mmsegment数据pipeline操作(七)
目录
1、数据项配置
2、voc数据集传入参数
3、CustomDataset数据读取
4、self.pipeline(results)
4.1、读图
4.2、数据增广
4.3、格式转换
4.4、测试
5、扩展和使用自定义管道
1、数据项配置
不使用数据增广,返回原始默认图像及标签:
from mmseg.datasets import build_dataset
train_cfg = dict(
type='PascalVOCDataset',
data_root=r'F:\dataset\voc2012',
img_dir='JPEGImages',
ann_dir='SegmentationClass',
split='ImageSets/Segmentation/train.txt',
pipeline=[
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations')
],
)
train_set = build_dataset(train_cfg)
print("train_set:", len(train_set))
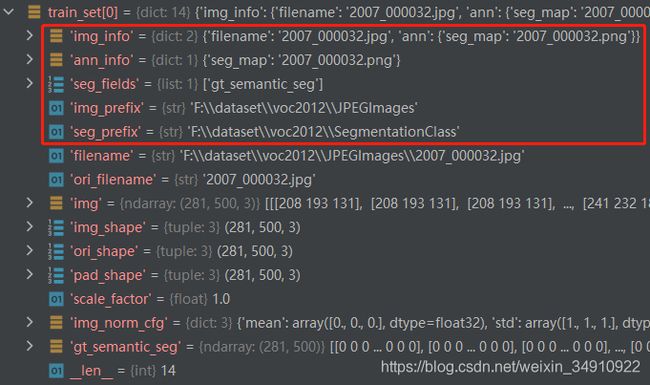
print(train_set[0])默认输出,train_set[0]元素如下,不读图像时,默认info信息为红框中5个参数:
所以,作为VOC数据集,主要提供了红框中的5个参数。执行pipeline操作需几个字段。
2、voc数据集传入参数
voc数据集类,封装覆盖基类4个参数,其它参数直接传入基类。
1)CLASSES、PALETTE分别为类别名称列表和类别所对应的颜色值;
2)img_suffix='.jpg', seg_map_suffix='.png',指定图像、标注文件后缀名。
class PascalVOCDataset(CustomDataset):
CLASSES = ('background', 'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat', 'bottle',
'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair', 'cow', 'diningtable', 'dog',
'horse', 'motorbike', 'person', 'pottedplant', 'sheep', 'sofa',
'train', 'tvmonitor')
PALETTE = [[0, 0, 0], [128, 0, 0], [0, 128, 0], [128, 128, 0], [0, 0, 128],
[128, 0, 128], [0, 128, 128], [128, 128, 128], [64, 0, 0],
[192, 0, 0], [64, 128, 0], [192, 128, 0], [64, 0, 128],
[192, 0, 128], [64, 128, 128], [192, 128, 128], [0, 64, 0],
[128, 64, 0], [0, 192, 0], [128, 192, 0], [0, 64, 128]]
def __init__(self, split, **kwargs):
super(PascalVOCDataset, self).__init__(
img_suffix='.jpg', seg_map_suffix='.png', split=split, **kwargs)
assert osp.exists(self.img_dir) and self.split is not None3、CustomDataset数据读取
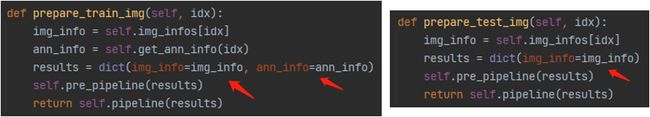
1)通过test_mode参数,选择输出有标记的训练数据还是无标签的测试数据。
def __getitem__(self, idx):
if self.test_mode:
return self.prepare_test_img(idx)
else:
return self.prepare_train_img(idx)具体区别如下,train中有标注信息,test只有图片:
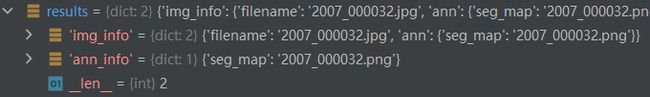
其中results字段内容形式如下,结合__init__初始化中保存的self成员变量,可确定具体的图像文件、标注文件路径和类别说明信息:
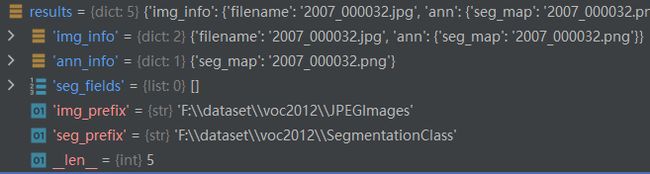
self.pre_pipeline(results)为results补齐完整字段,添加:
def pre_pipeline(self, results):
results['seg_fields'] = []
results['img_prefix'] = self.img_dir
results['seg_prefix'] = self.ann_dir
if self.custom_classes:
results['label_map'] = self.label_map经过self.pre_pipeline(results)后的results字段形如:
4、self.pipeline(results)
在__init__类初始化时,通过compose将字符串转为对应的注册pipelines操作:
self.pipeline = Compose(pipeline)Compose实现,通过build_from_cfg将字符串转为具体pipeline操作:
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class Compose(object):
def __init__(self, transforms):
assert isinstance(transforms, collections.abc.Sequence)
self.transforms = []
for transform in transforms:
if isinstance(transform, dict):
transform = build_from_cfg(transform, PIPELINES)
self.transforms.append(transform)
elif callable(transform):
self.transforms.append(transform)
else:
raise TypeError('transform must be callable or a dict')
def __call__(self, data):
for t in self.transforms:
data = t(data)
if data is None:
return None
return data4.1、读图
读图,将图像及标注文件夹和路径拼接,形成实际路径。读取图像及其info信息,填充后返回。loading.py
pipeline=[
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations')
]读取的图像及标签格式:
img = train_set[0]["img"]
gt_semantic_seg = train_set[0]["gt_semantic_seg"]
file_name = train_set[0]["filename"]
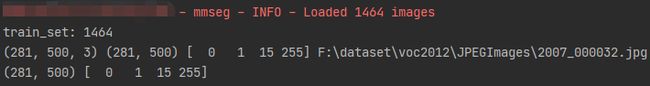
print(img.shape, gt_semantic_seg.shape, np.unique(gt_semantic_seg), file_name)
cv2.imwrite(r"F:\img.jpg", img)
cv2.imwrite(r"F:\gt_semantic_seg.png", gt_semantic_seg, [cv2.IMWRITE_PNG_COMPRESSION, 0])
gt_label = cv2.imread(r"F:\gt_semantic_seg.png", 0)
print(gt_label.shape, np.unique(gt_label))输出:
图像:
4.2、数据增广
通过LoadImageFromFile、LoadAnnotations分别读取图像及标签,通过Resize、RandomCrop、RandomFlip、PhotoMetricDistortion分别实现缩放、剪切、翻转、颜色等变换。
pipeline=[
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations'),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=(2048, 512), ratio_range=(0.5, 2.0)),
dict(type='RandomCrop', crop_size=(512, 512), cat_max_ratio=0.75),
dict(type='RandomFlip', prob=0.5), # prob表示有多少概率执行操作
dict(type='RandomRotate', prob=1, degree=30, auto_bound=True),
dict(type='PhotoMetricDistortion'),
]1)Resize参数
img_scale=(2048, 512); # None, (w, h)
multiscale_mode='range'; # 'range'
ratio_range=(0.5, 2.0); # None,
keep_ratio=True; # True执行方式:
step1、生成scale、scale_idx参数。
scale格式为(w,h),scale_idx为数字或None。
1)ratio_range不为空时,ratio_range=(0.5, 2.0)。若img_scale未设置,则使用当前图尺寸,若设置img_scale,则使用设置尺寸。从此看出,设置的img_scale为图像(宽,高)。
random_sample_ratio随机生成一个在ratio_range范围内的ratio,该ratio为尺寸放缩比例因子,返回的scale_idx为None。
scale = int(img_scale[0] * ratio), int(img_scale[1] * ratio);ratio_range为None:
2)img_scale为单个范围,则默认为固定尺寸scale, scale_idx=0。
3)img_scale数组多范围,range模式,在多组中范围内随机出scale, scale_idx=None。
4)img_scale数组多范围,value模式,在多组中范围内随机出某个index的scale, scale_idx=index。
def _random_scale(self, results):
if self.ratio_range is not None: # 1)
if self.img_scale is None:
h, w = results['img'].shape[:2]
scale, scale_idx = self.random_sample_ratio((w, h),
self.ratio_range)
else:
scale, scale_idx = self.random_sample_ratio(
self.img_scale[0], self.ratio_range)
elif len(self.img_scale) == 1: # 2)
scale, scale_idx = self.img_scale[0], 0
elif self.multiscale_mode == 'range': # 3)
scale, scale_idx = self.random_sample(self.img_scale)
elif self.multiscale_mode == 'value': # 4)
scale, scale_idx = self.random_select(self.img_scale)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
results['scale'] = scale
results['scale_idx'] = scale_idx依据scale进行图像resize,操作完成后保存相关参数入results字典中;真值标记图像使用results字典中保存的参数,进行近临插值。
new_gt_mask = cv2.resize(gt_semantic, (w, h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)2)RandomCrop参数
crop_size=(512, 512); # 必填参数
cat_max_ratio=0.75; # 1. ,某一个类别的有效标记区域占整图的比例要小于cat_max_ratio
ignore_index=255; # 255执行方式:
def get_crop_bbox(self, img):
margin_h = max(img.shape[0] - self.crop_size[0], 0)
margin_w = max(img.shape[1] - self.crop_size[1], 0)
offset_h = np.random.randint(0, margin_h + 1)
offset_w = np.random.randint(0, margin_w + 1)
crop_y1, crop_y2 = offset_h, offset_h + self.crop_size[0]
crop_x1, crop_x2 = offset_w, offset_w + self.crop_size[1]
return crop_y1, crop_y2, crop_x1, crop_x2在图像范围内,截取一个crop_size大小的区域。cat_max_ratio=0.75,表示标记图像的某一个类别的有效标记区域占整图的比例要小于cat_max_ratio。
if self.cat_max_ratio < 1.:
# Repeat 10 times
for _ in range(10):
seg_temp = self.crop(results['gt_semantic_seg'], crop_bbox)
labels, cnt = np.unique(seg_temp, return_counts=True)
cnt = cnt[labels != self.ignore_index]
if len(cnt) > 1 and np.max(cnt) / np.sum(
cnt) < self.cat_max_ratio:
break
crop_bbox = self.get_crop_bbox(img)3)RandomFlip参数
prob=0.5; # None, prob表示有多少概率执行操作
direction='horizontal'; # 'horizontal'随机Flip,prob表示有多少概率执行操作。
4)RandomRotate参数
prob=1; # 必填参数,
degree=30; # 必填参数, 取值[-degree, degree]
pad_val=0; # 0,
seg_pad_val=255; # 255,
center=None; # None,
auto_bound=True; # False,在正负degree中随机选取一个角度。使用mmcv.imrotate进行旋转。真值标签的旋转使用相同参数,插值方式interpolation='nearest'。实现方式,采用变换矩阵实现旋转:
def imrotate(img,
angle,
center=None,
scale=1.0,
border_value=0,
interpolation='bilinear',
auto_bound=False):
if center is not None and auto_bound:
raise ValueError('`auto_bound` conflicts with `center`')
h, w = img.shape[:2]
if center is None:
center = ((w - 1) * 0.5, (h - 1) * 0.5)
assert isinstance(center, tuple)
matrix = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, -angle, scale)
if auto_bound:
cos = np.abs(matrix[0, 0])
sin = np.abs(matrix[0, 1])
new_w = h * sin + w * cos
new_h = h * cos + w * sin
matrix[0, 2] += (new_w - w) * 0.5
matrix[1, 2] += (new_h - h) * 0.5
w = int(np.round(new_w))
h = int(np.round(new_h))
rotated = cv2.warpAffine(
img,
matrix, (w, h),
flags=cv2_interp_codes[interpolation],
borderValue=border_value)
return rotated5)PhotoMetricDistortion参数
brightness_delta=32; # 32
contrast_range=(0.5, 1.5); # (0.5, 1.5),下限-上限
saturation_range=(0.5, 1.5); # (0.5, 1.5),下限-上限
hue_delta=18; # 18只修改图像,不修改标签真值。
random.uniform(-self.brightness_delta, self.brightness_delta)4.3、格式转换
1)Normalize归一化。只对图像做归一化处理,cv2与numpy处理后仍为numpy类型。
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53],
std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375],
to_rgb=True)
pipeline=[...
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
]4.4、测试
多尺度剪裁测试。
pipeline=[
...,
dict(type='MultiScaleFlipAug'),
]数据集定义如何处理注释,数据管道定义所有准备数据字典的步骤。流水线由一系列操作组成。每个操作都将一个dict作为输入,并为下一个转换输出一个dict。
这些操作分为数据加载,预处理,格式化和测试和扩充。
对于每个操作,我们都列出了添加/更新/删除的相关字典字段。
数据载入
LoadImageFromFile
- 添加:img,img_shape,ori_shape
LoadAnnotations
- 添加:gt_semantic_seg,seg_fields
预处理
Resize
- 添加:scale,scale_idx,pad_shape,scale_factor,keep_ratio
- 更新:img,img_shape,* seg_fields
RandomFlip
- 添加:翻转
- 更新:img,* seg_fields
Pad
- 添加:pad_fixed_size,pad_size_divisor
- 更新:img,pad_shape,* seg_fields
RandomCrop
- 更新:img,pad_shape,* seg_fields
Normalize
- 添加:img_norm_cfg
- 更新:img
SegRescale
- 更新:gt_semantic_seg
PhotoMetricDistortion
- 更新:img
格式化
ToTensor
- 更新:由指定keys。
ImageToTensor
- 更新:由指定keys。
Transpose
- 更新:由指定keys。
ToDataContainer
- 更新:由指定fields。
DefaultFormatBundle
- 更新:img,gt_semantic_seg
Collect
- 添加:img_meta(img_meta的键由指定meta_keys)
- 删除:除由所指定的键外的所有其他键 keys
多尺度增强测试
MultiScaleFlipAug
5、扩展和使用自定义管道
1)在任何文件(例如)中编写新的管道my_pipeline.py。它以字典作为输入并返回一个字典。
from mmseg.datasets import PIPELINES
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class MyTransform:
def __call__(self, results):
results['dummy'] = True
return results2)导入新类。
from .my_pipeline import MyTransform3)在配置文件中使用它。
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53], std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375], to_rgb=True)
crop_size = (512, 1024)
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations'),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=(2048, 1024), ratio_range=(0.5, 2.0)),
dict(type='RandomCrop', crop_size=crop_size, cat_max_ratio=0.75),
dict(type='RandomFlip', flip_ratio=0.5),
dict(type='PhotoMetricDistortion'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size=crop_size, pad_val=0, seg_pad_val=255),
dict(type='MyTransform'),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_semantic_seg']),
]