leetcode-106:从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
LC 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 题目
- 解题
-
- 方法一:递归(用4个参数)
- 方法二:递归(用2个参数)
题目
题目链接
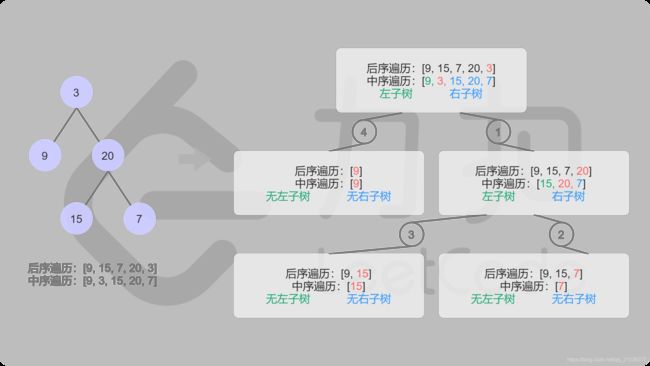
根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树。
注意:
你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
返回如下的二叉树:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
解题
方法一:递归(用4个参数)
和LC-105的一样的方式
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
def MyBuild(postorder_left,postorder_right,inorder_left,inorder_right):
if postorder_left>postorder_right:
return None
postorder_root = postorder_right
inorder_root = index[postorder[postorder_root]]
size_left_subtree = inorder_root-inorder_left
root = TreeNode(postorder[postorder_root])
root.left = MyBuild(postorder_left,postorder_left+size_left_subtree-1,inorder_left,inorder_root-1)
root.right = MyBuild(postorder_left+size_left_subtree,postorder_root-1,inorder_root+1,inorder_right)
return root
n = len(postorder)
index = {
element:i for i,element in enumerate(inorder)}
return MyBuild(0,n-1,0,n-1)
方法二:递归(用2个参数)
其实就是对上面的方法的一种改进,我们要获得根节点的值,从而从哈希表中找到根节点在中序遍历结果中的索引。
而获得根节点,就没必要像上面那样复杂,只需要从后序遍历结果的最后一个pop出来,就是根节点了。
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
def helper(in_left, in_right):
# 如果这里没有节点构造二叉树了,就结束
if in_left > in_right:
return None
# 选择 post_idx 位置的元素作为当前子树根节点
val = postorder.pop()
root = TreeNode(val)
# 根据 root 所在位置分成左右两棵子树
index = idx_map[val]
# 构造右子树
root.right = helper(index + 1, in_right)
# 构造左子树
root.left = helper(in_left, index - 1)
return root
# 建立(元素,下标)键值对的哈希表
idx_map = {
val:idx for idx, val in enumerate(inorder)}
return helper(0, len(inorder) - 1)
特别注意要先构建左子树
root.right = helper(index + 1, in_right)
root.left = helper(in_left, index - 1)
这两个不能换位置。因为postorderpop的结果就是依次是右子树,最后再左子树。
所以这个递归思想,有种深度优先搜索的思想。而方法一,可以换位置(每次递归都相当于处理一个新问题了),方法二,则都是在postorder.pop()限制下进行,要根据pop的顺序去构建