前言
声明:该文章中所有测试都是在JDK1.8的环境下。
该文章是我在学习Java中的异常处理这方面知识时,做的一些总结和记录。
如果有不正确的地方请大家多多包涵并作出指点,谢谢!
一、异常机制介绍
1.1 基本概念
什么是异常?顾名思义就是非正常的现象。就是Java程序在运行的时候出现不正常的情况。举个例子:我们有一个等式"10/0=?"需要计算,我们都知道,10除以0结果是无意义的,所以我们用Java程序计算该等式就会出现非正常现象。
1.2 异常类体系
在了解了异常的概念之后,那么接下来需要知道Java中异常是如何表示的。
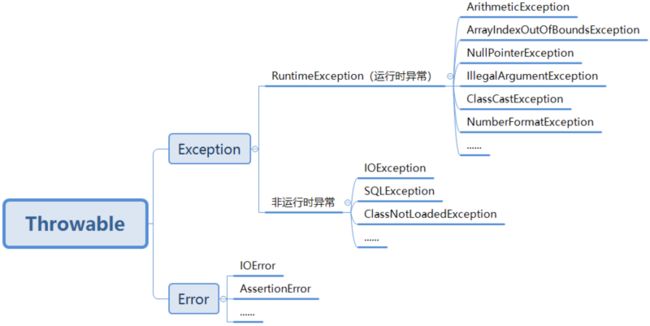
首先需要认识java.lang.Throwable类,这个类是Java中所有错误(Error)和异常(Exception)的超类。
- 错误(Error):一般是Java虚拟机相关的,无法解决的严重错误。例如系统崩溃,虚拟机错误。
- 异常(Exception):主要是一些编程错误,可以通过编写代码解决。比如上面讲的计算0作为除数的等式。
所以,我们重点需要学习的是能够通过编写代码解决问题的"异常(Exception)"。
1.3 异常的种类
java.lang.Exception这是所有异常的超类。然后我们查看java.lang.Exception类,发现该异常类下面有好多子类。那这么多异常类,该如何区分和记忆呢?
我们根据程序异常在编译时期能否被检测出来,把异常分为两种:
- RuntimeException:运行时异常,也叫非检测性异常。
- 其他异常:非运行时异常,也叫检测性异常。
下面给非检测性异常和检测性异常举例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.非检测性异常
System.out.println(10 / 0); //编译成功,程序可以直接运行,但是在运行代码时会发生算术异常(java.lang.ArithmeticException)
//2.检测性异常
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream("d:/a.txt"); //编译时直接错误,程序不能直接运行
}
}RuntimeException的主要子类:
- ArithmeticException:算术异常
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:数组下标越界异常
- NullPointerException:空指针异常
- IllegalArgumentException:不合法参数异常
- ClassCastException:类型转换异常
- NumberFormatException:数字格式异常
1.4 异常类结构体系图
根据上面列出的异常种类,可以构成以下的异常类结构体系图:
二、异常处理
开始前需要先明白为什么需要异常处理?
程序中出现异常,并且没对其进行处理,会导致程序的中断执行,一旦产生异常,异常之后的语句并不会被执行,而是直接结束程序。
2.1 异常的避免
可以用if条件判断语句进行运行时异常的避免,我们就根据上面最常见的几个子类举例子。
首选我们碰到如下三种异常:
public class ExceptionAvoid {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//出现算术异常
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
System.out.println(a / b);
//出现数组下标越界异常
int[] arr = new int[3];
int c = 3;
System.out.println(arr[c]);
//出现空指针异常
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());
}
}使用if条件判断语句进行异常避免:
public class ExceptionAvoid {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
//避免算术异常
if (0 != b) {
System.out.println(a / b);
}
int[] arr = new int[3];
int c = 3;
//避免数组下标越界异常
if (c >= 0 && c < 3) {
System.out.println(arr[c]);
}
String str = null;
//避免空指针异常
if (null != str) {
System.out.println(str.length());
}
}
}缺陷:虽然if条件判断语句可以很好的进行异常避免,但是过多会导致代码加长,可读性差。
2.2 异常的捕获
概念:对程序中可能出现的异常进行捕获处理,如果程序发生异常,则会被捕获,进行一些自定义操作。
语法格式:
try {
可能发生异常的代码
} catch (异常类型 引用变量名) {
出现异常后进行处理的代码
} finally {
无论是否发生异常都要执行的代码
}
注:catch代码块可以有多个,finally代码块可以没有不想使用if条件判断语句进行异常避免,或者该异常是非运行时异常,可以进行异常的捕获处理,如下所示。
public class ExceptionCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//运行时异常
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
try {
System.out.println(a / b);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("出现算术异常");
}
//非运行时异常
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:/a.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("出现文件未找到异常");
} finally {
System.out.println("该代码一定被执行");
}
}
}流程分析:
1、如果在try代码块中没有异常,则程序不会进入catch代码块,而是把try代码块中的程序走完,例子如下:
public class ExceptionCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 2;
try {
System.out.println("1");
System.out.println(a / b);
System.out.println("2");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("3");
}
}
}
则输出结果:
1
2
52、如果在try代码块中的某一行代码出现异常,则程序不会在try代码块中继续执行,而是直接进入catch代码块,并把catch代码块的程序走完,例子如下:
public class ExceptionCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
try {
System.out.println("1");
System.out.println(a / b);
System.out.println("2");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("3");
}
}
}
则输出结果:
1
33、无论异常是否出现并被捕获,finally代码块中代码一定会执行,例子如下:
public class ExceptionCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = ?;
try {
System.out.println("1");
System.out.println(a / b);
System.out.println("2");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("3");
} finally {
System.out.println("4");
}
}
}
如果b = 0;则输出结果:
1
3
4
如果b = 2;则输出结果:
1
2
44、如果有异常出现并被捕获,则程序不会被终止,例子如下:
public class ExceptionCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
try {
System.out.println("1");
System.out.println(a / b);
System.out.println("2");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("3");
} finally {
System.out.println("4");
}
System.out.println("5");
}
}
则输出结果:
1
3
4
5提出问题:代码中存在多个异常的可能,那该如何解决?
解决方法:使用多个catch代码块捕获可能出现的异常,最后一个catch代码块中使用Exception兜底。
public class ExceptionCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
div(4,0);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("出现算术异常");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("出现指正越界异常");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出现异常");
}
}
public static int div(int a, int b) {
int []arr = new int [a];
System.out.println(arr[4]);//制造的第一处异常
return a/b;//制造的第二处异常
}
}
注:在存在多个catch代码块的程序中,父类异常不能放在子类异常前面,例如:Exception不能放在ArithmeticException之前。
注:在存在多个catch代码块的程序中,父类异常不能放在子类异常前面,例如:Exception不能放在ArithmeticException之前。
2.3 异常的抛出
概念:
在某些特殊的情况下有些异常不能处理或者不便处理,就可以将该异常转移给该方法的调用者。当方法执行出现异常,则底层生成一个对象类抛出,此时异常代码后续的代码就不会再执行。
语法格式:
访问权限 返回值类型 方法名称(参数列表) throws 异常类型1,异常类型2....{方法体;}
public void test(int a) throws Exception {}示例代码:
public class ExceptionThrow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
show();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void show() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:/a.txt");
fileInputStream.close();
}
}根据示例代码,说明三个问题:
- 有时候为了集中处理异常,我们可以在存在异常的方法中进行异常抛出,到最后进行集中异常处理。而异常捕获只能在该方法中直接处理。
- 主方法中进行异常捕获而不是异常抛出是因为主方法再往上抛异常就把异常抛给了JVM,不利于异常处理。
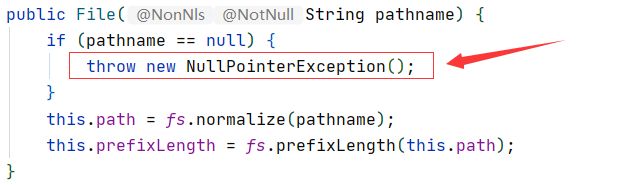
- show方法中的异常底层来源:
①首先进入FileInputStream类中,可以看到该构造方法中创建了File的实例。
②进入File类中,可以看到底层抛出的异常。
方法重写后抛出异常的注意事项:
子类不允许抛出的异常
- 比父类更大的异常
- 和父类平级但是不一样的异常
子类允许抛出的异常
- 能抛出一样的异常
- 能抛出更小的异常
- 子类可以不抛出异常
2.4 自定义异常
概念:
当程序需要表达年龄不合理时,java官方又没提供这个针对性的异常,此时程序员需要自定义异常加以描述。
自定义异常实现:
创建一个自定义异常类继承Exception类或其子类
public class AgeException extends Exception {
public AgeException() {
}
public AgeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
自定义异常类使用:
创建一个Person类,在setAge方法中抛出自定义异常。
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) throws AgeException {
setName(name);
setAge(age);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) throws AgeException {
if (age > 0 && age < 200) {
this.age = age;
} else {
throw new AgeException("年龄不合理哦")
}
}
}
执行主方法查看结果:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Person person = new Person("Bob",210);
} catch (AgeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出结果为:
AgeException: 年龄不合理哦
at Person.setAge(Person.java:36)
at Person.(Person.java:17)
at Test.main(Test.java:13) 三、总结
一个异常类结构体系图
三个异常处理方法
一个自定义异常