NMS(Non-Maximum Suppression)非极大值抑制的原理及实现
题目源于百度深度学习平台算法工程师面试
NMS 概念
非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression, NMS),顾名思义就是抑制那些不是极大值的元素,可以理解为局部最大值搜索。对于目标检测来说,非极大值抑制的含义就是对于重叠度较高的一部分同类候选框来说,去掉那些置信度较低的框,只保留置信度最大的那一个进行后面的流程,这里的重叠度高低与否是通过 NMS 阈值来判断的。
抑制非最大值算法

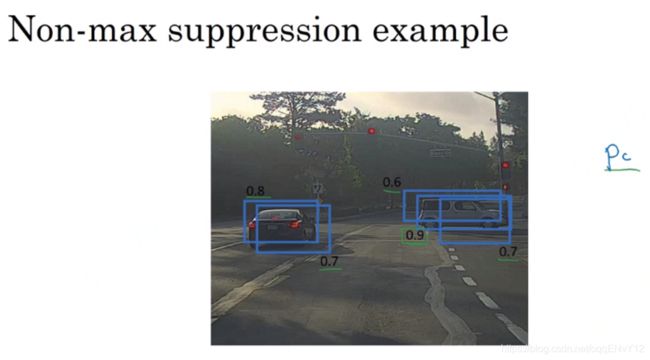
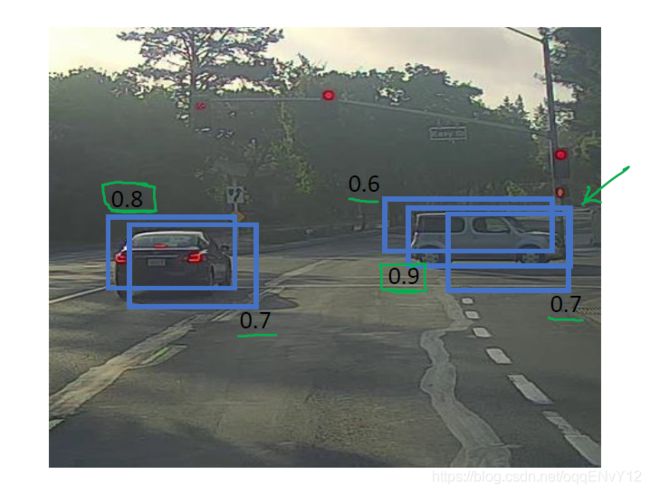
上图中反应的是单个目标的检测,对于多个目标,例如行人、汽车、摩托车等,只需要独立进行三次抑制非最大值算法,每个类别各做一次。
C++实现
// Martin Kersner, [email protected]
// 2016/12/18
// C++ version of http://www.pyimagesearch.com/2015/02/16/faster-non-maximum-suppression-python/
#include "nms.hpp"
using std::vector;
using cv::Rect;
using cv::Point;
vector nms(const vector> & boxes,
const float & threshold)
{
if (boxes.empty())
return vector();
// grab the coordinates of the bounding boxes
auto x1 = GetPointFromRect(boxes, XMIN);
auto y1 = GetPointFromRect(boxes, YMIN);
auto x2 = GetPointFromRect(boxes, XMAX);
auto y2 = GetPointFromRect(boxes, YMAX);
// compute the area of the bounding boxes and sort the bounding
// boxes by the bottom-right y-coordinate of the bounding box
auto area = ComputeArea(x1, y1, x2, y2);
auto idxs = argsort(y2);
int last;
int i;
vector pick;
// keep looping while some indexes still remain in the indexes list
while (idxs.size() > 0) {
// grab the last index in the indexes list and add the
// index value to the list of picked indexes
last = idxs.size() - 1;
i = idxs[last];
pick.push_back(i);
// find the largest (x, y) coordinates for the start of
// the bounding box and the smallest (x, y) coordinates
// for the end of the bounding box
auto idxsWoLast = RemoveLast(idxs);
auto xx1 = Maximum(x1[i], CopyByIndexes(x1, idxsWoLast));
auto yy1 = Maximum(y1[i], CopyByIndexes(y1, idxsWoLast));
auto xx2 = Minimum(x2[i], CopyByIndexes(x2, idxsWoLast));
auto yy2 = Minimum(y2[i], CopyByIndexes(y2, idxsWoLast));
// compute the width and height of the bounding box
auto w = Maximum(0, Subtract(xx2, xx1));
auto h = Maximum(0, Subtract(yy2, yy1));
// compute the ratio of overlap
auto overlap = Divide(Multiply(w, h), CopyByIndexes(area, idxsWoLast));
// delete all indexes from the index list that have
auto deleteIdxs = WhereLarger(overlap, threshold);
deleteIdxs.push_back(last);
idxs = RemoveByIndexes(idxs, deleteIdxs);
}
return BoxesToRectangles(FilterVector(boxes, pick));
}
vector GetPointFromRect(const vector> & rect,
const PointInRectangle & pos)
{
vector points;
for (const auto & p: rect)
points.push_back(p[pos]);
return points;
}
vector ComputeArea(const vector & x1,
const vector & y1,
const vector & x2,
const vector & y2)
{
vector area;
auto len = x1.size();
for (decltype(len) idx = 0; idx < len; ++idx) {
auto tmpArea = (x2[idx] - x1[idx] + 1) * (y2[idx] - y1[idx] + 1);
area.push_back(tmpArea);
}
return area;
}
template
vector argsort(const vector & v)
{
// initialize original index locations
vector idx(v.size());
std::iota(idx.begin(), idx.end(), 0);
// sort indexes based on comparing values in v
sort(idx.begin(), idx.end(),
[&v](int i1, int i2) {return v[i1] < v[i2];});
return idx;
}
vector Maximum(const float & num,
const vector & vec)
{
auto maxVec = vec;
auto len = vec.size();
for (decltype(len) idx = 0; idx < len; ++idx)
if (vec[idx] < num)
maxVec[idx] = num;
return maxVec;
}
vector Minimum(const float & num,
const vector & vec)
{
auto minVec = vec;
auto len = vec.size();
for (decltype(len) idx = 0; idx < len; ++idx)
if (vec[idx] > num)
minVec[idx] = num;
return minVec;
}
vector CopyByIndexes(const vector & vec,
const vector & idxs)
{
vector resultVec;
for (const auto & idx : idxs)
resultVec.push_back(vec[idx]);
return resultVec;
}
vector RemoveLast(const vector & vec)
{
auto resultVec = vec;
resultVec.erase(resultVec.end()-1);
return resultVec;
}
vector Subtract(const vector & vec1,
const vector & vec2)
{
vector result;
auto len = vec1.size();
for (decltype(len) idx = 0; idx < len; ++idx)
result.push_back(vec1[idx] - vec2[idx] + 1);
return result;
}
vector Multiply(const vector & vec1,
const vector & vec2)
{
vector resultVec;
auto len = vec1.size();
for (decltype(len) idx = 0; idx < len; ++idx)
resultVec.push_back(vec1[idx] * vec2[idx]);
return resultVec;
}
vector Divide(const vector & vec1,
const vector & vec2)
{
vector resultVec;
auto len = vec1.size();
for (decltype(len) idx = 0; idx < len; ++idx)
resultVec.push_back(vec1[idx] / vec2[idx]);
return resultVec;
}
vector WhereLarger(const vector & vec,
const float & threshold)
{
vector resultVec;
auto len = vec.size();
for (decltype(len) idx = 0; idx < len; ++idx)
if (vec[idx] > threshold)
resultVec.push_back(idx);
return resultVec;
}
vector RemoveByIndexes(const vector & vec,
const vector & idxs)
{
auto resultVec = vec;
auto offset = 0;
for (const auto & idx : idxs) {
resultVec.erase(resultVec.begin() + idx + offset);
offset -= 1;
}
return resultVec;
}
vector BoxesToRectangles(const vector> & boxes)
{
vector rectangles;
vector box;
for (const auto & box: boxes)
rectangles.push_back(Rect(Point(box[0], box[1]), Point(box[2], box[3])));
return rectangles;
}
template
vector FilterVector(const vector & vec,
const vector & idxs)
{
vector resultVec;
for (const auto & idx: idxs)
resultVec.push_back(vec[idx]);
return resultVec;
}
Python实现
# import the necessary packages
import numpy as np
# Malisiewicz et al.
def non_max_suppression_fast(boxes, overlapThresh):
# if there are no boxes, return an empty list
if len(boxes) == 0:
return []
# if the bounding boxes integers, convert them to floats --
# this is important since we'll be doing a bunch of divisions
if boxes.dtype.kind == "i":
boxes = boxes.astype("float")
# initialize the list of picked indexes
pick = []
# grab the coordinates of the bounding boxes
x1 = boxes[:,0]
y1 = boxes[:,1]
x2 = boxes[:,2]
y2 = boxes[:,3]
# compute the area of the bounding boxes and sort the bounding
# boxes by the bottom-right y-coordinate of the bounding box
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
idxs = np.argsort(y2)
# keep looping while some indexes still remain in the indexes
# list
while len(idxs) > 0:
# grab the last index in the indexes list and add the
# index value to the list of picked indexes
last = len(idxs) - 1
i = idxs[last]
pick.append(i)
# find the largest (x, y) coordinates for the start of
# the bounding box and the smallest (x, y) coordinates
# for the end of the bounding box
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idxs[:last]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idxs[:last]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idxs[:last]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idxs[:last]])
# compute the width and height of the bounding box
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
# compute the ratio of overlap
overlap = (w * h) / area[idxs[:last]]
# delete all indexes from the index list that have
idxs = np.delete(idxs, np.concatenate(([last],
np.where(overlap > overlapThresh)[0])))
# return only the bounding boxes that were picked using the
# integer data type
return boxes[pick].astype("int")
有一位网友分析的还不错,代码也很简略,推荐一下:
- NMS算法原理实现
直接把他的C++实现抄过来背下来
#include
#include
#include
struct Bbox {
int x1;
int y1;
int x2;
int y2;
float score;
Bbox(int x1_, int y1_, int x2_, int y2_, float s):
x1(x1_), y1(y1_), x2(x2_), y2(y2_), score(s) {};
};
float iou(Bbox box1, Bbox box2) {
float area1 = (box1.x2 - box1.x1 + 1) * (box1.y2 - box1.y1 + 1);
float area2 = (box2.x2 - box2.x1 + 1) * (box2.y2 - box2.y1 + 1);
int x11 = std::max(box1.x1, box2.x1);
int y11 = std::max(box1.y1, box2.y1);
int x22 = std::min(box1.x2, box2.x2);
int y22 = std::min(box1.y2, box2.y2);
float intersection = (x22 - x11 + 1) * (y22 - y11 + 1);
return intersection / (area1 + area2 - intersection);
}
std::vector nms(std::vector &vecBbox, float threshold) {
auto cmpScore = [](Bbox box1, Bbox box2) {
return box1.score < box2.score; // 升序排列, 令score最大的box在vector末端
};
std::sort(vecBbox.begin(), vecBbox.end(), cmpScore);
std::vector pickedBbox;
while (vecBbox.size() > 0) {
pickedBbox.emplace_back(vecBbox.back());
vecBbox.pop_back();
for (size_t i = 0; i < vecBbox.size(); i++) {
if (iou(pickedBbox.back(), vecBbox[i]) >= threshold) {
vecBbox.erase(vecBbox.begin() + i);
}
}
}
return pickedBbox;
}
int main() {
std::vector vecBbox;
vecBbox.emplace_back(Bbox(187, 82, 337, 317, 0.9));
vecBbox.emplace_back(Bbox(150, 67, 305, 282, 0.75));
vecBbox.emplace_back(Bbox(246, 121, 368, 304, 0.8));
auto pickedBbox = nms(vecBbox, 0.5);
for (auto box : pickedBbox) {
std::cout << box.x1 << ", " <<
box.y1 << ", " <<
box.x2 << ", " <<
box.y2 << ", " <<
box.score << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
算法说明
对检测结果做NMS后的如果剩余多个bbox,表明检测到了多个物体。NMS并没有对多个框进行组合从何合成一个大的检测框(天哪为什么我开始会有这样的想法?)。
举例说明:
From:: 知乎
一张图里,有2辆车,10个regions;
任务是保留最优的2个regions,排除剩下的8个regions。
NMS
先找到车辆概率最高的region1;
再计算所有车辆region与region1之间的IoU值;
再设定一个阈值,比如0.7;
抹去所有IoU值>=0.7的车辆region;
这样一来,region1周边的(与region1高度重合的)车辆region都被排除了;
留下的其他车辆region,大概率是其他车辆的region(方框);
repeat, 实现对另一个车辆方框region选择和排除。
- 个人认为NMS有一种假设:bbox分数最高的框最大,能框住整个目标物体,所以同一个物体的其他候选框如果是目标的局部或者重叠率很高的区域,那么就应该被剔除掉。剩下的候选框通常指向的是图像中其他区域的另外的同类物体。
- NMS是一种贪婪算法,其获取的边框很可能存在相对较大的误差。