.next;
}
else{
tar.next=l2;
l2=l2.next;
}
tar=tar.next;
}
tar.next=l1!=null?l1:l2; //将剩下的拼接
return list.next;
}
6.合并K个升序链表
思路
一、小根堆
先将k个链表头节点输入小根堆,然后创建新列表,插入小根堆的poll(最小的出队),将其下一个节点再入小根堆(排序)
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
Queue<ListNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> v1.val - v2.val); //重写比较器,参数传为节点的值
for (ListNode node: lists) {
if (node != null) {
pq.offer(node); //将链表头加入
}
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); //新链表
ListNode tail = dummyHead; //tail作为指针
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
ListNode minNode = pq.poll(); //取出优先级队列中最小的
tail.next = minNode; //最小值插入新链表
tail = minNode;
if (minNode.next != null) {
pq.offer(minNode.next); //将最小值的下一个值插进优先级队列中排序
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
二、两两合并对 1 进行优化,时间复杂度:O(NlogK)
时间复杂度分析:KK 条链表的总结点数是 NN,平均每条链表有 N/KN/K 个节点,因此合并两条链表的时间复杂度是 O(N/K)O(N/K)。从 KK 条链表开始两两合并成 11 条链表,因此每条链表都会被合并 logKlogK 次,因此 KK 条链表会被合并 K * logKK∗logK 次,因此总共的时间复杂度是 KlogKN/KK∗logK∗N/K 即 O(NlogK)O(NlogK)。
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
int k = lists.length;
while (k > 1) {
int idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i += 2) {
if (i == k - 1) {
lists[idx++] = lists[i];
} else {
lists[idx++] = merge2Lists(lists[i], lists[i + 1]); //merge2Lists为合并两个有序链表
}
}
k = idx;
}
return lists[0];
}
7.从尾到头打印链表
思路
辅助栈法
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
while(head != null) {
stack.push(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int[] res = new int[stack.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++)
res[i] = stack.pop();
return res;
}
}
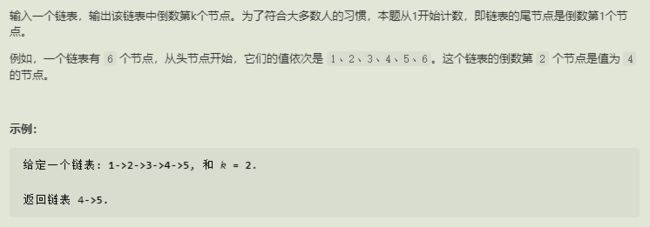
8.链表中倒数第k个节点
思路
双指针,前面的former先走k,再latter和former同时走,
class Solution {
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode former = head, latter = head;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
former = former.next;
while(former != null) {
former = former.next;
latter = latter.next;
}
return latter;
}
}
9.删除链表的节点(剑指)
思路
只有需要找到并删除一个值,用cur定位改值,让pre.next = cur.next即可
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head.val == val) return head.next;
ListNode pre = head, cur = head.next;
while(cur != null && cur.val != val) {
//跳出循环时cur.val == val
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
if(cur != null) pre.next = cur.next; //相当于跳过cur
return head;
}
}
10.删除排序链表中的重复元素
判断current和current.next是否相等,相等则current.next指向current.next.next
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode current = head;
while (current != null && current.next != null) {
if (current.next.val == current.val) {
//如果重复,则next指向next.next
current.next = current.next.next;
} else {
current = current.next;
}
}
return head;
}
11.删除链表中重复的结点(剑指)
思路
1.构造pre和cur,初始化时pre.next = pHead,构造了伪头节点
2.当cur.next == cur,则不断cur = cur.next,跳出循环时cur是最后一个重复数,仍需处理 cur = cur.next, pre.next = cur;
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead){
if(pHead == null || pHead.next == null){
return pHead;
}
// 自己构建辅助头结点
ListNode head = new ListNode(0); //构造链表头
ListNode pre = head;
head.next = pHead; //链表头下一个才是Head,便于讨论pHead重复的情况
ListNode cur = pHead;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.next != null && cur.next.val == cur.val){
// 相同结点一直前进
while(cur.next != null && cur.next.val == cur.val){
cur = cur.next;
}
// 退出循环时,cur 指向重复值,也需要删除,而 cur.next 指向第一个不重复的值
// cur 继续前进
cur = cur.next;
// pre 连接新结点
pre.next = cur;
}else{
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head.next;
}
}
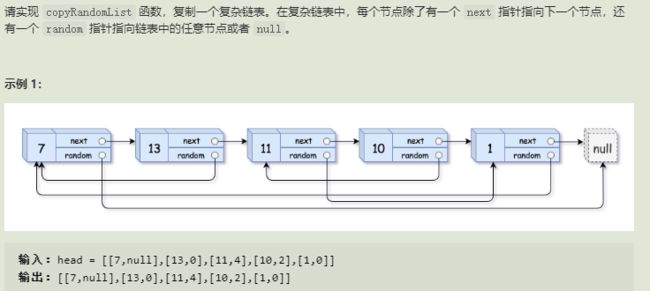
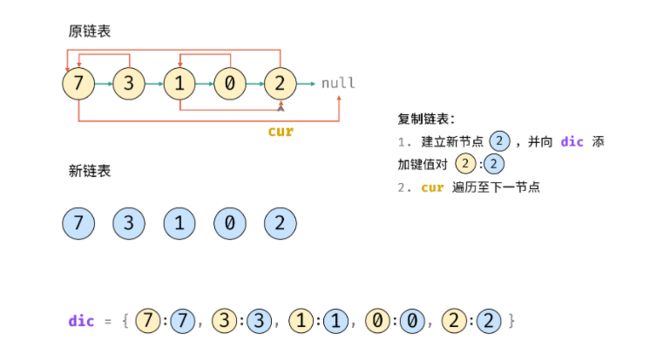
12.复杂链表的复制(剑指)
思路
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Node cur = head;
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
// 3. 复制各节点,并建立 “原节点 -> 新节点” 的 Map 映射
while(cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
// 4. 构建新链表的 next 和 random 指向
while(cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 5. 返回新链表的头节点
return map.get(head);
}
}
总结
链表题型整理完毕,其余类型
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:动态规划
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:字符串
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:二叉树(上)
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:二叉树(下)
JAVA-高频面试题汇总:回溯