springcloud gateway ribbon使用_闷棍暴打面试官 SpringCloud源码系列 : (一) SpringCloud的前世今生
单机架构 VS 微服务架构 哪个是21世纪的Web领域的趋势 ?
答案: 微服务架构是单机架构的未来, 但不是银弹多用于增长型业务!
如果你是一位软件行业从业者,尤其是从事服务器端或者后台系统软件开发,相信近年来一定被层出不穷的商业名词所包围:NoSQL、Big Data、Web-scale、Sharding、Eventual consistency、ACID、CAP理论、云服务、MapReduce和Real-time等, 所有这些其实都围绕着如何构建高效存储与数据处理这一核心主题。
过去十年,在数据库领域与分布式系统方面涌现了许多引人瞩目的进展,由此深刻地影响了如何构建上层应用系统。分析这些激动人心的变化背后,你会发现有以下几个非常重要的驱动因素: 互联网公司,包括Google、Yahoo! 、Amazon、Facebook、LinkedIn、Microsoft,以及Twitter等, 它们每天都在面对海量数据和负载,迫使其不断创新,并改进支撑系统以更有效地处理这种量级的数据。
商业方面因素,如敏捷开发、测试驱动和对市场机会做出快速反应等,都要求尽量缩短产品开发周期,因此系统中的数据模型也要足够灵活以方便调整。 硬件方面,CPU主频增长日趋缓慢,而多核系统成为新常态,网络速度则依旧保持快速发展,这就意味着并行分布式系统将会成为业界主流。
<数据密集型应用系统设计>
先有SpringCloud 还是先有 微服务 ?
答案: 先有微服务后有SpringCloud !' 2014年3月25日 敏捷开发教父 Martin Fowler 在 Microservices 一文中 对于 Microservice Architecture 进行了条理清晰的论述, 向世人展示了进可攻退可守的微服务架构思想, 奠定了后来者对 微服务的认知.
早期 SpringCloud & Angel 系列基于Spring Boot 1.2.x, 而1.2版本最早诞生于 2014年12月11日,也就是说至少晚了8个月多! 其中很多设计思想也来源于前者! (数据来源: github) 又一个活生生的学术界驱动工业界的例子. 所以大家有空还是要关注一下 学术界大牛们的新作.才能保证走在技术最前沿.
微服务的定义
笔者通过翻阅 Martin Fowler 发表的文章 Microservices , 将微服务理念梳理为 以下 7 点
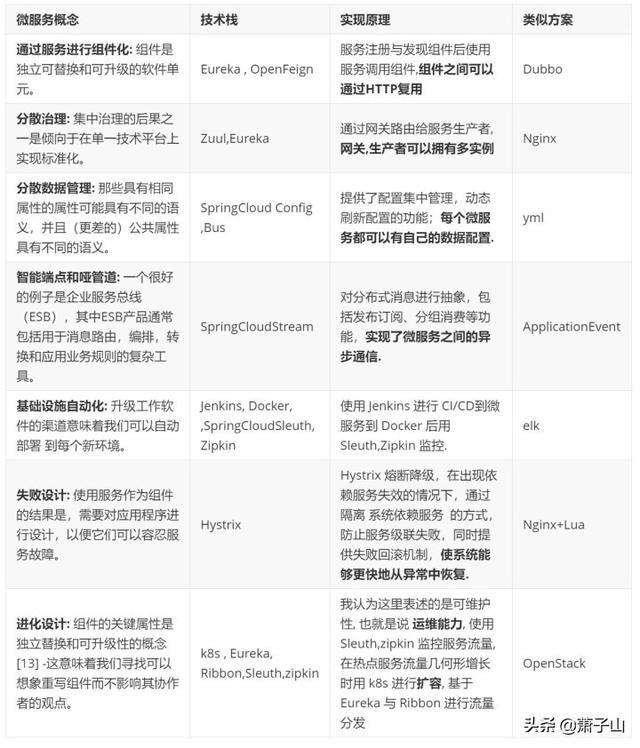
- 通过服务进行组件化: 组件是独立可替换和可升级的软件单元。微服务架构将使用库,但是它们将自己的软件组成组件的主要方式是分解成服务。我们将库定义为链接到程序并使用内存中函数调用进行调用的组件,而服务则是进程外组件,它们通过某种机制(例如Web服务请求或远程过程调用)进行通信。
- 分散治理: 集中治理的后果之一是倾向于在单一技术平台上实现标准化。经验表明,这种方法是束手无策的-并非每个问题都是钉子,也不是每个解决方案都是锤子。我们更喜欢使用正确的工具来完成工作,而整体式应用程序可以在一定程度上利用不同的语言,但这并不常见。
- 分散数据管理: 数据管理的分散化以多种不同的方式呈现。从最抽象的角度讲,这意味着系统的世界概念模型将有所不同。在大型企业中进行集成时,这是一个常见问题,客户的销售视图将与支持视图不同。在销售视图中被称为客户的某些内容可能根本不会出现在支持视图中。那些具有相同属性的属性可能具有不同的语义,并且(更差的)公共属性具有不同的语义。
- 智能端点和哑管道: 在不同流程之间建立通信结构时,我们已经看到了许多产品和方法,这些产品和方法强调在通信机制本身中投入大量智慧。一个很好的例子是企业服务总线(ESB),其中ESB产品通常包括用于消息路由,编排,转换和应用业务规则的复杂工具。
- 基础设施自动化: 我们希望尽可能地放心我们的软件正在运行,因此我们运行了许多自动化测试。升级工作软件的渠道意味着我们可以自动部署 到每个新环境。
- 失败设计: 使用服务作为组件的结果是,需要对应用程序进行设计,以便它们可以容忍服务故障。由于供应商不可用,任何服务呼叫都可能失败,客户必须尽可能优雅地响应此请求。与单片设计相比,这是一个缺点,因为它引入了额外的处理复杂性。结果是微服务团队不断反思服务故障如何影响用户体验。Netflix的Simian Army 在工作日内导致服务甚至数据中心发生故障,以测试应用程序的弹性和监视能力。
- 进化设计: 每当您尝试将软件系统分解为组件时,您都会面临如何划分各个部分的决定-我们决定对应用程序进行分割的原则是什么?组件的关键属性是独立替换和可升级性的概念[13] -这意味着我们寻找可以想象重写组件而不影响其协作者的观点。实际上,许多微服务组通过明确期望许多服务将被废弃而不是长期发展而将其进一步发展。
没接触过微服务的小伙伴看完晕倒了过去, 过一会醒来疯狂挠头, 这知识不过脑子啊 !
轻点,注意发量哈 其实每一个点对应的都是一种微服务场景的解决方案。 而这些解决方案可能是 Spring 官方提供,有可能是 别的公司提供. 或者两者都有...
微服务之我见
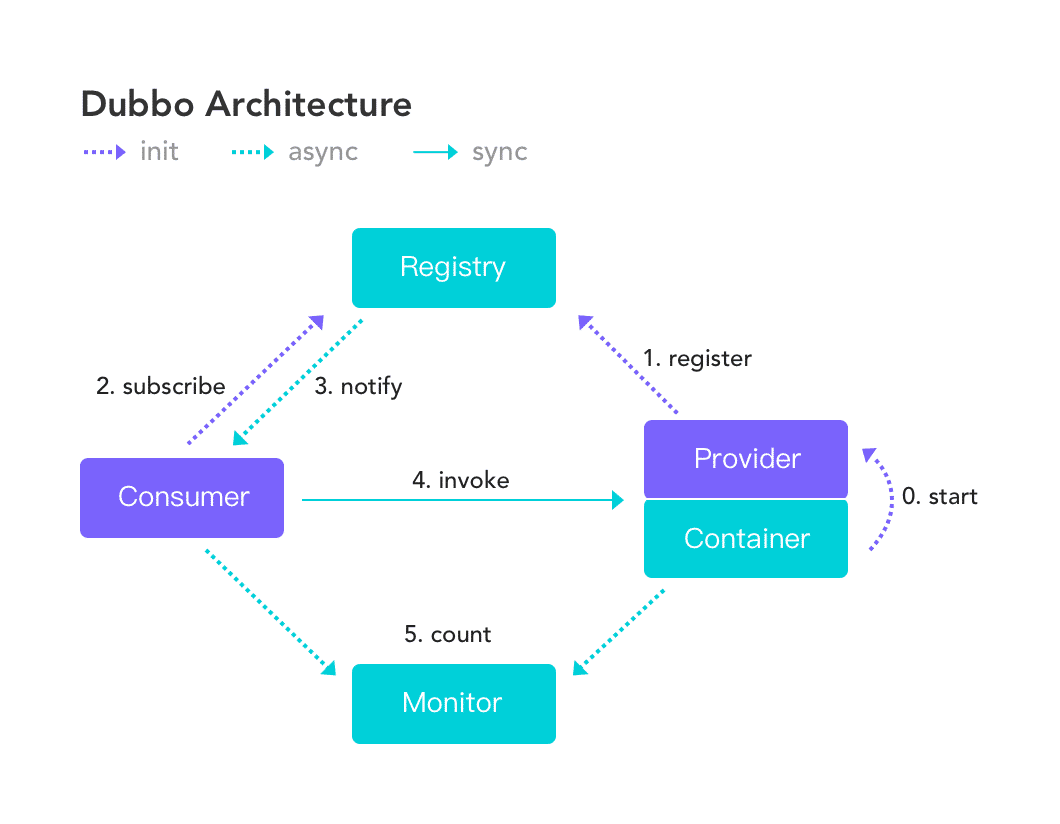
笔者才毕业时那会业内流行 Dubbo , 只要涉及到有点难度的项目 别管并发,数据量怎么样, 都一律上 Dubbo 生产者消费者分离, 和今天小伙伴们使用 SpringCloud 的热情如出一辙, 但是那时候 微服务这个概念并不是很火热 !
Dubbo 官方定义: Apache Dubbo |ˈdʌbəʊ| 是一款高性能、轻量级的开源Java RPC框架,它提供了三大核心能力:面向接口的远程方法调用,智能容错和负载均衡,以及服务自动注册和发现。
SpringCloud 官方定义: SpringCloud基于SpringBoot为开发人员提供了组件,以快速构建分布式系统中的一些常见模式(例如,配置中心,服务发现,断路器,智能路由,微代理,控制总线,一次性令牌,全局锁,领导选举,分布式会话,群集状态)。分布式系统的协调导致样板式样,并且使用Spring Cloud开发人员可以快速站起来实现这些样板的服务和应用程序。它们可以在任何分布式环境中正常工作,包括开发人员自己的笔记本电脑,裸机数据中心以及Cloud Foundry等托管平台。
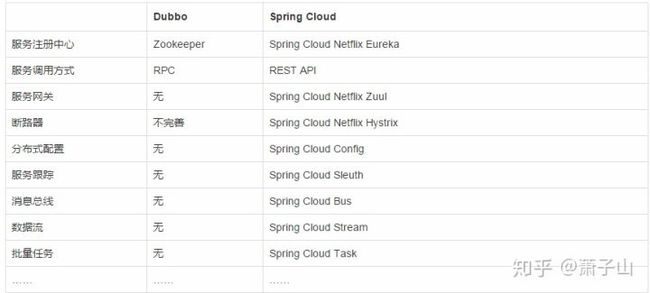
那么 Dubbo 和 SpringCloud 有什么区别呢?
从技术栈上来看
dubbo:zookeeper+dubbo+springmvc/springboot
通信方式:rpc
注册中心:zookeeper,nacos
配置中心:diamond(淘宝开发)
spring cloud:spring+Netflix
通信方式:http restful
注册中心:eureka,consul,nacos
配置中心:config
断路器:hystrix
网关:zuul,gateway
分布式追踪系统:sleuth+zipkin诚然 Dubbo 已经跟不上目前 微服务思想的发展了, 我们在做微服务的时候 首选 SpringCloud.那 SpringCloud 有那么多组合我们选哪个好呢?
SpringCloud 组合大PK
SpringCloud 有哪些主流组合呢?
- SpringCloud-Alibaba
- Sentinel:把流量作为切入点,从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度保护服务的稳定性。
- Nacos:一个更易于构建云原生应用的动态服务发现、配置管理和服务管理平台。
- RocketMQ:一款开源的分布式消息系统,基于高可用分布式集群技术,提供低延时的、高可靠的消息发布与订阅服务。
- Dubbo:Apache Dubbo™ 是一款高性能 Java RPC 框架。
- Seata:阿里巴巴开源产品,一个易于使用的高性能微服务分布式事务解决方案。
- Alibaba Cloud ACM:一款在分布式架构环境中对应用配置进行集中管理和推送的应用配置中心产品。
- Alibaba Cloud OSS: 阿里云对象存储服务(Object Storage Service,简称 OSS),是阿里云提供的海量、安全、低成本、高可靠的云存储服务。您可以在任何应用、任何时间、任何地点存储和访问任意类型的数据。
- Alibaba Cloud SchedulerX: 阿里中间件团队开发的一款分布式任务调度产品,提供秒级、精准、高可靠、高可用的定时(基于 Cron 表达式)任务调度服务。
- Alibaba Cloud SMS: 覆盖全球的短信服务,友好、高效、智能的互联化通讯能力,帮助企业迅速搭建客户触达通道。
- SpringCloud-Netflix
- Eureka :服务注册和发现,它提供了一个服务注册中心、服务发现的客户端,还有一个方便的查看所有注册的服务的界面。 所有的服务使用Eureka的服务发现客户端来将自己注册到Eureka的服务器上。
- Zuul : 网关,所有的客户端请求通过这个网关访问后台的服务。它可以使用一定的路由配置来判断某一个URL由哪个服务来处理。并从Eureka获取注册的服务来转发请求。
- Ribbon :即负载均衡,Zuul网关将一个请求发送给某一个服务的应用的时候,如果一个服务启动了多个实例,就会通过Ribbon来通过一定的负载均衡策略来发送给某一个服务实例。
- Feign :服务客户端,服务之间如果需要相互访问,可以使用RestTemplate,也可以使用Feign客户端访问。它默认会使用Ribbon来实现负载均衡。
- Hystrix : 监控和断路器。我们只需要在服务接口上添加Hystrix标签,就可以实现对这个接口的监控和断路器功能。
- Hystrix Dashboard : 监控面板,它提供了一个界面,可以监控各个服务上的服务调用所消耗的时间等。
- Turbine : 监控聚合,使用Hystrix监控,我们需要打开每一个服务实例的监控信息来查看。而Turbine可以帮助我们把所有的服务实例的监控信息聚合到一个地方统一查看。
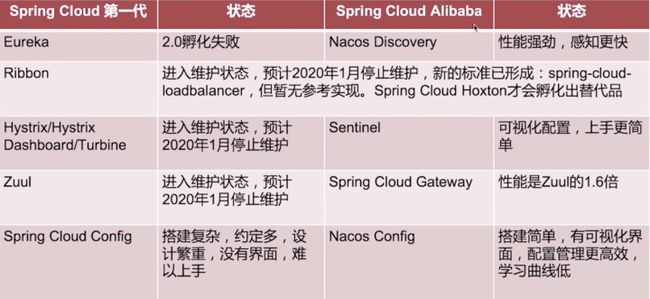
两者的优缺点: SpringCloud 是一项标准而不是一门技术, 你可以在它们互相兼容的前提下同时使用两大阵营的组件, 两者最大的不同在于, Netflix 的服务通信基于 Feign 组件倾向于 HTTP RestFul, 而 Alibaba 的服务通信 基于 Dubbo 组件 的 RPC 调用, 从这里不难看出来, 它们的基本盘分别是 SpringBoot 与 Dubbo, 如果你的项目基于 SpringBoot 就首选 Netflix , 如果你的项目基于 Dubbo 就首选 Alibaba 这样对于重构系统来说会减少很多工作量, 从社区的角度看, 大家都知道 2018-12-12日,Netflix宣布Spring Cloud Netflix 除了 Eureka 其它组件都进入维护状态(不会推出新功能), 但不等于 Netflix 就毫无希望, 最近 Netflix 推出了 PRE 3.0 M1 对 Eureka 进行迭代, 而 Alibaba 这个后起之秀的 GitHub Fork 数为 3.8 K 而 Netflix 为 2K 近乎两倍, 对拥有国内 70% 市场的 Netflix 来说 进入维护状态的 组件可以, 用别的组件来替代就可以, 而如果使用了 Alibaba 就被被捆绑销售了 一堆自己的技术以及阿里云的东西 ... 技术选型上面没有银弹, 选择最适合项目的技术即可 !
SpringCloud-Alibaba 太香了 , 我选 SpringCloud-Netflix !
推荐 SpringCloud-Netflix组合
- 服务注册与发现组件:Eureka,Zookeeper,Consul,Nacos等。Eureka基于REST风格的。
- 服务调用组件:Hystrix(熔断降级,在出现依赖服务失效的情况下,通过隔离 系统依赖服务 的方式,防止服务级联失败,同时提供失败回滚机制,使系统能够更快地从异常中恢复),Ribbon(客户端负载均衡,用于提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法,提供了一系列完善的配置项:连接超时、重试等),OpenFeign(优雅的封装Ribbon,是一个声明式RESTful网络请求客户端,它使编写Web服务客户端变得更加方便和快捷)。
- 网关:路由和过滤。Zuul,Gateway。
- 配置中心:提供了配置集中管理,动态刷新配置的功能;配置通过Git或者其它方式来存储。
- 消息组件:Spring Cloud Stream(对分布式消息进行抽象,包括发布订阅、分组消费等功能,实现了微服务之间的异步通信)和Spring Cloud Bus(主要提供服务间的事件通信,如刷新配置)
- 安全控制组件:Spring Cloud Security 基于OAuth2.0开放网络的安全标准,提供了单点登录、资源授权和令牌管理等功能。
- 链路追踪组件:Spring Cloud Sleuth(收集调用链路上的数据),Zipkin(对Sleuth收集的信息,进行存储,统计,展示)
SpringCloud-Netflix 中的微服务理念
SpringCloud-Netflix 组件源码简析
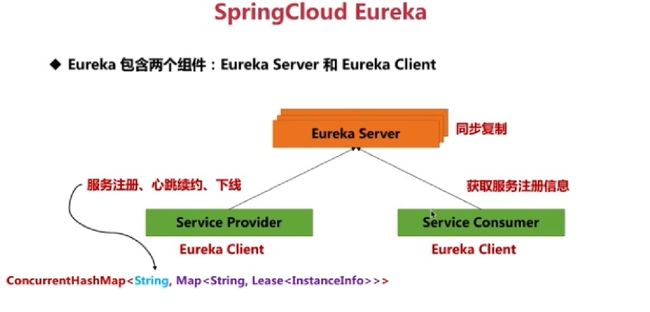
Eureka
注册中心 (场景: 服务注册与服务发现, 可以理解为 IM服务器)
从eureka-core 包中的 AbstractInstanceRegistry 类看起
* Handles all registry requests from eureka clients.
*
*
* Primary operations that are performed are the
* Registers, Renewals, Cancels, Expirations, and Status Changes The
* registry also stores only the delta operations
*
* @author Karthik Ranganathan
*
*/
private final ConcurrentHashMap>> registry
= new ConcurrentHashMap>>();
/* 第一层的 Map , K 是应用名称. V 是Map 多实例元信息
第二层 Map 为保持更多实例信息, K 为 实例名称, V 为实例详细信息(注册信息,ip地址,实例id,端口, 状态等)
Eureka 通过维护 这个 ConcurrentHashMap 实现服务注册以及发现.
建议可以从 193行 public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) 微服务注册方法看起
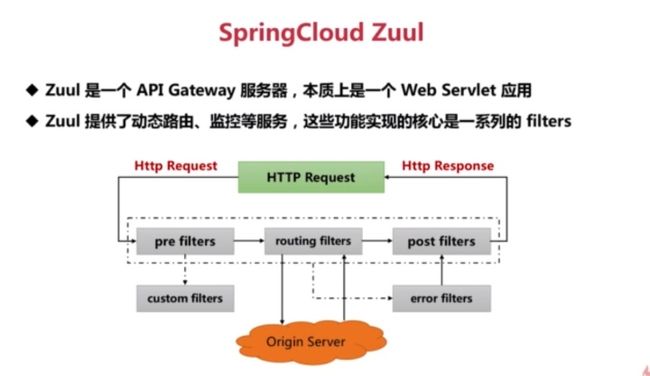
*/ Zuul
API 网关 (场景: 动态路由, 监控, 可以理解为 快递揽件配送)
- pre filters: 在调用 Origin Server 之前执行, 场景: 用于身份验证. 记录调试信息, 择优选择微服务等
- routing filters: 调用 Origin Server 时执行, 场景: 用于请求微服务. 获得响应等
- post filters: 在调用 Origin Server 之后执行, 场景: 用于为响应添加标准 HTTP 头, 收集统计信息和指标, 将响应从微服务返回给客户端等
- error filters: 在调用 Origin Server 过程中, 场景: 获取错误信息跳转 post filters.
- custom filters: 在调用 Origin Server 任意场景执行, 场景: 自定义过滤需求
从 org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.filters.support FilterConstants 类看起
这个类中是有和 上面的Filters 相关的常量
// Zuul Filter TYPE constants -----------------------------------
/**
* {@link ZuulFilter#filterType()} error type.
*/
public static final String ERROR_TYPE = "error";
/**
* {@link ZuulFilter#filterType()} post type.
*/
public static final String POST_TYPE = "post";
/**
* {@link ZuulFilter#filterType()} pre type.
*/
public static final String PRE_TYPE = "pre";
/**
* {@link ZuulFilter#filterType()} route type.
*/
public static final String ROUTE_TYPE = "route";
// OTHER constants -----------------------------------
对这几个 常量全局搜索 会找到与上述功能相同的过滤器类
PreDecorationFilter
SendForwardFilter
SendResponseFilter
SendErrorFilter
PreDecorationFilter 128行 初始化请求参数映射
RequestContext ctx = RequestContext.getCurrentContext(); ...
之后 通过转发过滤实现上述功能 !
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = ctx.getRequest().getRequestDispatcher(path);RestTemplate
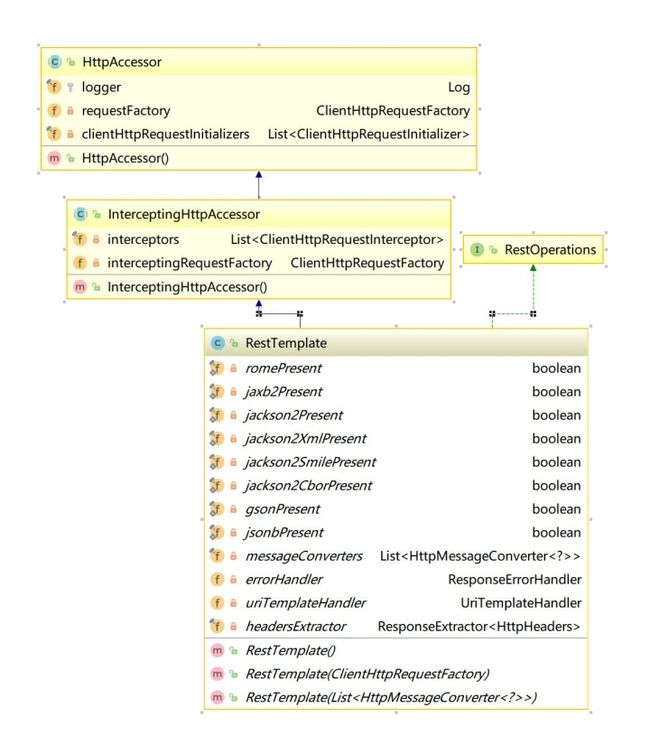
RestTemplate (场景: 简化 HTTP 通信方式,统一了RESTful的标准并为 执行复杂任务提供了一种具有默认行为的简化方法, 可以理解为 GOF中的 模板模式)
- HttpMessageConverter: 对象转换器
- ClientHttpRequestFactory: 提供了多种便捷访问远程Http服务的方法,能够大大提高客户端的编写效率。
- ResponseErrorHandler: 异常处理
- ClientHttpRequestInterceptor: 请求拦截器
Spring 核心 HTTP 消息转换器HttpMessageConverter
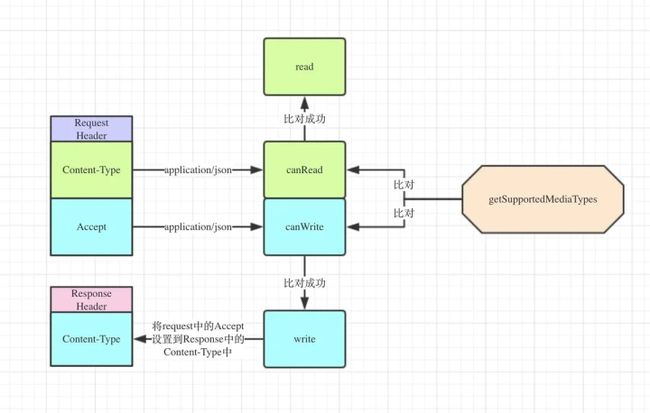
Rest自描述信息: 媒体类型 (MediaType) : text/html; text/xml; application/json
HTTP 协议特点: 纯文本协议 ,需要自我描述
- REST 客户端
- REST 服务端
反序列化 : 文本(通信) ---> 对象(程序使用)
序列化: 对象(程序) ----> 文本(通信)
分析 HttpMessageConverter
// 策略接口,它指定了一个转换器,可以将请求和响应转换为HTTP请求和响应。
public interface HttpMessageConverter {
// 判断当前 泛型是否可以反序列化
boolean canRead(Class clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
// 判断当前 泛型是否可以序列化
boolean canWrite(Class clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
// 当前支持的媒体类型
List getSupportedMediaTypes();
// 反序列化对象
T read(Class clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException;
}
特别提醒: SpringWebMVC 依赖于 Servlet, Spring 在设计早期时, 它就考虑到了去 Servlet 化.
HttpInputMessage 类似于 HttpServletRequest
RestTemplate 利用 HttpMessageConverter 对一些媒体类型进行通用的序列化和反序列化
- JSON
- XML
- TEXT
- ByteArrays
它不依赖于 Servlet 它自定义实现, 对于 服务端而言. 将 ServletAPI 适配或 HttpInputMessage 以及 HttpOutputMessage .
RestTemplate 对应多个 HttpMessageConverter 那么如何决策正确的媒体类型
将各种常用 HttpMessageConverter 支持的MediaType 和 JavaType 以及对应关系总结在此处:
RestTemplate 对应多个 HttpMessageConverter 那么如何决策正确的媒体类型
// 同志们 顺着方法调用栈追踪源码. 别怕, 前方安全, 有注释 !
// 建议 Debug 行点.
// RestTemplate: 190,419,673,769,850
// HttpMessageConverterExtractor: 89
@Test
public void getForObject() throws Exception {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(
new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory());
// restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
// restTemplate = new RestTemplate(new OkHttp3ClientHttpRequestFactory());
// 设置拦截器记录HTTP请求到响应时间
restTemplate.setInterceptors(Arrays.asList(new TimeInterceptor()));
String result = restTemplate.getForObject("https://example.com",String.class);
}
// 记录响应时间拦截器
class TimeInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest request, byte[] body, ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
// 举一反三: 也可以在请求前进行负载均衡到具体 IP
long frontNow = System.currentTimeMillis();
ClientHttpResponse response = execution.execute(request, body);
// 获取请求消耗时间
System.out.println("消耗时间"+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - frontNow) / 1000 + "秒");
return response;
}
}// 从 SpringWeb包 org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate 类看起
>public class RestTemplate extends InterceptingHttpAccessor implements RestOperations{
private final List> messageConverters = new ArrayList<>();
static {
// 初始化时 判断 第三方 HttpMessageConverter 实现是否存在
ClassLoader classLoader = RestTemplate.class.getClassLoader();
jackson2XmlPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.xml.XmlMapper", classLoader); gsonPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.google.gson.Gson", classLoader);
...
}
public RestTemplate() {
// 存在的默认内置 HttpMessageConverter以及第三方实现 按顺序装入 messageConverters
this.messageConverters.add(new ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter());
if (jackson2XmlPresent) {
this.messageConverters.add(new MappingJackson2XmlHttpMessageConverter());
}
if(..){...}
....
}
public RestTemplate(ClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory) {
this();
// 设置 requestFactory 适配器进行 http 请求
this.setRequestFactory(requestFactory);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public T getForObject(String url, Class responseType, Object... uriVariables) throws RestClientException {
// 用期望 返回对象.class 初始 RequestCallback 对象, 响应后的用于反序列化
RequestCallback requestCallback = acceptHeaderRequestCallback(responseType);
// 根据 HttpMessageConverter 初始化 HttpMessageConverterExtractor 用来处理拿到响应后的反序列化策略
HttpMessageConverterExtractor responseExtractor =
new HttpMessageConverterExtractor<>(responseType, getMessageConverters(), logger);
// 调用抽象执行层
return execute(url, HttpMethod.GET, requestCallback, responseExtractor,uriVariables);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public T execute(String url, HttpMethod method, @Nullable RequestCallback requestCallback, @Nullable ResponseExtractor responseExtractor, Object... uriVariables) throws RestClientException {
// 将 URL 与 动态参数 拼装为 真实URL
URI expanded = getUriTemplateHandler().expand(url, uriVariables);
return doExecute(expanded, method, requestCallback, responseExtractor);
}
@Nullable
protected T doExecute(URI url, @Nullable HttpMethod method, @Nullable RequestCallback requestCallback,
@Nullable ResponseExtractor responseExtractor) throws RestClientException {
// URL 与 method 不可为空
Assert.notNull(url, "URI is required");
Assert.notNull(method, "HttpMethod is required");
ClientHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 创建通用 ClientHttpRequestFactory 请求对象
ClientHttpRequest request = createRequest(url, method);
if (requestCallback != null) {
// 给请求头 Accept 设置 可序列化的 HttpMessageConverter.MediaType 策略
requestCallback.doWithRequest(request);
}
// 执行请求拦截器链并使用 ClientHttpRequestFactory 适配实现类发送请求, 获取 响应文本报文
response = request.execute();
// 处理给定的响应,执行适当的日志记录并调用 ResponseErrorHandler 处理异常
handleResponse(url, method, response);
// 使用 extractData() 将文本数据按 messageConverters匹配顺序反序列化为 期望返回对象
return (responseExtractor != null ? responseExtractor.extractData(response) : null);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
String resource = url.toString();
String query = url.getRawQuery();
resource = (query != null ? resource.substring(0, resource.indexOf('?')) : resource);
throw new ResourceAccessException("I/O error on " + method.name() +
" request for "" + resource + "": " + ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
finally {
if (response != null) {
// 因为当前 response 对象是 接口所以无法使用 jdk7自动关闭流, 需手动关闭
response.close();
}
}
}
public void doWithRequest(ClientHttpRequest request) throws IOException {
if (this.responseType != null) {
List allSupportedMediaTypes = (List)RestTemplate.this.getMessageConverters().stream().filter((converter) -> {
return this.canReadResponse(this.responseType, converter);
}).flatMap(this::getSupportedMediaTypes).distinct().sorted(MediaType.SPECIFICITY_COMPARATOR).collect(Collectors.toList());
// debug 模式 打印日志
if (RestTemplate.this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
RestTemplate.this.logger.debug("Accept=" + allSupportedMediaTypes);
}
// 给请求头 Accept 设置 可序列化的 HttpMessageConverter.MediaType 策略
request.getHeaders().setAccept(allSupportedMediaTypes);
}
}
}
// 其实可以看出来 源码阅读不是很难, 读者朋友们以后可以和面试官吹你看过 spring http 的核心源码了 SpringCloudOpenFeign
SpringCloudOpenFeign 服务调用(场景: Feign 是一个声明式Web Service客户端。使用Feign能让编写Web Service客户端更加简单, 它的使用方法是定义一个接口,然后在上面添加注解,同时也支持JAX-RS标准的注解。Feign 也支持可拔插式的编码器和解码器。SpringCloud对Feign 进行了封装,使其支持了Spring MVC标准注解和HttpMessageConverters 从而成为 SpringCloudOpenFeign 。SpringCloudOpenFeign可以与Eureka和Ribbon组合使用以支持负载均衡,或者与Hystrix组合使用支持FallBack 服务降级。可以理解为 标准化调用流程)
REST 服务端框架纵向比较
Feign 的灵感来自于 JAX-RS(Java REST 标准), 但是太多人基于 JAX-RS 重复发明轮子了
JAX-RS: Java_REST标准. 可移植性高, Jersey (Servlet 容器), Weblogic.
JSR-RS 参考链接: https:// github.com/mercyblitz/j sr/tree/master/REST
技术栈HTTP请求方式表达变量路径请求参数JAX-RS@Get@RathParam@FormParamFeign@RequestLine("GET@Param@ParamSpring Web MVC@GetMapping@PathVariable@RequestParamSpringCloudOpenFeign@GetMapping@PathVariable@RequestParam
举个栗子: SpringCloudOpenFeign-Demo
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-openfeign
// SpringCloudOpenFeign 配置类 , 如要运行 demo 请对 TODO 进行替换
@Configuration
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "com.my.TODO")
public class FeignConfiguration {
/**
* Set the Feign specific log level to log client REST requests.
*/
@Bean
feign.Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
return feign.Logger.Level.BASIC;
}
}SpringCloudOpenFeign客户端代码
import feign.hystrix.FallbackFactory;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
// 如要运行 demo 请对 TODO 进行替换
@FeignClient(value = "TODO 你要调用微服务的 spring.application.name", fallbackFactory = UserServiceFallbackFactory.class)
public interface DemoServiceClient {
@PutMapping(value = "/demo/keys/{key}", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public Boolean setKey(@PathVariable(value = "key") String key, @RequestParam("value") String value);
@GetMapping(value = "/demo/keys/{key}", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public String getKey(@PathVariable(value = "key") String key);
}
@Component
@Slf4j
class UserServiceFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory {
@Override
public DemoServiceClient create(final Throwable throwable) {
return new DemoServiceClient() {
@Override
public Boolean setKey(String key, String value) {
log.warn("Fallback reason={}", throwable.getMessage());
return false;
}
@Override
public String getKey(String key) {
log.warn("Fallback reason={}", throwable.getMessage());
return null;
}
};
}
} 客户端web接口代码
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/openfeign-demo")
@Slf4j
public class DemoResource {
@Autowired
private DemoServiceClient demoServiceClient;
@ApiOperation(value = "根据 K 查看 V值", notes="根据 K 查看 V值 notes")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "key" , value = "key", required = true, dataType = "string", paramType = "path"),
})
@GetMapping(value = "/{key}", produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public String getValue(@PathVariable String key) {
return demoServiceClient.getKey(key);
}
@ApiOperation(value = "设置 K/V", notes="设置 K/V notes")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "key", value = "key", required = true, dataType = "string", paramType = "path"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "value", value = "value", required = true, dataType = "string", paramType = "query")
})
@PutMapping(value = "/{key}", produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public Boolean setValue(@PathVariable String key, @RequestParam("value") String value) {
return demoServiceClient.setKey(key,value);
}
}SpringCloudOpenFeign服务端代码
spring:
application:
name: TODO服务端Web接口代码
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
private static volatile ConcurrentHashMap kv = new ConcurrentHashMap(20);
static {
kv.put("1024","hello OpenFeign");
}
@ApiOperation(value = "根据 K 查看 V值", notes="根据 K 查看 V值 notes")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "key" , value = "key", required = true, dataType = "string", paramType = "path"),
})
@GetMapping(value = "/keys/{key}", produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public String getValue(@PathVariable String key) {
return String.valueOf(kv.get(key));
}
@ApiOperation(value = "设置 K/V", notes="设置 K/V notes")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "key", value = "key", required = true, dataType = "string", paramType = "path"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "value", value = "value", required = true, dataType = "string", paramType = "query")
})
@PutMapping(value = "/keys/{key}", produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public Boolean setValue(@PathVariable String key, @RequestParam("value") String value) {
Object put = kv.put(key, value);
return kv.containsKey(key);
}
} SpringCloudOpenFeign测试用例代码
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.client.HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
@SpringBootTest(classes = TODORun.class)
public class DemoResourceTest {
@SneakyThrows
@Test
public void b_Key() throws Exception {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory());
Boolean setKeyRespond = restTemplate.exchange("http://TODO客户端ip端口/openfeign-demo/1025?value=gczy",HttpMethod.PUT,new HttpEntity(new HttpHeaders()),Boolean.class).getBody();
String getKeyRespond = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8081/openfeign-demo/1024", String.class);
String getsetKeyRespond = restTemplate.getForObject("http://TODO客户端ip端口/openfeign-demo/1025", String.class);
assertEquals(setKeyRespond,Boolean.TRUE);
assertEquals(getKeyRespond, "hello OpenFeign");
assertEquals(getsetKeyRespond, "gczy");
}
} SpringCloudOpenFeign源码分析
- @FeignClient(value="todo")
- @EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "com.todo.node")
- @RequestParam() @GetMapping()
// 节选部分源码 SpringCloudOpenFeign-core 2.2.2
// 同志们 顺着方法调用栈追踪源码. 别怕, 前方安全, 有注释 !
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableFeignClients {
String[] basePackages() default {};
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FeignClient {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
}
// 实现接口的中的方法完成 Feign 注册bean
class FeignClientsRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, ResourceLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private Environment environment;
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//
registerDefaultConfiguration(metadata, registry);
registerFeignClients(metadata, registry);
}
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
private void registerDefaultConfiguration(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 获得 @EnableFeignClients() 注解的自定义属性
Map defaultAttrs = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableFeignClients.class.getName(), true);
// 当前项目是否使用 SpringCloudOpenFeign - @EnableFeignClients()
if (defaultAttrs != null && defaultAttrs.containsKey("defaultConfiguration")) {
String name;
// 判断当前标识 @EnableFeignClients() 的配置类是否为封闭类
if (metadata.hasEnclosingClass()) {
name = "default." + metadata.getEnclosingClassName();
}
else {
name = "default." + metadata.getClassName();
}
// 初始化注册客户端配置为bean
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
defaultAttrs.get("defaultConfiguration"));
}
}
public void registerFeignClients(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 初始化包扫描器和类加载器
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider scanner = getScanner();
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
Set basePackages;
// 获得 @EnableFeignClients() 注解的自定义属性
Map attrs = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableFeignClients.class.getName());
// 初始化包含类型筛选器
AnnotationTypeFilter annotationTypeFilter = new AnnotationTypeFilter(
FeignClient.class);
// 查看 @EnableFeignClients() clients属性是否指定 FeignClient客户端
final Class[] clients = attrs == null ? null
: (Class[]) attrs.get("clients");
// 如果没有指定就根据 @EnableFeignClients() 属性获得客户端全部包名
if (clients == null || clients.length == 0) {
scanner.addIncludeFilter(annotationTypeFilter);
basePackages = getBasePackages(metadata);
}
else {
// 指定clients属性则走原有逻辑
final Set clientClasses = new HashSet<>();
basePackages = new HashSet<>();
for (Class clazz : clients) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz));
clientClasses.add(clazz.getCanonicalName());
}
AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter filter = new AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter() {
@Override
protected boolean match(ClassMetadata metadata) {
String cleaned = metadata.getClassName().replaceAll("$", ".");
return clientClasses.contains(cleaned);
}
};
scanner.addIncludeFilter(
new AllTypeFilter(Arrays.asList(filter, annotationTypeFilter)));
}
// 根据全部自定义包名寻找 @FeignClient 类客户端
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
// 将 @FeignClient 类全部初始化为 bean
Set candidateComponents = scanner
.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidateComponent : candidateComponents) {
if (candidateComponent instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// verify annotated class is an interface
AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidateComponent;
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata();
// 过滤 @FeignClient 非接口形式的客户端.
Assert.isTrue(annotationMetadata.isInterface(),
"@FeignClient can only be specified on an interface");
// 获取 @FeignClient 类的全部属性
Map attributes = annotationMetadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(
FeignClient.class.getCanonicalName());
// 获取调用微服务名称
String name = getClientName(attributes);
// 注册 @FeignClient 类为bean
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
attributes.get("configuration"));
// 将@FeignClient 服务接口形成代理实现 @RequestParam() @GetMapping()
registerFeignClient(registry, annotationMetadata, attributes);
}
}
}
}
} 下期预告-(二) JHipster 让 SpringCloud架构变得简单
扫码回复 "加群" 和我一起月入 20K+
深入浅出分享 Java 干货 , 找回对代码的 Passion , 助力月入 20K+