『Python』matplotlib的imshow用法
热力图是一种数据的图形化表示,具体而言,就是将二维数组中的元素用颜色表示。热力图之所以非常有用,是因为它能够从整体视角上展示数据,更确切的说是数值型数据。
使用imshow()函数可以非常容易地制作热力图。
1. 函数imshow()
imshow(X, cmap=None, norm=None, aspect=None,
interpolation=None, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None,
origin=None, extent=None, shape=None, filternorm=1,
filterrad=4.0, imlim=None, resample=None, url=None, **kwargs)主要用到的参数含义如下:
-
X
可以使类似数组的对象,或者是PIL类型图像,其中,数组对象可选shape为:(M, N)
单纯的二维数组,元素是标量数据,会通过colormap展示(M, N, 3)
RGB三通道图像,元素值可以是\(0-1\)之间的float或者\(0-255\)之间的int(M, N, 4)
RGBA图像,多出来的一维属性,比如是透明度,其元素值和3通道的一样,可以是\(0-1\)之间的float或者\(0-255\)之间的int
※
M代表rows,N代表colums※ 超过元素限定范围的元素值将被clipped
-
cmapstr或matplotlib.colors.Colormap类型,用于将标量数据映射到颜色的Colormap实例或已注册的Colormap名称。※ 只对二维数组有效,RGB(A)将自动忽略
-
norm
在使用cmap之前,用来将二维数组数据归一化到\([0, 1]\),默认是线性的,最小值对应\(0\),最大值对应\(1\)。这要注意,不然每次画图最大最小值不一样,色彩不好比较。
-
interpolation
插值方法,默认'nearest',可以支持的方法有:'none''nearest''bilinear''bicubic''spline16''spline36''hanning''hamming''hermite''kaiser''quadric''catrom''gaussian''bessel''mitchell''sinc''lanczos'
-
alpha
透明度,\(0\)表示透明,\(1\)表示不透明 -
vmin,vmax
当输入的时二维数组标量数据并且没有明确的norm时,vmin和vmax定义colormap覆盖的数据范围,默认情况下,colormap覆盖所提供的值的完整范围数据当
norm给定时,这两个参数无效 -
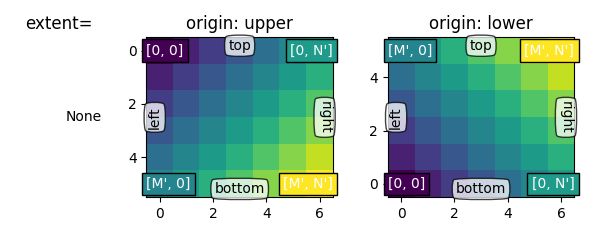
origin
坐标轴的样式,可选值为upper和lower,其对应坐标系样式如下图※
M代表rows,N代表colums
2. 定制colorbars
2.1 基本连续colorbar绘制
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 1))
fig.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.5)
cmap = mpl.cm.cool
norm = mpl.colors.Normalize(vmin=5, vmax=10)
fig.colorbar(mpl.cm.ScalarMappable(norm=norm, cmap=cmap),
cax=ax, orientation='horizontal', label='Some Units')当然,也可以竖起来画
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(1, 6))
fig.subplots_adjust(right=0.5)
cmap = mpl.cm.cool
norm = mpl.colors.Normalize(vmin=5, vmax=10)
fig.colorbar(mpl.cm.ScalarMappable(norm=norm, cmap=cmap),
cax=ax, orientation='vertical', label='Some Units')2.2 离散间隔colorbar
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 1))
fig.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.5)
cmap = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['red', 'green', 'black', 'blue', 'cyan'])
cmap.set_over('0.25')
cmap.set_under('0.75')
bounds = [1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8]
norm = mpl.colors.BoundaryNorm(bounds, cmap.N)
fig.colorbar(
mpl.cm.ScalarMappable(cmap=cmap, norm=norm),
cax=ax,
boundaries=[0] + bounds + [13],
extend='both',
ticks=bounds,
spacing='proportional',
orientation='horizontal',
label='Discrete intervals, some other units',
)2.3 带有自定义扩展名长度的colorbar
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 1))
fig.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.5)
cmap = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['royalblue', 'cyan',
'yellow', 'orange'])
cmap.set_over('red')
cmap.set_under('blue')
bounds = [-1.0, -0.5, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0]
norm = mpl.colors.BoundaryNorm(bounds, cmap.N)
fig.colorbar(
mpl.cm.ScalarMappable(cmap=cmap, norm=norm),
cax=ax,
boundaries=[-10] + bounds + [10],
extend='both',
extendfrac='auto',
ticks=bounds,
spacing='uniform',
orientation='horizontal',
label='Custom extension lengths, some other units',
)
plt.show()3. 控制所有图的colorbar和图中元素对应颜色一致
import matplotlib as mpl
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
im = ax.imshow(data, interpolation="bicubic", vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax, cmap="jet")
fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax)
plt.show()关键是要设置
vmin和vmax