Nginx-1.18 +Https(免费版) + openresty-1.17.8.2 + LVS+keepalived实战(Centos7.8)
Nginx-1.18 + Https(免费版) + openresty-1.17.8.2 + LVS+keepalived实战(Centos7.8)
一.nginx的介绍
Nginx (engine x) 是一个高性能的HTTP和反向代理web服务器,同时也提供了IMAP/POP3/SMTP服务。Nginx是由伊戈尔·赛索耶夫为俄罗斯访问量第二的Rambler.ru站点(俄文:Рамблер)开发的,第一个公开版本0.1.0发布于2004年10月4日。
其将源代码以类BSD许可证的形式发布,因它的稳定性、丰富的功能集、示例配置文件和低系统资源的消耗而闻名。2011年6月1日,nginx 1.0.4发布。
Nginx是一款轻量级的Web 服务器/反向代理服务器及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代理服务器,在BSD-like 协议下发行。其特点是占有内存少,并发能力强,事实上nginx的并发能力在同类型的网页服务器中表现较好,中国大陆使用nginx网站用户有:百度、京东、新浪、网易、腾讯、淘宝等。
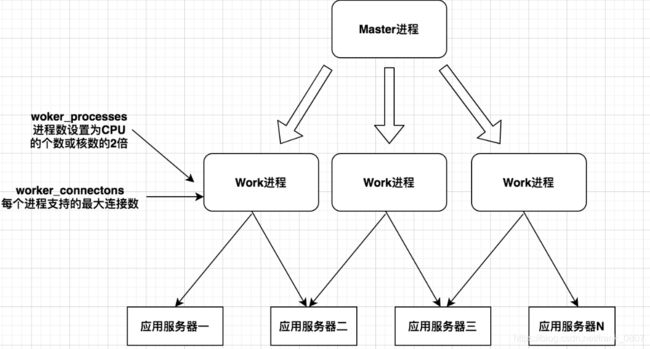
二.Centos7.x 下 nginx的骨架搭建
1.nginx下载
点击进入nginx首页
选择Stable version下的版本(稳定版本)
2.nginx服务器部署
安装相关依赖:
yum -y install gcc zlib zlib-devel pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel
导入安装包进行解压
tar -zxvf xxx
在nginx根目录进行编译:
./configure
make
make install
默认安装路径:
cd /usr/local/nginx
nginx基本操作:
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin
./nginx #默认配置文件启动
./nginx -s reload #重启,加载默认配置文件
./nginx -s stop #停止
./nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf #启动指定某个配置文件
关闭进程,nginx有master process 和worker process,关闭master即可
ps -ef | grep “nginx”
kill -9 PID `
查看nginx进程
ps -ef | grep "nginx"
3.nginx配置文件
打开配置文件
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf
vim nginx.conf
# 每个配置项由配置指令和指令参数 2 个部分构成
#user root; # 指定Nginx Worker进程运行以及用户组
worker_processes 1; # 一般和cpu核数一致
#error_log logs/error.log; # 错误日志的存放路径 和错误日志
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid; # 进程PID存放路径
# 事件模块指令,用来指定Nginx的IO模型,Nginx支持的有select、poll、kqueue、epoll 等。不同的是epoll用在Linux平台上,而kqueue用在BSD系统中,对于Linux系统,epoll工作模式是首选
events {
use epoll;
# 定义Nginx每个进程的最大连接数, 作为服务器来说: worker_connections * worker_processes,
# 作为反向代理来说,最大并发数量应该是worker_connections * worker_processes/2。因为反向代理服务器,每个 并发会建立与客户端的连接和与后端服务的连接,会占用两个连接
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# 自定义服务的访问日志
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
# 是否开启高效传输模式 on开启 off关闭
sendfile on;
#减少网络报文段的数量
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
# 客户端连接保持活动的超时时间,超过这个时间之后,服务器会关闭该连接
keepalive_timeout 65;
#压缩,可节省带宽
#gzip on;
# 虚拟主机的配置
server {
listen 80; # 虚拟主机的服务端口
server_name localhost; #用来指定IP地址或域名,多个域名之间用空格分开
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#URL地址匹配
location / {
root html; # 服务默认启动目录
index index.html index.htm; #默认访问文件,按照顺序找
}
#error_page 404 /404.html; #错误状态码的显示页面
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
三.实战
1.文件服务器实战
server {
listen 80; # 虚拟主机的服务端口
server_name localhost; #用来指定IP地址或域名,多个域名之间用空格分开
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#URL地址匹配
location /app/img {
alias /usr/local/software/img/; #图片存储的路径
}
#error_page 404 /404.html; #错误状态码的显示页面
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
2.accessLog日志挖掘实战
- 配置文件:
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for" $upstream_cache_status $request_time';
server {
listen 80;
server_name aabbcc.com;
location / {
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
index xxx.html;
}
#charset koi8-r;
#启用虚拟主机下的access_log和存储路径
access_log logs/host.access.log main;
}
- 日志:
122.70.148.18 - - [04/Aug/2020:14:46:48 +0800] "GET /user/api/v1/product/order/query_state?product_id=1&token=xeyJhbGciOJE HTTP/1.1" 200 48 "https://x.net/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/84.0.4147.89 Safari/537.36"
- 解析:
$remote_addr 对应的是真实日志里的122.70.148.18,即客户端的IP。
$remote_user 对应的是第二个中杠“-”,没有远程用户,所以用“-”填充。
[$time_local]对应的是[04/Aug/2020:14:46:48 +0800]。
“$request”对应的是"GET /user/api/v1/product/order/query_state?product_id=1&token=xeyJhbGciOJE HTTP/1.1"。
$status对应的是200状态码,200表示正常访问。
$body_bytes_sent对应的是48字节,即响应body的大小。
“$http_referer” 对应的是”https://x.net/“,若是直接打开域名浏览的时,referer就会没有值,为”-“。
“$http_user_agent” 对应的是”Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.12; rv:56.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/56.0”。如果为空可能是爬出
“$http_x_forwarded_for” 对应的是”-“或者空。
$upstream_response_time:指从Nginx向后端建立连接开始到接受完数据然后关闭连接为止的时间
$request_time一般会比upstream_response_time大,因为用户网络较差,或者传递数据较大时,前者会耗时大很多
- 日常使用
查看访问最频繁的前100个IP
awk '{print $1}' access_temp.log | sort -n |uniq -c | sort -rn | head -n 100
统计访问最多的url 前20名
cat access_temp.log |awk '{print $7}'| sort|uniq -c| sort -rn| head -20 | more
统计耗时接口, 列出传输时间超过 2 秒的接口,显示前5条
cat xxx.log|awk '($NF > 2){print $7}'|sort -n|uniq -c|sort -nr|head -5
备注:$NF 表示最后一列, awk '{print $NF}'
- 基础
awk 是文本处理工具,默认按照空格切分,$N 是第切割后第N个,从1开始
sort命令用于将文本文件内容加以排序,-n 按照数值排,-r 按照倒序来排
案例的sort -n 是按照第一列的数值大小进行排序,从小到大,倒序就是 sort -rn
uniq 去除重复出现的行列, -c 在每列旁边显示该行重复出现的次数。
3.负载均衡实战
- 配置案例: 轮询策略(适合静态文件服务器)
upstream lbs {
server 192.168.0.106:8080;
server 192.168.0.106:8081;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_redirect default;
}
}
- 配置案例: 权重策略
upstream lbs {
server 192.168.0.106:8080 weight=5;
server 192.168.0.106:8081 weight=10;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_redirect default;
}
}
- 配置案例: ip hash(使用场景:websocket)
upstream lbs {
ip_hash
server 192.168.0.106:8080;
server 192.168.0.106:8081;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_redirect default;
}
}
- 配置案例: 其它
upstream lbs {
server 192.168.0.106:8080 down;
server 192.168.0.106:8081;
server 192.168.0.106:8082 backup;
#允许nginx与后端节点尝试失败的次数,和60s后再重新尝试,可以通过指令proxy_next_upstream来配置什么是失败的尝试,proxy_next_upstream来配置。
server 192.168.0.106:8084 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=60s;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
#proxy_next_upstream来配置
proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_500 http_503 http_404
}
}
4.全局异常兜底数据返回实战
upstream lbs {
server 192.168.0.106:8080 down;
server 192.168.0.106:8081;
server 192.168.0.106:8082 backup;
#允许nginx与后端节点尝试失败的次数,和60s后再重新尝试,可以通过指令proxy_next_upstream来配置什么是失败的尝试,proxy_next_upstream来配置。
server 192.168.0.106:8084 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=60s;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_redirect default;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_503 non_idempotent;
#开启错误拦截配置,一定要开启
proxy_intercept_errors on;
}
# 不加 =200,则返回的就是原先的http错误码;配上后如果出现500等错误都返回给用户200状态,并跳转至/default_api
error_page 404 500 502 503 504 =200 /default_api;
location = /default_api {
default_type application/json;
return 200 '{"code":"-1","msg":"invoke fail, not found "}';
5.后端服务获取用户真是ip实战
upstream lbs {
server 192.168.0.106:8080 down;
server 192.168.0.106:8081;
server 192.168.0.106:8082 backup;
#允许nginx与后端节点尝试失败的次数,和60s后再重新尝试,可以通过指令proxy_next_upstream来配置什么是失败的尝试,proxy_next_upstream来配置。
server 192.168.0.106:8084 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=60s;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_redirect default;
# 存放用户的真实ip
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
6.ip封禁实战
在conf目录下创建一个文件
touch blacklist.conf
修改文件内容
vim blacklist.conf
deny 192.168.11.1;
deny 192.168.11.2;
deny 192.168.11.3;
配置主配置文件
vim nginx.conf
单独网站屏蔽IP的方法,把include xxx; 放到网址对应的在server{
}语句块,虚拟主机
所有网站屏蔽IP的方法,把include xxx; 放到http {
}语句块。
nginx配置如下:
http{
# ....
include blacklist.conf;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_redirect default;
}
拓展-自动化封禁思路
编写shell脚本
AWK统计access.log,记录每秒访问超过60次的ip,然后配合nginx或者iptables进行封禁
crontab定时跑脚本
7.浏览器跨域配置实战
只针对后端的接口服务
location / {
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $http_origin;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
#如果有不同需要自行添加
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' 'DNT,web-token,token,app-token,Authorization,Accept,Origin,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Mx-ReqToken,X-Data-Type,X-Auth-Token,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Range';
#如果有不同需要自行添加
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods 'GET,POST,OPTIONS';
#如果预检请求则返回成功,不需要转发到后端
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' 1728000;
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain; charset=utf-8';
add_header 'Content-Length' 0;
return 200;
}
}
8.websocket实战
server {
listen 80;
server_name abc.net;
location / {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_read_timeout 300s; //websocket空闲保持时长
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
#核心是下面的配置 其他和普通反向代理没区别, 表示请求服务器升级协议为WebSocket
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
}
}
服务器处理完请求后,响应如下报文# 状态码为101
HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: upgrade
9.缓存前置实战
upstream lbs {
server 192.168.0.106:8080;
server 192.168.0.106:8081;
}
#全局缓存配置,优先级最高,默认缓存get、head请求,在没人访问的情况下60m删除缓存(非活跃状态下)
proxy_cache_path /root/cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=xd_cache:10m max_size=1g inactive=5s use_temp_path=off;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_cache xd_cache;
#只要到时间就会删除(活跃状态的)
proxy_cache_valid 200 304 1m;
proxy_cache_valid 404 1m;
proxy_cache_key $host$uri$is_args$args;
add_header Nginx-Cache "$upstream_cache_status";
}
}
10.文件压缩实战(节省带宽)
#开启gzip,减少我们发送的数据量
gzip on;
gzip_min_length 1k;
#4个单位为16k的内存作为压缩结果流缓存
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
#gzip压缩比,可在1~9中设置,1压缩比最小,速度最快,9压缩比最大,速度最慢,消耗CPU
gzip_comp_level 4;
#压缩的类型
gzip_types application/javascript text/plain text/css application/json application/xml text/javascript;
#给代理服务器用的,有的浏览器支持压缩,有的不支持,所以避免浪费不支持的也压缩,所以根据客户端的HTTP头来判断,是否需要压缩
gzip_vary on;
#禁用IE6以下的gzip压缩,IE某些版本对gzip的压缩支持很不好
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6].";
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#静态资源存储路径
location /static {
alias /usr/local/software/static
}
}
四.规则应用(可略过)
1.location
正则
^ 以什么开始
$ 以什么结束
^/api/user$
location 路径匹配
语法 location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { … }
location = /uri
= 表示精准匹配,只要完全匹配上才能生效
location /uri
不带任何修饰符,表示前缀匹配
location ^~ /uri/
匹配任何已 /uri/ 开头的任何查询并且停止搜索
location /
通用匹配,任何未匹配到其他location的请求都会匹配到
正则匹配
区分大小写匹配(~)
不区分大小写匹配(~*)
优先级(不要写复杂,容易出问题和遗忘)
精准匹配 > 字符串匹配(若有多个匹配项匹配成功,那么选择匹配长的并记录) > 正则匹配
案例
server {
server_name abc.net;
location ~^/api/pub$ {
...
}
}
^/api/pub$这个正则表达式表示字符串必须以/开始,以b $结束,中间必须是/api/pub
http://abc.net/api/v1 匹配(完全匹配)
http://abc.net/API/PUB 不匹配,大小写敏感
http://abc.net/api/pub?key1=value1 匹配
http://abc.net/api/pub/ 不匹配
http://abc.net/api/public 不匹配,不能匹配正则表达式
测试
location = /img/test.png {
return 1;
}
location /img/test.png {
return 2;
}
location ^~/img/ {
return 3;
}
location = / {
return 4;
}
location / {
return 5;
}
2.rewrite重定向
在location中添加
语法 rewrite regex replacement[flag]
rewrite ^/(.*) http://xxx.net/$1 permanent
#这是一个正则表达式,匹配完整的域名和后面的路径地址
#replacement部分是https://xxx.net/$1,$1是取自regex部分()里的内容
| 标记符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| last | 本条规则匹配完成后继续向下匹配新的location URI规则 |
| break | 本条规则匹配完成后终止,不在匹配任何规则 |
| redirect | 返回302临时重定向 |
| permanent | 返回301永久重定向 |
五.nginx整合https
可以通过阿里云进行SSL免费证书申请并下载
证书名称如下:
5022224_custompang.net.key
5022224_custompang.net.pem
将证书放入/usr/local/software/biz/key/中
先删除原生的nginx
cd /usr/local
rm -rf nginx
进入nginx根目录执行
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module
make
make install
进入安装后的nginx配置目录
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf
打开nginx.conf找到如下内容
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name custompang.net;
#导入证书
ssl_certificate /usr/local/software/biz/key/5022224_custompang.net.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/software/biz/key/5022224_custompang.net.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
六.nginx整合OpenResty
1.介绍
由章亦春发起,是基于Ngnix和Lua的高性能web平台,内部集成精良的LUa库、第三方模块、依赖, 开发者可以方便搭建能够处理高并发、扩展性极高的动态web应用、web服务、动态网关。
OpenResty将Nginx核心、LuaJIT、许多有用的Lua库和Nginx第三方模块打包在一起
Nginx是C语言开发,如果要二次扩展是很麻烦的,而基于OpenResty,开发人员可以使用 Lua 编程语言对 Nginx 核心模块进行二次开发拓展
性能强大,OpenResty可以快速构造出1万以上并发连接响应的超高性能Web应用系统
官网:http://openresty.org
阿里、腾讯、新浪、酷狗音乐等都是 OpenResty 的深度用户
2.OpenResty安装
网站:http://openresty.org/en/linux-packages.html#centos
yum install wget
wget https://openresty.org/package/centos/openresty.repo
sudo mv openresty.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/
sudo yum check-update
sudo yum install openresty
安装命令行工具
sudo yum install openresty-resty
列出所有 openresty 仓库里的软件包
sudo yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="openresty" list available
查看版本
resty -V
默认安装路径
/usr/local/openresty
3.OpenResty实战
(1)helloworld开发实战
编辑:vim /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
使用代码块形式:
http{
# 虚拟机主机块
server{
# 监听端口
listen 80;
# 配置请求的路由
location /{
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_block{
ngx.say("hello world; 123");
}
}
}
}
访问 curl 127.0.0.1
如果浏览器访问会出现文件下载,因为没有Html头信息
使用文件扫描方式:
#使用其他方式
http{
# 虚拟机主机块,还需要配置lua文件扫描路径
lua_package_path "$prefix/lualib/?.lua;;";
lua_package_cpath "$prefix/lualib/?.so;;";
server{
# 监听端口
listen 80;
# 配置请求的路由
location /{
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_file lua/123.lua;
}
}
}
(2)内网访问限制实战(配置白名单)
配置文件:
http{
upstream lbs {
server 192.168.159.138:8080
}
# 这里设置为 off,是为了避免每次修改之后都要重新 reload 的麻烦。
# 在生产环境上需要 lua_code_cache 设置成 on。
lua_code_cache off;
# lua_package_path可以配置openresty的文件寻址路径,$PREFIX 为openresty安装路径
# 文件名使用“?”作为通配符,多个路径使用“;”分隔,默认的查找路径用“;;”
# 设置纯 Lua 扩展库的搜寻路径
lua_package_path "$prefix/lualib/?.lua;;";
# 设置 C 编写的 Lua 扩展模块的搜寻路径(也可以用 ';;')
lua_package_cpath "$prefix/lualib/?.so;;";
server {
location / {
access_by_lua_file lua/white_ip_list.lua;
proxy_pass http://lbs;
}
}
lua脚本编写
cd /usr/local/openresty/nginx/
mkdir lua
cd lua
touch white_ip_list.lua
#定义一个变量
local white_ips = {
["127.0.0.1","192.168.1.1"]=true}
local ip = ngx.var.remote_addr
if true ~= white_ips[ip] then
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN)
return;
end
(3)下载限速实战
配置文件:
http{
# 这里设置为 off,是为了避免每次修改之后都要重新 reload 的麻烦。
# 在生产环境上需要 lua_code_cache 设置成 on。
lua_code_cache off;
# lua_package_path可以配置openresty的文件寻址路径,$PREFIX 为openresty安装路径
# 文件名使用“?”作为通配符,多个路径使用“;”分隔,默认的查找路径用“;;”
# 设置纯 Lua 扩展库的搜寻路径
lua_package_path "$prefix/lualib/?.lua;;";
# 设置 C 编写的 Lua 扩展模块的搜寻路径(也可以用 ';;')
lua_package_cpath "$prefix/lualib/?.so;;";
server {
location /download {
access_by_lua_block {
#当前请求的响应上限是 每秒 300K 字节
ngx.var.limit_rate = "300K"
}
alias /usr/local/software/app;
}
七.nginx实现高可用
1.介绍
-
官网 www.linuxvirtualserver.org
-
LVS是Linux Virtual Server,Linux虚拟服务器,是一个虚拟的服务器集群系统
项目是由章文嵩博士成立,是中国国内最早出现的自由软件项目之一
Linux2.4 内核以后,LVS 已经是 Linux 标准内核的一部分
提供了10多种调度算法: 轮询、加权轮询、最小连接、目标地址散列、源地址散列等 -
三种负载均衡转发技术
-
NAT:数据进出都通过 LVS, 前端的Master既要处理客户端发起的请求,又要处理后台RealServer的响应信息,将RealServer响应的信息再转发给客户端, 容易成为整个集群系统性能的瓶颈; (支持任意系统且可以实现端口映射)
-
DR: 移花接木,最高效的负载均衡规则,前端的Master只处理客户端的请求,将请求转发给RealServer,由后台的RealServer直接响应客户端,不再经过Master, 性能要优于LVS-NAT; 需要LVS和RS集群绑定同一个VIP(支持多数系统,不可以实现端口映射)
-
TUNL:隧道技术,前端的Master只处理客户端的请求,将请求转发给RealServer,然后由后台的RealServer直接响应客户端,不再经过Master;(支持少数系统,不可以实现端口映射))
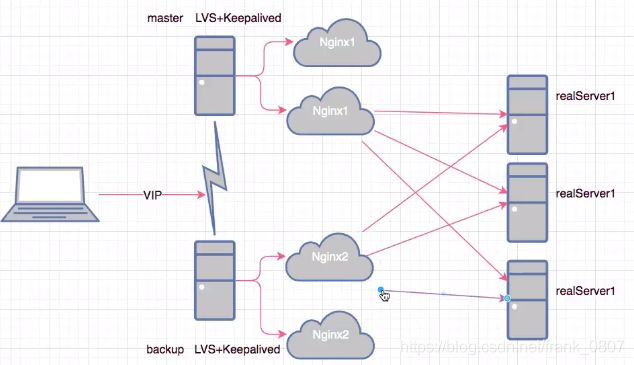
-
keepalived是一个类似于交换机制的软件,核心作用是检测服务器的状态,如果有一台web服务器工作出现故障,Keepalived将检测到并将有故障的服务器从系统中剔除,使用其他服务器代替该服务器的工作,当服务器工作正常后Keepalived自动将服务器加入到服务器群中,这些工作全部自动完成。
后来加入了vrrp(虚拟路由器冗余协议),除了为lvs提供高可用还可以为其他服务器比如Mysql、Haproxy等软件提供高可用方案
2.lvs+keepalived实战
- 系统环境:centos7.8
Linux frank20210105 3.10.0-1127.19.1.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Tue Aug 25 17:23:54 UTC 2020 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
- 添加相关依赖:
yum install -y gcc
yum install -y openssl-devel
yum install -y libnl libnl-devel
yum install -y libnfnetlink-devel
yum install -y net-tools
yum install -y vim wget
yum install -y keepalived
systemctl stop firewalld
setenforce 0
vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux 修改selinux=disabled
cd /etc/keepalived
service keepalived start
通过ps -ef | grep keepalived 查看是否启动成功
- 具体配置:
先关闭keepalived进行配置:service keepalived stop
具体配置文件如下:
- Master:
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id LVS_DEVEL # 设置lvs的id,在一个网络内应该是唯一的
enable_script_security #允许执行外部脚本
}
#配置vrrp_script,主要用于健康检查及检查失败后执行的动作。
vrrp_script chk_real_server {
#健康检查脚本,当脚本返回值不为0时认为失败
script "/usr/local/software/conf/chk_server.sh"
#检查频率,以下配置每2秒检查1次
interval 2
#当检查失败后,将vrrp_instance的priority减小5
weight -5
#连续监测失败3次,才认为真的健康检查失败。并调整优先级
fall 3
#连续监测2次成功,就认为成功。但不调整优先级
rise 2
user root
}
#配置对外提供服务的VIP vrrp_instance配置
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
#指定vrrp_instance的状态,是MASTER还是BACKUP主要还是看优先级。
state MASTER
#指定vrrp_instance绑定的网卡,最终通过指定的网卡绑定VIP
interface ens33
#相当于VRID,用于在一个网内区分组播,需要组播域内内唯一。
virtual_router_id 51
#本机的优先级,VRID相同的机器中,优先级最高的会被选举为MASTER
#主备不同,需要修改
priority 100
#心跳间隔检查,默认为1s,MASTER会每隔1秒发送一个报文告知组内其他机器自己还活着。
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
#定义虚拟IP(VIP)为192.168.159.100,可多设,每行一个
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.159.100
}
#本vrrp_instance所引用的脚本配置,名称就是vrrp_script 定义的容器名
track_script {
chk_real_server
}
}
# 定义对外提供服务的LVS的VIP以及port
virtual_server 192.168.159.100 80 {
# 设置健康检查时间,单位是秒
delay_loop 6
# 设置负载调度的算法为rr
lb_algo rr
# 设置LVS实现负载的机制,有NAT、TUN、DR三个模式
lb_kind NAT
# 会话保持时间
persistence_timeout 50
#指定转发协议类型(TCP、UDP)
protocol TCP
# 指定real server1的IP地址
#主备不同,需要修改,主备相同,不需要改
real_server 192.168.159.145 80 {
# 配置节点权值,数字越大权重越高
weight 1
# 健康检查方式
TCP_CHECK {
# 健康检查方式
connect_timeout 10 # 连接超时
retry 3 # 重试次数
delay_before_retry 3 # 重试间隔
connect_port 80 # 检查时连接的端口
}
}
}
- Backup:
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
router_id LVS_DEVEL # 设置lvs的id,在一个网络内应该是唯一的
enable_script_security #允许执行外部脚本
}
#配置vrrp_script,主要用于健康检查及检查失败后执行的动作。
vrrp_script chk_real_server {
#健康检查脚本,当脚本返回值不为0时认为失败
script "/usr/local/software/conf/chk_server.sh"
#检查频率,以下配置每2秒检查1次
interval 2
#当检查失败后,将vrrp_instance的priority减小5
weight -5
#连续监测失败3次,才认为真的健康检查失败。并调整优先级
fall 3
#连续监测2次成功,就认为成功。但不调整优先级
rise 2
user root
}
#配置对外提供服务的VIP vrrp_instance配置
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
#指定vrrp_instance的状态,是MASTER还是BACKUP主要还是看优先级。
state BACKUP
#指定vrrp_instance绑定的网卡,最终通过指定的网卡绑定VIP
interface ens33
#相当于VRID,用于在一个网内区分组播,需要组播域内内唯一。
virtual_router_id 51
#本机的优先级,VRID相同的机器中,优先级最高的会被选举为MASTER
#主备不同,需要修改
priority 50
#心跳间隔检查,默认为1s,MASTER会每隔1秒发送一个报文告知组内其他机器自己还活着。
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
#定义虚拟IP(VIP)为192.168.159.100,可多设,每行一个
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.159.100
}
#本vrrp_instance所引用的脚本配置,名称就是vrrp_script 定义的容器名
track_script {
chk_real_server
}
}
#定义对外提供服务的LVS的VIP以及port
virtual_server 192.168.159.100 80 {
# 设置健康检查时间,单位是秒
delay_loop 6
# 设置负载调度的算法为rr
lb_algo rr
# 设置LVS实现负载的机制,有NAT、TUN、DR三个模式
lb_kind NAT
# 会话保持时间
persistence_timeout 50
#指定转发协议类型(TCP、UDP)
protocol TCP
# 指定real server1的IP地址
#主备不同,需要修改,主备相同,不需要改
real_server 192.168.159.146 80 {
# 配置节点权值,数字越大权重越高
weight 1
# 健康检查方式
TCP_CHECK {
# 健康检查方式
connect_timeout 10 # 连接超时
retry 3 # 重试次数
delay_before_retry 3 # 重试间隔
connect_port 80 # 检查时连接的端口
}
}
}
创建chk_server.sh实现:
当nginx服务挂掉时,也将本机的keepalived 关闭掉
vim /usr/local/software/conf/chk_server.sh
#!/bin/bash
#检查nginx进程是否存在
counter=$(ps -C nginx --no-heading|wc -l)
if [ "${counter}" -eq "0" ]; then
service keepalived stop
echo 'nginx server is died.......'
fi
两台设备分别启动
service keepalived start
查看节点状态
service keepalived status
启动成功后通过ip -a 查看虚拟ip,默认挂载到Master主机的网卡
- 配置注意
router_id后面跟的自定义的ID在同一个网络下是一致的
state后跟的MASTER和BACKUP必须是大写;否则会造成配置无法生效的问题
interface 网卡ID;要根据自己的实际情况来看,可以使用以下方式查询 ip a 查询
在BACKUP节点上,其keepalived.conf与Master上基本一致,修改state为BACKUP,priority值改小即可
authentication主备之间的认证方式,一般使用PASS即可;主备的配置必须一致,不能超过8位
特别注意: 需要关闭selinux,不然sh脚本可能不生效
getenforce 查看
setenforce 0 关闭 将Enforcing 状态变为 Permissive
如果实在启动不成功,那么可以重新下载进行配置:
yum remove keepalived
yum install -y keepalived
配置文件替换为keepalived
- 生产环境问题
VIP : 阿里云(LBS)、华为云、腾讯云、AWS
八.nginx内置变量
提供丰富的内置变量, openresty里面使用参考下面的文档
https://github.com/openresty/lua-nginx-module#ngxvarvariable
名称 说明
$arg_name 请求中的name参数
$args 请求中的参数
$content_length HTTP请求信息里的"Content-Length"
$content_type 请求信息里的"Content-Type"
$host 请求信息中的"Host",如果请求中没有Host行,则等于设置的服务器名
$hostname 机器名使用 gethostname系统调用的值
$http_cookie cookie 信息
$http_referer 引用地址
$http_user_agent 客户端代理信息
$http_via 最后一个访问服务器的Ip地址。
$http_x_forwarded_for 相当于网络访问路径
$is_args 如果请求行带有参数,返回“?”,否则返回空字符串
$limit_rate 对连接速率的限制
$nginx_version 当前运行的nginx版本号
$pid worker进程的PID
$query_string 与$args相同
$remote_addr 客户端IP地址
$remote_port 客户端端口号
$request 用户请求
$request_method 请求的方法,比如"GET"、"POST"等
$request_uri 请求的URI,带参数
$scheme 所用的协议,比如http或者是https
$server_name 请求到达的服务器名
$server_port 请求到达的服务器端口号
$server_protocol 请求的协议版本,"HTTP/1.0"或"HTTP/1.1"
$uri 请求的URI,可能和最初的值有不同,比如经过重定向之类的
nginx对于请求的处理分多个阶段,Nginx , 从而让第三方模块通过挂载行为在不同的阶段来控制, 大致如下
- 初始化阶段(Initialization Phase)
init_by_lua_file
init_worker_by_lua_file
- 重写与访问阶段(Rewrite / Access Phase)
rewrite_by_lua_file
access_by_lua_file
- 内容生成阶段(Content Phase)
content_by_lua_file
日志记录阶段(Log Phase)。。。。
如果大家有更多的资源希望能一起分享,谢谢大家!!!