spring boot整合thymeleaf以及介绍一些thymeleaf标签
文章目录
-
- 整合环境准备
- 编写入门程序
- 常用的标签使用介绍
-
- 1.标准表达式:
- 2.选择变量表达式
- 3.URL 表达式
- 4.常见属性:
- 5.字面量
- 6.Thymeleaf 字符串拼接
- 7.Thymeleaf 三元运算判断
- 8.Thymeleaf 运算和关系判断
- 9.Thymaleaf 内置对象
- 10.Thymaleaf 表达式功能对象
官网: https://www.thymeleaf.org/

模板引擎的一种,在web环境类似jsp,在非web环境可以静态展示页面。Springboot 使用 thymeleaf 作为视图展示,约定将模板文件放置在
src/main/resource/templates 目 录 下 , 静 态 资 源 放 置 在
src/main/resource/static 目录下。
整合环境准备
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintagegroupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engineartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
编写入门程序
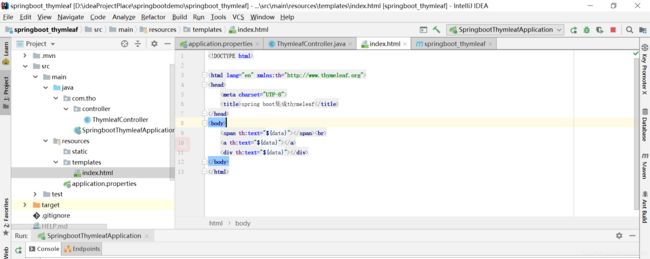
默认是在template下面放html页面,声明头html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">,就会有智能提醒,我就是因为没有智能提醒发现原来我打错了。
接下来,编写一个controller类:
package com.tho.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class ThymleafController {
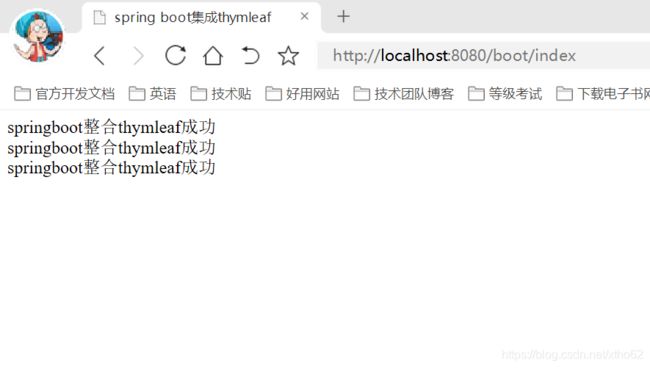
@RequestMapping("/boot/index")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("data","springboot整合thymleaf成功");
return "index";
}
}

resouces下:application.properties关闭缓存
#开发阶段,建议关闭thymleaf的缓存
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
常用的标签使用介绍
1.标准表达式:
语法:${...}
变量表达式用于访问容器(tomcat)上下文环境中的变量,功能和
JSTL 中的 ${} 相同;
Thymeleaf 中的变量表达式使用 ${变量名} 的方式获取其中的数
据,如上图的案例。
2.选择变量表达式
语法:*{…}
选择变量表达式,也叫星号变量表达式,使用 th:object 属性来绑定对象,先创建User对象,然后编写一下代码
@RequestMapping(value="/userinfo")
public String userinfo (Model model) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setNick("zhangsanfeng");
user.setPhone("13700020000");
user.setAddress("beijing");
model.addAttribute("user", user);
model.addAttribute("hello", "helloworld");
return "user";
}
前端接收代码
nick: 张
phone: 三
email: 北京
address: 北京
选择表达式首先使用 th:object 来邦定后台传来的 User 对象,然后
使用 * 来代表这个对象,后面 {} 中的值是此对象中的属性;
选择变量表达式 *{...} 是另一种类似于变量表达式 ${...} 表示变量
的方法;
选择表达式首先使用 th:object 来邦定后台传来的 User 对象,然后
使用 * 来代表这个对象,后面 {} 中的值是此对象中的属性;
选择变量表达式 *{…} 是另一种类似于变量表达式 ${…} 表示变量
的方法;
选择变量表达式在执行时是在选择的对象上求解,而 ${...}是在上下文
的变量 Model 上求解;
3.URL 表达式
语法:@{…}URL
表达式可用于
<script src="...">、<link href="...">、
<a href="...">、<form action="...">
等
1、绝对 URL,比如:
查看
2、相对 URL,相对于页面,比如:
查看
3、相对 URL,相对于项目上下文,比如:
查看(项目的上下文名会被自动添加)
4.常见属性:
1.th:action
定义后台控制器的路径,类似<form>标签的 action 属性,比如:
<form id="login" th:action="@{/login}">......form>
th:method
设置请求方法,比如:
<form id="login" th:action="@{/login}" th:method="post">
......
form>
2.th:href
定义超链接,比如:
<a class="login" th:href="@{/login}">登录a>
3.th:src
用于外部资源引入,比如<script>标签的 src 属性,<img>标签的
src 属性,常与@{
}表达式结合使用;
<script th:src="@{/static/js/jquery-2.4.min.js}">script>
<img th:src="@{/static/image/logo.png}"/>
4.th:id
类似 html 标签中的 id 属性,比如:
<span th:id="${hello}">aaaspan>
5.th:name
设置表单名称,比如:
<input th:type="text" th:id="userName" th:name="userName">
6.th:value
类似 html 标签中的 value 属性,能对某元素的 value 属性进行赋值,
比如:
<input type="hidden" id="userId" name="userId"
th:value="${userId}">
7.th:attr
该属性也是用于给 HTML 中某元素的某属性赋值,但该方式写法不
够优雅,比如上面的例子可以写成如下形式:
<input type="hidden" id="userId" name="userId"
th:attr="value=${userId}">
8.th:text
用于文本的显示,比如:
<input type="text" id="realName" name="reaName"
th:text="${realName}">
9.th:each
这个属性非常常用,比如从后台传来一个对象集合那么就可以使用此
属性遍历输出,它与 JSTL 中的<c: forEach>类似,此属性既可以循
环遍历集合,也可以循环遍历数组及 Map,比如:
<tr th:each="user, interStat : ${userlist}">
<td th:text="${interStat.index}">td>
<td th:text="${user.id}">td>
<td th:text="${user.nick}">td>
<td th:text="${user.phone}">td>
<td th:text="${user.email}">td>
<td th:text="${user.address}">td>
tr>
以上代码解读如下:
th:each="user, iterStat : ${userlist}" 中的 ${userList} 是后台
传来的 Key,user 是${userList} 中的一个数据,
iterStat 是 ${userList} 循环体的信息,
其中 user 及 iterStat 自己可以随便写;
interStat 是循环体的信息,通过该变量可以获取如下信息:
index、size、count、even、odd、first、last,其含义如下:
index: 当前迭代对象的 index(从 0 开始计算)
count: 当前迭代对象的个数(从 1 开始计算)
size: 被迭代对象的大小
current: 当前迭代变量
even/odd: 布尔值,当前循环是否是偶数/奇数(从 0 开始计算)
first: 布尔值,当前循环是否是第一个
last: 布尔值,当前循环是否是最后一个
注意:循环体信息 interStat 也可以不定义,则默认采用迭代变量加
上 Stat 后缀,即 userStat
Map 类型的循环:
<div th:each="myMapVal : ${myMap}">
<span th:text="${myMapVal.key}">span>
<span th:text="${myMapVal.value}">span>
<br/>
div>
${myMapVal.key} 是获取 map 中的 key,${myMapVal.value} 是
获取 map 中的 value;
数组类型的循环:
<div th:each="myArrayVal : ${myArray}">
<div th:text="${myArrayVal}">div>
div>
10.th:if
条件判断,比如后台传来一个变量,判断该变量的值,1 为男,2 为
女:
<span th:if="${sex} == 1" >
男:<input type="radio" name="se" th:value="男" />
span> <span th:if="${sex} == 2">
女:<input type="radio" name="se" th:value="女" />
span>
11.th:unless
th:unless 是 th:if 的一个相反操作,上面的例子可以改写为:
<span th:unless="${sex} == 1" >
女:<input type="radio" name="se" th:value="女" />
span> <span th:unless="${sex} == 2">
男:<input type="radio" name="se" th:value="男" />
span>
12.th:switch/th:case
switch,case 判断语句,比如:
<div th:switch="${sex}">
<p th:case="1">性别:男p>
<p th:case="2">性别:女p>
<p th:case="*">性别:未知p>
div>
一旦某个 case 判断值为 true,剩余的 case 则都当做 false,“*”表
示默认的 case,前面的 case 都不匹配时候,执行默认的 case;
13.th:object
用于数据对象绑定
通常用于选择变量表达式(星号表达式)
14.th:onclick
点击事件,th:οnclick="'getCollect()'"
15.th:style
设置样式,th:style="'display:none;'"
16.th:inline
内联文本、内联脚本
th:inline 有三个取值类型 (text, javascript 和 none)
该属性使用内联表达式[[…]]展示变量数据,比如:
<span th:inline="text">Hello, [[${user.nick}]]span>
等同于:
<span>Hello, <span th:text="${user.nick}">span>span>
th:inline 写在任何父标签都可以,比如如下也是可以的:
<body th:inline="text">
...
<span>[[${user.nick}]]span>
...
body>
内联脚本
<script th:inline="javascript" type="text/javascript">
var user = [[${
user.phone}]];
alert(user);
script> <script th:inline="javascript" type="text/javascript">
var msg = "Hello," + [[${
user.phone}]];
alert(msg);
script>
5.字面量
文本字面量:
用单引号'...'包围的字符串为文本字面量,比如:
<a th:href="@{
'api/getUser?id=' + ${user.id}}">修改a>
数字字面量:
<p>今年是<span th:text="2017">1949span>年p>
<p>20 年后, 将是<span th:text="2017 + 20">1969span>年p>
布尔字面量:
true 和 false
<p th:if="${isFlag == true}">
执行操作
p>
null 字面量:
<p th:if="${userlist == null}">
userlist 为空
p> <p th:if="${userlist != null}">
userlist 不为空
p>
6.Thymeleaf 字符串拼接
一种是字面量拼接:
<span th:text="'当前是第'+${sex}+'页 ,共'+${sex}+'页'">span>
另一种更优雅的方式,使用“|”减少了字符串的拼接:
<span th:text="|当前是第${sex}页,共${sex}页|">span>
7.Thymeleaf 三元运算判断
未知
8.Thymeleaf 运算和关系判断
算术运算:+ , - , * , / , %
关系比较: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
相等判断:== , != ( eq , ne )
9.Thymaleaf 内置对象
1、模板引擎提供了一组内置的对象,这些内置的对象可以直接在模
板中使用,这些对象由#号开始引用:
2、官方手册:
http://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
#request:相当于 HttpServletRequest 对象,这是 3.x 版本,
若是 2.x 版本使用 #httpServletRequest;
${#request.getContextPath()}
${#request.getAttribute("phone")}
#session:
相当于 HttpSession 对象,这是 3.x 版本,若是 2.x 版本使用
#httpSession;
需要在后台 controller 中设置了 session
${#session.getAttribute("phone")}
${#session.id}
${#session.lastAccessedTime}
10.Thymaleaf 表达式功能对象
1、模板引擎提供的一组功能性内置对象,可以在模板中直接使用这
些对象提供的功能方法:
2、工作中常使用的数据类型,如集合,时间,数值,可以使用
thymeleaf 的提供的功能性对象来处理它们;
3、内置功能对象前都需要加#号,内置对象一般都以 s 结尾;
4、官方手册:
http://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
#dates: java.util.Date 对象的实用方法,
#calendars: 和 dates 类似, 但是 java.util.Calendar 对象;
#numbers: 格式化数字对象的实用方法;
#strings: 字符串对象的实用方法: contains, startsWith,
prepending/appending 等;
#objects: 对 objects 操作的实用方法;
#bools: 对布尔值求值的实用方法;
#arrays: 数组的实用方法;
#lists: list 的实用方法,比如
#sets: set 的实用方法;
#maps: map 的实用方法;
#aggregates: 对数组或集合创建聚合的实用方法;