spring day01
-
- 什么是Spring
Spring是分层的、JavaSE/EE一站式(full-stack)、轻量级开源框架。
- 1JavaEE分层
JavaEE规范的三层结构体系:
- 表现层(页面数据显示、页面跳转调度),例如jsp/servlet
- 业务层(业务处理和功能逻辑、事务控制),例如service
- 持 o
如图:
- 一站式
Spring提供了JavaEE各层的解决方案:
表现层:struts1、struts2、Spring MVC
业务层:Ioc、AOP、事务控制
持久层:JdbcTemplate、HibernateTemplate、ORM框架(对象关系映射)整合
- 轻量级:Spring的出现取代了EJB的臃肿、低效、繁琐复杂、脱离现实。
![]()
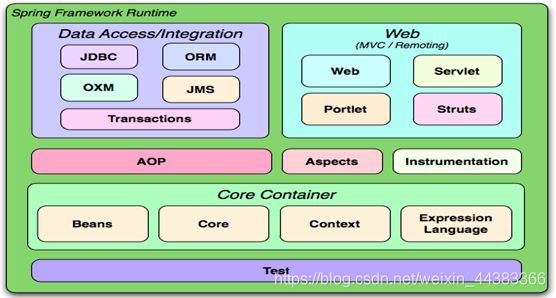
- 2Spring的体系结构
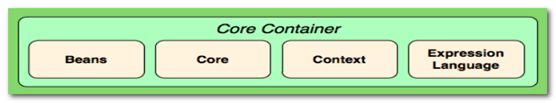
Spring框架是一个分层架构,它包含一系列的功能要素并被分为大于20个模块。这些模块分为Core Container、Data Access/Integration、Web、AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)、Instrumentation和测试部分,如图:
核心容器(Core Container) 包括Core、Beans、Context、EL模块。
1:Core和Beans模块提供了Spring最基础的功能,提供IoC和依赖注入特性。这里的基础概念是BeanFactory,它提供对Factory模式的经典实现来消除对程序性单例模式的需要,并真正地允许你从程序逻辑中分离出依赖关系和配置。
2:Context模块基于Core和Beans来构建,它提供了用一种框架风格的方式来访问对象,有些像JNDI注册表。Context封装包继承了beans包的功能,还增加了国际化(I18N),事件传播,资源装载,以及透明创建上下文,例如通过servlet容器,以及对大量JavaEE特性的支持,如EJB、JMX。核心接口是ApplicationContext。
3:Expression Language,表达式语言模块,提供了在运行期间查询和操作对象图的强大能力。支持访问和修改属性值,方法调用,支持访问及修改数组、容器和索引器,命名变量,支持算数和逻辑运算,支持从Spring 容器获取Bean,它也支持列表投影、选择和一般的列表聚合等。
数据访问/集成部分(Data Access/Integration)lk
1:JDBC模块,提供对JDBC的抽象,它可消除冗长的JDBC编码和解析数据库厂商特有的错误代码。
2:ORM模块,提供了常用的"对象/关系"映射APIs的集成层。 其中包括JPA、JDO、Hibernate 和 iBatis 。利用ORM封装包,可以混合使用所有Spring提供的特性进行"对象/关系"映射,如简单声明性 事务管理 。
3:OXM模块,提供一个支持Object和XML进行映射的抽象层,其中包括JAXB、Castor、XMLBeans、JiBX和XStream。
4:JMS模块,提供一套"消息生产者、消费者"模板用于更加简单的使用JMS,JMS用于用于在两个应用程序之间,或分布式系统中发送消息,进行异步通信。
5:Transaction模块,支持程序通过简单声明性 事务管理,只要是Spring管理对象都能得到Spring管理事务的好处,即使是POJO,也可以为他们提供事务。
Web
1:Web模块,提供了基础的web功能。例如多文件上传、集成IoC容器、远程过程访问、以及Web Service支持,并提供一个RestTemplate类来提供方便的Restful services访问
2:Web-Servlet模块,提供了Web应用的Model-View-Controller(MVC)实现。Spring MVC框架提供了基于注解的请求资源注入、更简单的数据绑定、数据验证等及一套非常易用的JSP标签,完全无缝与Spring其他技术协作。
3:Web-Struts模块, 提供了对Struts集成的支持,这个功能在Spring3.0里面已经不推荐了,建议你迁移应用到使用Struts2.0或Spring的MVC。
4:Web-Portlet模块,提供了在Portlet环境下的MVC实现
AOP
1:AOP模块,提供了符合AOP 联盟规范的面向方面的编程实现,让你可以定义如方法拦截器和切入点,从逻辑上讲,可以减弱代码的功能耦合,清晰的被分离开。而且,利用源码级的元数据功能,还可以将各种行为信息合并到你的代码中 。
2:Aspects模块,提供了对AspectJ的集成。
3:Instrumentation模块, 提供一些类级的工具支持和ClassLoader级的实现,可以在一些特定的应用服务器中使用。
Test
1:Test模块,提供对使用JUnit和TestNG来测试Spring组件的支持,它提供一致的ApplicationContexts并缓存这些上下文,它还能提供一些mock对象,使得你可以独立的测试代码。
- 3Spring的核心
IoC(Inverse of Control 控制反转): 将对象创建权利交给Spring工厂进行管理。
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming 面向切面编程),基于动态代理的功能增强方式。
百度百科:Spring 是基于IOC和AOP的一套编程框架。
今天的主要学习IoC
- 4Spring的优点
Spring 出现为了解决JavaEE 实际问题
(1)方便解耦,简化开发
Spring就是一个大工厂,可以将所有对象创建和依赖关系维护,交给Spring管理
(2)AOP编程的支持
Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便的实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等功能
(3)声明式事务的支持
只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无需手动编程
(3)方便程序的测试
Spring对Junit4支持,可以通过注解方便的测试Spring程序
(5)方便集成各种优秀框架
Spring不排斥各种优秀的开源框架,其内部提供了对各种优秀框架(如:Struts、Hibernate、MyBatis、Quartz、webservice、activity等)的直接支持
(6)降低JavaEE API的使用难度
Spring 对JavaEE开发中非常难用的一些API(JDBC、JavaMail、远程调用等),都提供了封装,使这些API应用难度大大降低
关于框架的特性,我们也会俗称Spring为开发架构的粘合剂。
2.Spring IoC快速入门
Spring核心内容的基本开发步骤:
- 下载开发包,导入jar包
- 编写代码(基础代码和调用代码)
- 编写配置文件(XML)
- 测试
开发包的下载 Spring官方:http://spring.io/
Spring4.2版本开发包目录结构:
第一步:其中docs:
查看docs\spring-framework-reference\pdf中的spring-framework-reference.pdf规范文档中基本内容了解
第二步:其中jar:
打开spring-framework-4.2.4.RELEASE-dist\spring-framework-4.2.4.RELEASE\libs
开发过程中还需要其他开源技术框架依赖Jar包集(dependencies,作用是方便依赖的其他技术的jar的导入):
第三步:其中schema:
打开:spring-framework-4.2.4.RELEASE-schema\beans,查看spring配置文件的规范约束
2.1 开发环境测试搭建(Jar的导入)
第一步:新建Web工程Spring4_d01_c03,
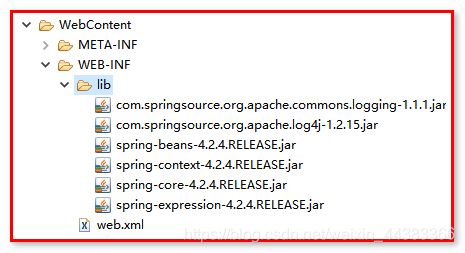
第二步:导入jar包
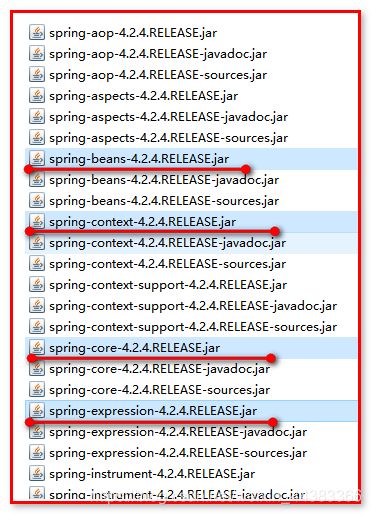
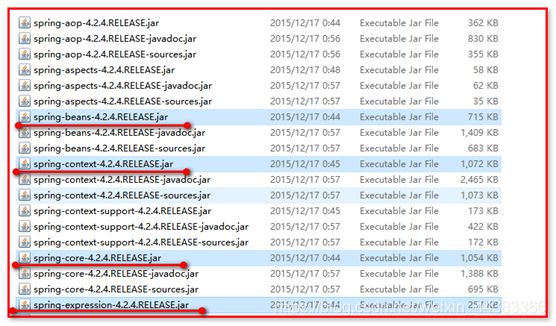
1.Spring项目的核心容器的最基本Jar包(4个):
打开spring-framework-4.2.4.RELEASE-dist\spring-framework-4.2.4.RELEASE\libs,可以看到
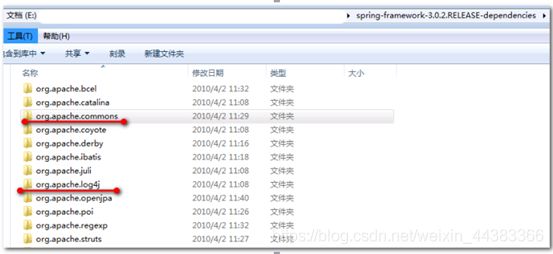
2.Spring框架所需的日志包(2个,依赖jar库中找):
默认采用apache commons-logging(JCL)日志框架+log4j的日志实现,还需要添加log4j的配置文件。
打开:课前资料,spring-framework-3.0.2.RELEASE-dependencies
找到:org.apache.commons文件夹和org.apache.log4j文件夹
添加log4j.properties文件放置到src下。
### direct log messages to stdout ###
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.err
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
### direct messages to file mylog.log ###
log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
log4j.appender.file.File=c\:mylog.log
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
### set log levels - for more verbose logging change 'info' to 'debug' ###
log4j.rootLogger=info, stdout
- 3 IoC控制反转的实现
- 3.3.1Spring核心配置文件的编写
IoC控制反转的理解和实现
第一步:在src下建立applicationContext.xml (位置:applicationContext.xml文件放置到任何目录都可以,习惯上放在src目录或者 WEB-INF目录)
引入xml的头部信息bean schema约束,可以参考规范文档中的spring-framework-4.2.4.RELEASE\docs\spring-framework-reference\html
xsd-configuration.html
找到下列章节的示例,拷贝到工程中即可:
搜索
40.2.12 the beans schema
结果如下:
|
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
|
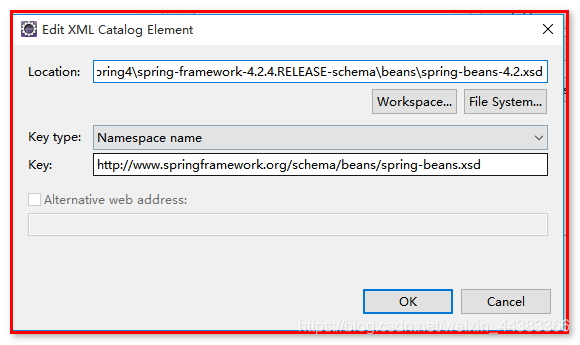
问题:发现引入规范约束后,没有关联对应的配置,原因是:
配置本地提示:点击eclipse属性——>选择XML Catalog
applicationContext.xml核心配置文件编写:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDao" class="com.igeek.spring.UserDaoImpl"/>
beans>
3.3.2 通过Spring的工厂获取Bean完成相关操作
基本过程是:在程序中读取Spring配置文件,得到Spring的Bean工厂,通过Spring框架获得Bean,完成相应操作
创建包:com.igeek.spring
复制代码:到com.igeek包
修改UserServiceImpl 代码,编写:
//业务层实现
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService{
public void login() {
System.out.println("UserServiceImpl-service层被调用了。。。");
//spring的配置方式,IOC控制反转
//构建一个spring的工厂,使用applicationContext.xml(spring的核心配置文件)获取对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//从spring工厂中使用对象的标识获取对象
IUserDao userDao = (IUserDao) ac.getBean("userDao");
userDao.findByUsernameAndPassword();
}
}
使用SpringTest类进行测试:
//测试
public class SpringTest {
@Test
//模拟表现层
public void testOld(){
IUserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
userService.login();
}
测试结果:
3.3.3 ID和name
DI依赖注入的实现
DI:Dependency Injection 依赖注入,在Spring框架负责创建Bean对象时,动态的将依赖对象注入到Bean组件(简单的说,可以将另外一个bean对象动态的注入到另外一个bean中。)
【面试题】IoC和DI的区别 ?
DI和IoC是同一件事情,都是将对象控制权交给第三方(Spring)管理,只是站在不同角度而已。
IoC:
即:Spring创建了Service、Dao对象,在配置中将Dao传入Servcie,那么Service对象就包含了Dao对象的引用。
Spring的核心配置文件applicationContext.xml:
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDao" class="com.igeek.spring.UserDaoImpl"/>
<bean name="userService" class="com.igeek.spring.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
bean>
beans>
Service业务层代码:
//业务层实现
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService{
//定义属性
private IUserDao userDao;
//提供set方法,使用setXxx方法完成属性的注入
public void setUserDao(IUserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
//使用依赖注入的方式获取dao
public void login() {
System.out.println("UserServiceImpl-service层被调用了。。。");
userDao.findByUsernameAndPassword();
}
}
springTest.java测试代码:
//测试
public class SpringTest {
@Test
//模拟表现层
public void testOld(){
//spring的配置方式,IOC控制反转
//构建一个spring的工厂,使用applicationContext.xml(spring的核心配置文件)获取对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//从spring工厂中使用对象的标识获取对象
IUserService userService = (IUserService) ac.getBean("userService");
userService.login();
}
}
3.3.4 Spring工厂的直接获取(两种方式)-了解
src:开发的时候,工程里的一个目录,存放的文件,会在编译发布后,放入classes下。
applicationContext应用上下文,加载Spring框架配置文件
方法一:从classpath路径加载
在类路径下寻找配置文件来实例化容器
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"applicationContext.xml"});
可以在整个类路径中寻找xml文件
* 通过这种方式加载。需要将spring的配置文件放到当前项目的classpath路径下
* classpath路径指的是当前项目的src目录,该目录是java源文件的存放位置。
方法二:从磁盘路径加载
在文件系统路径下寻找配置文件来实例化容器
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{“d:\\applicationContext.xml”});
- Spring的配置文件可以指定多个,可以通过String数组传入。
(2)通过getBean方法获得Spring容器管理Bean对象
如何选择:
- 如果applicationContext.xml 在 src下, ClassPathXmlApplication读取
- 如果applicationContext.xml 在WEB-INF下,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext读取
【扩展】
Bean获取的两种方式:
/**1:使用spring容器中的标识获取对象*/
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//IUserService userService=(IUserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
/**
* 2:根据bean的类型来获取:自动到spring容器中查找哪个bean是这个类型
* 如果 Object instanceOf(IUserService.class)或者Object instanceOf(UserServiceImpl.class)
* 类型获取有个郁闷的情况:如果容器中有两个同样的类型,则会报错!!!!!
*/
//IUserService userService=(IUserService) applicationContext.getBean(IUserService.class);
IUserService userService=(IUserService) applicationContext.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class);//一般不会使用实现类
//业务方法
userService.login();
常用根据名称获取(id/name),即第一种方式,使用spring容器中的标识获取对象
如果根据类型获取,配置了多个类型的话,则抛出异常:
例如spring容器中配置:
<bean name="userService" class="com.igeek.spring.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
bean>
<bean name="userService1" class="com.igeek.spring.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
bean>
使用代码进行测试
IUserService userService=(IUserService) applicationContext.getBean(UserServiceImpl.class);//一般不会使用实现类
则抛出异常
4 IoC容器装配Bean_基于XML配置方式
- 实例化Bean的四种方式 (了解)
创建web项目:spring4_d01_c04,导入项目所需的6个jar包,拷贝上个项目的配置文件applicationContext.xml
log4j.properties
创建包:com.igeek
第一种方式 无参数构造器 (最常用)
第一步:创建Bean1.java
//1。默认构造器(spring在创建bean的时候自动调用无参构造器来实例化,相当于new Bean1())
public class Bean1 {
}
第二步:在spring容器applicationContext.xml中配置
<bean id="bean1" class="com.igeek.Bean1"/>
第三步:创建测试文件SpringTest.java
@Test
public void test1(){
//先构建实例化获取spring的容器(工厂、上下文)
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//1。默认构造器获取bean的对象
Bean1 bean1=(Bean1) applicationContext.getBean("bean1");
System.out.println(bean1);
}
运行结果:
【错误演示】:
//1。默认构造器(spring在创建bean的时候自动调用无参构造器来实例化,相当于new Bean1())
public class Bean1 {
private String name;
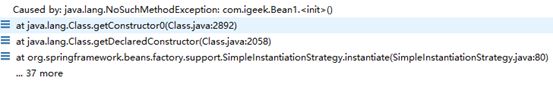
//错误原因:没有无参构造器
//如果设置一个有参数的构造器,会覆盖无参数的构造器,会报错。无法实例化Bean
public Bean1(String name){
this.name = name;
}
}
【报错】:
第二种方式: 静态工厂方法
第一步:创建Bean2.java
//1.静态工厂方法构造:用来在初始化bean2的时候,可以初始化其他的东西
public class Bean2 {
//静态方法,用来返回对象的实例
public static Bean2 getBean2(){
//在做实例化的时候,可以做其他的事情,即可以在这里写初始化其他对象的代码
//Connection conn....
return new Bean2();
}
}
第二步:Spring的容器applicationContext.xml
<bean id="bean2" class="com.igeek.Bean2" factory-method="getBean2"/>
第三步:测试类进行测试
@Test
public void test2(){
//先构建实例化获取spring的容器(工厂、上下文)
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.静态工厂
Bean2 bean2=(Bean2) applicationContext.getBean("bean2");
System.out.println(bean2);
}
第三种方式: 实例工厂方法
第一步:创建Bean3.java
//第三种bean,实例工厂方式创建
public class Bean3 {
}
第二步:创建实例工厂Bean3Factory类
//实例工厂:必须new工厂--》bean
public class Bean3Factory {
//普通的方法,非静态方法
public Bean3 getBean3(){
//初始化实例对象返回
return new Bean3();
}
}
第三步:Spring容器的配置:applicationContext.xml
<bean id="bean3Factory" class="com.igeek.Bean3Factory"/>
<bean id="bean3" factory-bean="bean3Factory" factory-method="getBean3"/>
第四步:使用测试代码,进行测试:
@Test
public void test3(){
//先构建实例化获取spring的容器(工厂、上下文)
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//3.实例工厂
Bean3 bean3=(Bean3) applicationContext.getBean("bean3");
System.out.println(bean3);
}
第四种方式:FactoryBean方式。(源码底层用的多)
第一步:创建Bean4.java
public class Bean4 {
}
第二步:创建工厂Bean,Bean4FactoryBean.java,实现FactoryBean
//4。实现FactoryBean接口的方式
//泛型:你要返回什么类型的对象,泛型就是什么
public class Bean4FactoryBean implements FactoryBean
//用来获取bean的实例,对象
public Bean4 getObject() throws Exception {
//写一些初始化数据库连接等等其他代码
return new Bean4();
}
public Class getObjectType() {
return null;
}
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
}
FactoryBean提供getObject方法,返回目标类型对象.
第三步:spring容器中的配置
<bean id="bean4" class="com.igeek.Bean4FactoryBean"/>
Bean4对象是 Bean4的类型(FactoryBean的getObject返回类型 )
第四步:测试
@Test
public void test4(){
//先构建实例化获取spring的容器(工厂、上下文)
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//3.实例工厂
Bean4 bean4=(Bean4) applicationContext.getBean("bean4");
System.out.println(bean4);
}
小结:
Spring容器的配置:看一下4种方式
| xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="bean1" class="com.igeek.Bean1"/>
<bean id="bean2" class="com.igeek.Bean2" factory-method="getBean2"/>
<bean id="bean3Factory" class="com.igeek.Bean3Factory"/>
<bean id="bean3" factory-bean="bean3Factory" factory-method="getBean3"/>
<bean id="bean4" class="com.igeek.Bean4FactoryBean"/>
beans> |
【四种方式】小结:
第一种:最常用
- 第三种:一些框架初始化的时候用的多。
- 第四种:spring底层用的多。
【面试题】 BeanFactory和FactoryBean的区别?
BeanFactory:是一个工厂(其实是构建了一个spring上下文的环境,容器),用来管理和获取很多Bean对象,例如:加载applicationContext.xml文件。
FactoryBean:是一个Bean生成工具,是用来获取一种类型对象的Bean,它是构造Bean实例的一种方式。
- Bean的作用域
由spring创建的bean对象在什么情况下有效。
【附录】:什么是Portal,参考百度百科
项目开发中通常会使用:singleton 单例、 prototype多例
Singleton: 在一个spring容器中,对象只有一个实例。(默认值)
Prototype: 在一个spring容器中,存在多个实例,每次getBean 返回一个新的实例。
建立包:com.igeek.scope
第一步:创建类SingletonBean.java和PrototypeBean.java
创建类SingletonBean.java类
//多例bean
public class PrototypeBean {
public PrototypeBean() {
System.out.println("--PrototypeBean初始化了多例的");
}
}
第二步:定义spring容器,applicationContext.xml:
<bean id="singletonBean" class="com.igeek.scope.SingletonBean"/>
<bean id="prototypeBean" class="com.igeek.scope.PrototypeBean" scope="prototype"/>
第三步:测试代码,创建SpringTest.java:
//newbean的方式
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void testScope(){
//先构建实例化获取spring的容器(工厂、上下文)
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//目标1:看看多次获取bean的时候,是不是同一个
//目标2:看看bean什么时候初始化的
//获取单例的bean:应该是同一个
//单例:每次从spring容器中获取的对象,是同一个对象
//单例初始化:是在spring容器初始化的时候,就初始化了
SingletonBean singletonBean1=(SingletonBean)applicationContext.getBean("singletonBean");
SingletonBean singletonBean2=(SingletonBean)applicationContext.getBean("singletonBean");
System.out.println(singletonBean1);
System.out.println(singletonBean2);
//获取多例的bean:
//多例:每次从spring容器中获取的对象,不是同一个对象
//多例初始化:是在getBean的时候初始化,相当于每次getbean就是在new Bean()
PrototypeBean prototypeBean1=(PrototypeBean)applicationContext.getBean("prototypeBean");
PrototypeBean prototypeBean2=(PrototypeBean)applicationContext.getBean("prototypeBean");
System.out.println(prototypeBean1);
System.out.println(prototypeBean2);
}
}
运行查看,测试结果:
【注意】
单例是默认值,如果需要单例对象,则不需要配置scope。
- Bean的生命周期
通过spring工厂,可以控制bean的生命周期。
- 在xml配置Bean的初始化和销毁方法
通过 init-method属性 指定初始化后的调用方法
通过 destroy-method属性 指定销毁对象前的方法
创建包com.igeek.xmllifecycle
第一步:创建LifeCycleBean,指定一个init的方法,和一个destroy的方法。
//测试生命周期过程中的初始化和销毁bean
public class LifeCycleBean {
//定义构造方法
public LifeCycleBean() {
System.out.println("LifeCycleBean构造器调用了");
}
//初始化后自动调用方法:方法名随意,但也不能太随便,一会要配置
public void init(){
System.out.println("LifeCycleBean-init初始化时调用");
}
// 业务方法
public void save(){
System.out.println("第六步:调用了LifeCycleBean类的save方法!");
}
//bean销毁时调用的方法
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("LifeCycleBean-destroy销毁时调用");
}
}
第二步:Spring的核心容器,applicationContext.xml的配置
<bean id="lifeCycleBean" class="com.igeek.xmllifecycle.LifeCycleBean" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy" scope="singleton"/>
第三步:SpringTest.java测试代码:
@Test
public void test(){
//先获取spring的容器,工厂,上下文
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//对于单例此时已经被初始化
//获取bean
LifeCycleBean lifeCycleBean=(LifeCycleBean) applicationContext.getBean("lifeCycleBean");
System.out.println(lifeCycleBean);
lifeCycleBean.save();
//为什么没有销毁方法调用。
//原因是:使用debug模式jvm直接就关了,spring容器还没有来得及销毁对象。
//解决:手动关闭销毁spring容器,自动销毁单例的对象
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)applicationContext).close();
}
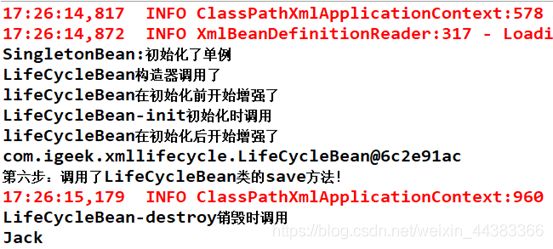
测试查看控制台打印,发现销毁方法没有执行。
原因:销毁方法的执行必须满足两个条件:
- 单例(singleton)的bean才会可以手动销毁。
- 必须手动关闭容器(调用close的方法)时,才会执行手动销毁的方法。
换成单列模式scope="singleton",控制台输出结果是:
【扩展】
关于数据(一些属性等等)的初始化的。
-
- 直接赋值
- 在构造器中初始化
- 使用单独的初始化的方法
//测试生命周期过程中的初始化和销毁bean
public class LifeCycleBean {
//成员变量
private String name="Tom";//1.赋值成员变量
//2.构造器初始化
public LifeCycleBean() {
System.out.println("LifeCycleBean构造器调用了");
this.name="Rose";
}
//初始化后自动调用方法:方法名随意,但也不能太随便,一会要配置
public void init(){
System.out.println("LifeCycleBean-init初始化时调用");
//3.单独的初始化方法来初始化数据
this.name="Jack";
}
//bean销毁时调用的方法
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("LifeCycleBean-destroy销毁时调用");
System.out.println(name);
}
}
三种方式:根据代码情况任选。
第一种方式:直接的,但耦合性最强。一般用于给默认值的。
第二种方式:使用有参构造来初始化。代码new的时候就能直接将属性初始化,但有点耦合。
使用set方法对属性进行赋值。
第三种方式:使用单独的方法,来初始化。完全解耦,初始化方法专门用来写初始化的一系列代码,构造器,只是用来构造class对象。
- 后处理Bean(BeanPostProcessor接口) 了解
后处理Bean也称之为Bean的后处理器,作用是:在Bean初始化的前后,对Bean对象进行增强。它既可以增强一个指定的Bean,也可以增强所有的Bean,底层很多功能(如AOP等)的实现都是基于它的,Spring可以在容器中直接识别调用。
【示例】
要对“所有”的bean的初始化的时候进行增强(打印一句话)
第一步:创建MyBeanPostProcessor类,实现接口BeanPostProcessor
//后处理bean,:用来对bean进行功能增强,可以实现,对所有,或某个bean的初始化进行增强
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor{
//初始化时(之前)调用的
//参数1:bean对象,参数2,bean的名字,id、name
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
// System.out.println(beanName+"在初始化前开始增强了");
//如何只增强一个bean
if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")){
System.out.println(beanName+"在初始化前开始增强了");
}
return bean;//放行
}
//初始化时(之后)调用
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
// System.out.println(beanName+"在初始化后开始增强了");
if(beanName.equals("lifeCycleBean")){
System.out.println(beanName+"在初始化后开始增强了");
}
return bean;
}
}
第二步:定义applicationContext.xml文件
<bean class="com.igeek.xmllifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor"/>
执行任意bean操作的测试,控制台输出:
注意调用顺序。
BeanPostProcessor接口,提供增强途径,在不修改原来代码情况下,增添新的功能!
- Bean属性的依赖注入
创建包com.igeek.xmlpropertydi
- 属性依赖注入的三种方式
什么是Bean属性的注入?就是对一个对象的属性赋值。有三种方式:
- 第一种:构造器参数注入
- 第二种:setter方法属性注入(setter方法的规范需要符合JavaBean规范)
- 第三种:接口注入
Spring 框架规范中通过配置文件配置的方式,只支持构造器参数注入和setter方法属性注入,不支持接口注入 !
- 构造器参数注入 constructor-arg
【示例】
第一步:构造器参数注入属性值。
创建包com.igeek.xmlpropertydi,创建Car类,定义构造方法
//目标,构造器参数注入,new car直接将参数的值直接赋值
public class Car {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double price;
//有参构造
public Car(Integer id, String name, Double price) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
//取值要用getter
public Integer getId(){
return this.id;
}
public String toString() {
return "Car [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
第二步:配置applicationContext.xml
<bean id="car" class="com.igeek.xmlpropertydi.Car">
<constructor-arg index="0" name="id" value="1"/>
<constructor-arg name="name" >
<value>宝马2代value>
constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.Double" value="99999d"/>
bean>
第三步:使用SpringTest.java测试:
@Test
public void test(){
//spring容器
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取car
Car car =(Car) applicationContext.getBean("car");
System.out.println(car);
}
【补充】
1.定位属性的标签,可以混用
<constructor-arg index="0" name="id" value="1"/>
2.自标签的属性赋值问题,可以使用子标签的value,效果和value属性一样
等同于
<constructor-arg name="name" >
<value>宝马2代value>
constructor-arg>
- setter方法属性注入 property
使用的默认的构造器(new Bean()),但必须提供属性的setter方法,使用setter方法也是企业经常使用的属性注入方式。
两步:在类中加入setter方法,在配置文件中使用
【示例】
第一步:创建Person.java,定义id、name、car属性
/**
* 定义人类
* setter方法属性注入
* 相当于new Person();
*/
public class Person {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Car car;
//必须提供setter属性方法
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", car=" + car + "]";
}
}
第二步:配置spring容器applicationContext.xml
<bean id="person" class="com.igeek.xmlpropertydi.Person">
<property name="id" value="1001"/>
<property name="name" value="Tom"/>
<property name="car">
<ref bean="car"/>
property>
bean>
第三步:使用SpringTest.java测试:
@Test
public void test1(){
//spring容器
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取人
Person person=(Person)applicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
【扩展】
<property name="car">
<ref bean="car"/>
property>
2.深入理解setter方法的属性注入
抛出问题:
可以的!
修改Person.java类。
public class Person {
private Integer id;
private String pname;//其中pname和setName方法的属性不一致,而
private Car car;
//必须提供setter属性方法
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.pname = name;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", pname=" + pname + ", car=" + car + "]";
}
}
- p名称空间的使用-了解
什么是名称空间?
作用:Schema区分同名元素。(有点类似于java的包)
回顾:Xmlns没有前缀是默认的名称空间。
为简化XML文件的配置,Spring2.5版本开始引入了一个新的p名称空间。简单的说,它的作用是为了简化setter方法属性依赖注入配置的,它不是真正的名称空间。
它的使用方法:
p:<属性名>="xxx" 引入常量值
p:<属性名>-ref="xxx" 引用其它Bean对象
操作步骤:
第一步:引入p名称空间
| xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> |
第二步:将
<bean id="person2" class="com.igeek.xmlpropertydi.Person" p:id="1002" p:name="关羽" p:car-ref="car"/>
第三步:测试
@Test
public void test2(){
//spring容器
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person2=(Person)applicationContext.getBean("person2");
System.out.println(person2);
}
配置时不需要
- spEL表达式的使用 –会用即可
spEL(Spring Expression Language)是一种表达式语言,它是spring3.x版本的新特性。
它的作用是:支持在运行时操作和查询对象,其语法类似统一的EL语言,但是SpEL提供了额外的功能,功能更强大。
【面试题】什么是EL、OGNL、spEL?
EL:操作servlet相关的一些对象和相关的值,${request.name}
OGNL:主要操作struts2值栈,
spEL:操作bean相关的
语法: #{…} , 引用另一个Bean 、属性、 方法
SpEL表达式的使用功能比较多,Bean操作相关的通常有:
- #{beanid} 引用Bean(具体对象)
- #{beanId.属性} 引用Bean的属性
- #{beanId.方法(参数)} 调用Bean的方法
案例一:配置applicationContext.xml
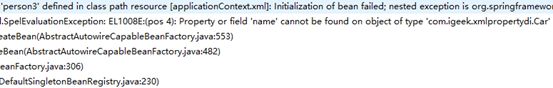
<bean id="person3" class="com.igeek.xmlpropertydi.Person" p:id="#{car.id}" p:name="#{car.name}" p:car="#{car}"/>
如果抛出异常:
需要在Car对象中调用getId和getName的方法,获取id和name的属性值,然后赋值到Person对象name的属性中。
public class Car {
//取值要用getter
public Integer getId(){
return this.id;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
}
案例二:配置applicationContext.xml
<bean id="person4" class="com.igeek.xmlpropertydi.Person" p:id="#{ 1+1}" p:name="#{'Jack'.toUpperCase()}" p:car="#{car}"/>
- 集合类型属性注入 (了解-使用时查看即可)
作用:主要用于框架整合配置。
Java.utils包中常用集合
(1)List
(2)Set
(3)Map
(4)Properties
Spring为集合提供了对应的标签:
注入 list元素
第一步:创建类CollectionBean.java,并提供set方法用作集合的注入
public class CollectionBean {
private List
private Set
private Map
private Properties properties;//特殊类型的map,key和value都是String
public void setList(List
this.list = list;
}
public void setSet(Set
this.set = set;
}
public void setMap(Map
this.map = map;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
public String toString() {
return "CollectionBean [list=" + list + ", set=" + set + ", map=" + map
+ ", properties=" + properties + "]";
}
}
第二步:配置spring的核心容器applicationContext.xml
<bean id="collectionBean" class="com.igeek.xmlpropertydi.CollectionBean">
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>Tomvalue>
<value>Jackvalue>
list>
property>
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>12value>
<value>15value>
set>
property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="name" value="张三"/>
<entry key="age" value="22"/>
<entry key="car" value-ref="car">entry>
map>
property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="name">李四prop>
<prop key="age">33prop>
props>
property>
bean>
第三步:使用SpringTest类进行测试
@Test
public void test5(){
//spring容器
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CollectionBean collectionBean=(CollectionBean)applicationContext.getBean("collectionBean");
System.out.println(collectionBean);
}
第四步:输出结果:
- Spring的多个配置文件的开发
一种:创建工厂的时候加载多个配置文件:
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml","applicationContext2.xml");
二种:在一个配置文件中包含另一个配置文件:
- 案例代码
- 搭建环境:
-
-
- 创建web项目,引入jar包.
-
-
Spring进行Bean管理:
* Spring开发的基本的包
-
-
-
- 引入配置文件:
-
-
Spring:
* applicationContext.xml
* log4j.properties
-
-
-
- 引入页面:
-
-
-
-
-
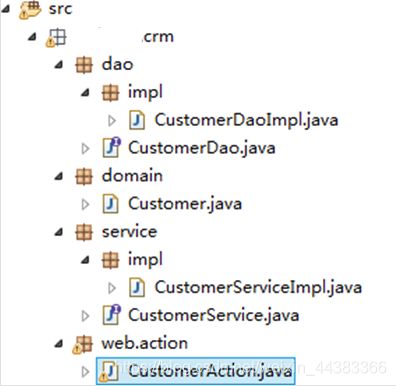
- 创建包结构和类:
-
-
-
-
-
- 在Action调用业务层:
-
-
将业务层类配置到Spring中:
<bean id="customerService" class="com.igeek.crm.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl">
bean>
在Action中获取业务层类:
public void save(){
System.out.println("Action中的save方法执行了...");
System.out.println(customer);
// 传统方式:
/*CustomerService customerService = new CustomerServiceImpl();
customerService.save(customer);*/
// Spring的方式进行操作:
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CustomerService customerService = (CustomerService) applicationContext.getBean("customerService");
customerService.save(customer);
}
【思考、阅读】直接new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext()有什么缺点?
缺点:在创建Spring容器同时,需要对容器中对象初始化。而每次初始化容器的时候,都创建了新的容器对象,消耗了资源,降低了性能。
解决思路:保证容器对象只有一个。
解决方案:将Spring容器绑定到Web Servlet容器上,让Web容器来管理Spring容器的创建和销毁。
分析:ServletContext在Web服务运行过程中是唯一的, 其初始化的时候,会自动执行ServletContextListener 监听器 (用来监听上下文的创建和销毁),具体步骤为:
编写一个ServletContextListener监听器,在监听ServletContext到创建的时候,创建Spring容器,并将其放到ServletContext的属性中保存(setAttribute(Spring容器名字,Spring容器对象) )。
我们无需手动创建该监听器,因为Spring提供了一个叫ContextLoaderListener的监听器,它位于spring-web-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar中。
- Spring整合WEB项目
开发步骤:
第一步:导入spring web的jar
第二步:在web.xml 配置Spring的核心监听器
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
第三步:启动tomcat服务器,结果发现异常,因为默认会加载
根据异常提示:发现spring的BeanFactory没有初始化,说明没有找到spring容器,即applicationContext.xml文件
第四步:在web容器中配置spring文件路径
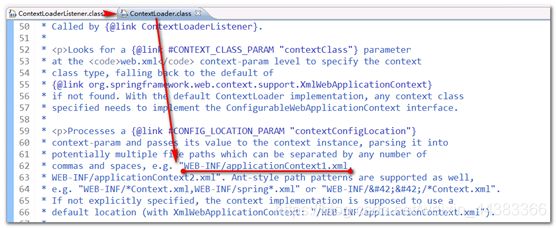
为什么没有找到applicationContext.xml文件呢?因为此时加载的是WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml,而不是src下的applicationContext.xml文件
原因:找到ContextLoaderListener.class,再找到ContextLoader.class,发现默认加载的WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
解决方案:需要在web.xml中配置,加载spring容器applicationContext.xml文件的路径
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
重新启动tomcat服务器,没有异常,问题解决。
第五步:修改Servlet代码。在Servlet 中通过ServletContext 获取Spring容器对象
第一种方式: 使用getAttribute
//每次获取的都是一个spring容器
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
(ApplicationContext)this.getServletContext().getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
第二种方式:使用WebApplicationContextUtils (推荐)
//工具类
WebApplicationContext applicationContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext());
- 改写Action:
/**
* 保存客户的执行的方法:save
*/
public void save(HttpServletRequest req){
// 传统方式:
/*CustomerService customerService = new CustomerServiceImpl();
customerService.save(customer);*/
// Spring的方式进行操作:
/*ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CustomerService customerService = (CustomerService) applicationContext.getBean("customerService");*/
WebApplicationContext applicationContext =WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(req.getServletContext());
CustomerService customerService = (CustomerService) applicationContext.getBean("customerService");
System.out.println("Action中的save方法执行了...");
System.out.println(customer);
customerService.save(customer);
}
- 编写Dao并配置:
<bean id="customerDao" class="com.igeek.crm.dao.impl.CustomerDaoImpl">
bean>
- 业务层调用DAO:
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
private CustomerDao customerDao;
public void setCustomerDao(CustomerDao customerDao) {
this.customerDao = customerDao;
}
…
}
<bean id="customerService" class="com.igeek.crm.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl">
<property name="customerDao" ref="customerDao"/>
bean>
第一天总结:
- 复习Spring学习路线
- IoC和DI概念区分
- XML配置
实例化Bean方式 ,区分BeanFactory和FactoryBean
作用域 singleton和prototype
初始化和销毁 ------ 了解 BeanPostProcessor 后处理Bean
依赖注入(2种):构造器注入
了解 p名称空间 spEL 表达式