用Python制作五子棋人机对弈(人工智障版和升级AI版)
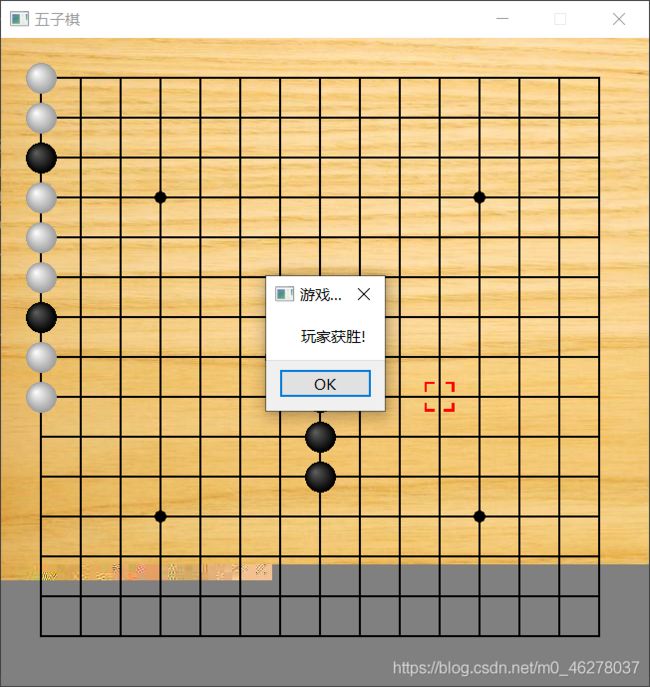
智障版截图:
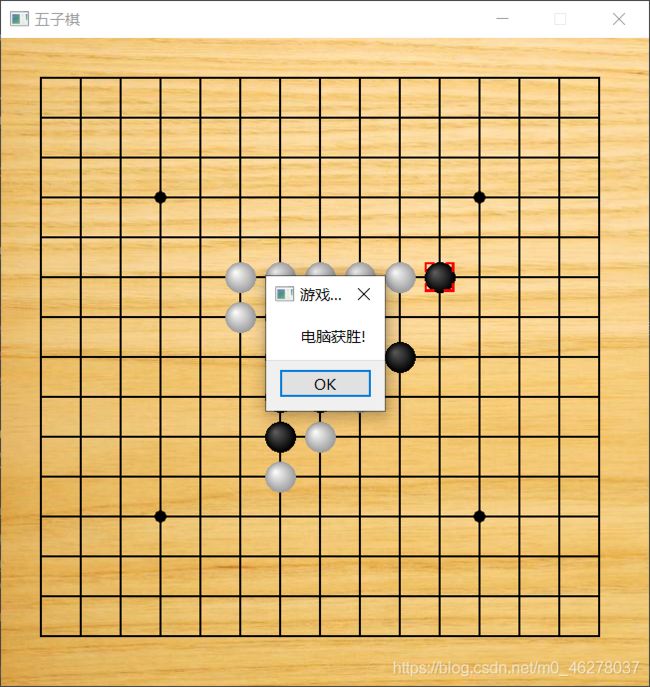
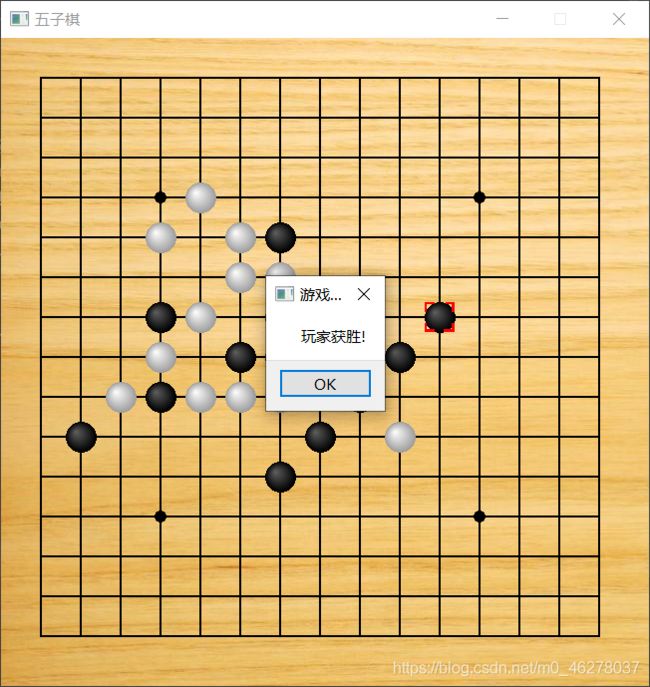
智能版截图:
可能遇到的问题:
No module named ‘pyqt5‘解决办法
智障版源码:
背景:
window.py
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QMessageBox
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPainter, QPen, QColor, QPalette, QBrush, QPixmap, QRadialGradient
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt, QPoint, QTimer
import traceback
from game import Gomoku
from corner_widget import CornerWidget
def run_with_exc(f):
"""游戏运行出现错误时,用messagebox把错误信息显示出来"""
def call(window, *args, **kwargs):
try:
return f(window, *args, **kwargs)
except Exception:
exc_info = traceback.format_exc()
QMessageBox.about(window, '错误信息', exc_info)
return call
class GomokuWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.init_ui() # 初始化游戏界面
self.g = Gomoku() # 初始化游戏内容
self.last_pos = (-1, -1)
self.res = 0 # 记录那边获得了胜利
self.operate_status = 0 # 游戏操作状态。0为游戏中(可操作),1为游戏结束闪烁过程中(不可操作)
def init_ui(self):
"""初始化游戏界面"""
# 1. 确定游戏界面的标题,大小和背景颜色
self.setObjectName('MainWindow')
self.setWindowTitle('五子棋')
self.setFixedSize(650, 650)
# self.setStyleSheet('#MainWindow{background-color: green}')
palette = QPalette()
palette.setBrush(QPalette.Window, QBrush(QPixmap('imgs/muzm.jpg')))
self.setPalette(palette)
# 2. 开启鼠标位置的追踪。并在鼠标位置移动时,使用特殊符号标记当前的位置
self.setMouseTracking(True)
# 3. 鼠标位置移动时,对鼠标位置的特殊标记
self.corner_widget = CornerWidget(self)
self.corner_widget.repaint()
self.corner_widget.hide()
# 4. 游戏结束时闪烁的定时器
self.end_timer = QTimer(self)
self.end_timer.timeout.connect(self.end_flash)
self.flash_cnt = 0 # 游戏结束之前闪烁了多少次
self.flash_pieces = ((-1, -1), ) # 哪些棋子需要闪烁
# 5. 显示初始化的游戏界面
self.show()
@run_with_exc
def paintEvent(self, e):
"""绘制游戏内容"""
def draw_map():
"""绘制棋盘"""
qp.setPen(QPen(QColor(0, 0, 0), 2, Qt.SolidLine)) # 棋盘的颜色为黑色
# 绘制横线
for x in range(15):
qp.drawLine(40 * (x + 1), 40, 40 * (x + 1), 600)
# 绘制竖线
for y in range(15):
qp.drawLine(40, 40 * (y + 1), 600, 40 * (y + 1))
# 绘制棋盘中的黑点
qp.setBrush(QColor(0, 0, 0))
key_points = [(4, 4), (12, 4), (4, 12), (12, 12), (8, 8)]
for t in key_points:
qp.drawEllipse(QPoint(40 * t[0], 40 * t[1]), 5, 5)
def draw_pieces():
"""绘制棋子"""
# 绘制黑棋子
qp.setPen(QPen(QColor(0, 0, 0), 1, Qt.SolidLine))
# qp.setBrush(QColor(0, 0, 0))
for x in range(15):
for y in range(15):
if self.g.g_map[x][y] == 1:
if self.flash_cnt % 2 == 1 and (x, y) in self.flash_pieces:
continue
radial = QRadialGradient(40 * (x + 1), 40 * (y + 1), 15, 40 * x + 35, 40 * y + 35) # 棋子的渐变效果
radial.setColorAt(0, QColor(96, 96, 96))
radial.setColorAt(1, QColor(0, 0, 0))
qp.setBrush(QBrush(radial))
qp.drawEllipse(QPoint(40 * (x + 1), 40 * (y + 1)), 15, 15)
# 绘制白棋子
qp.setPen(QPen(QColor(160, 160, 160), 1, Qt.SolidLine))
# qp.setBrush(QColor(255, 255, 255))
for x in range(15):
for y in range(15):
if self.g.g_map[x][y] == 2:
if self.flash_cnt % 2 == 1 and (x, y) in self.flash_pieces:
continue
radial = QRadialGradient(40 * (x + 1), 40 * (y + 1), 15, 40 * x + 35, 40 * y + 35) # 棋子的渐变效果
radial.setColorAt(0, QColor(255, 255, 255))
radial.setColorAt(1, QColor(160, 160, 160))
qp.setBrush(QBrush(radial))
qp.drawEllipse(QPoint(40 * (x + 1), 40 * (y + 1)), 15, 15)
if hasattr(self, 'g'): # 游戏还没开始的话,就不用画了
qp = QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
draw_map() # 绘制棋盘
draw_pieces() # 绘制棋子
qp.end()
@run_with_exc
def mouseMoveEvent(self, e):
# 1. 首先判断鼠标位置对应棋盘中的哪一个格子
mouse_x = e.windowPos().x()
mouse_y = e.windowPos().y()
if 25 <= mouse_x <= 615 and 25 <= mouse_y <= 615 and (mouse_x % 40 <= 15 or mouse_x % 40 >= 25) and (mouse_y % 40 <= 15 or mouse_y % 40 >= 25):
game_x = int((mouse_x + 15) // 40) - 1
game_y = int((mouse_y + 15) // 40) - 1
else: # 鼠标当前的位置不对应任何一个游戏格子,将其标记为(01, 01
game_x = -1
game_y = -1
# 2. 然后判断鼠标位置较前一时刻是否发生了变化
pos_change = False # 标记鼠标位置是否发生了变化
if game_x != self.last_pos[0] or game_y != self.last_pos[1]:
pos_change = True
self.last_pos = (game_x, game_y)
# 3. 最后根据鼠标位置的变化,绘制特殊标记
if pos_change and game_x != -1:
self.setCursor(Qt.PointingHandCursor)
if pos_change and game_x == -1:
self.setCursor(Qt.ArrowCursor)
if pos_change and game_x != -1:
self.corner_widget.move(25 + game_x * 40, 25 + game_y * 40)
self.corner_widget.show()
if pos_change and game_x == -1:
self.corner_widget.hide()
@run_with_exc
def mousePressEvent(self, e):
"""根据鼠标的动作,确定落子位置"""
if not (hasattr(self, 'operate_status') and self.operate_status == 0):
return
if e.button() == Qt.LeftButton:
# 1. 首先判断按下了哪个格子
mouse_x = e.windowPos().x()
mouse_y = e.windowPos().y()
if (mouse_x % 40 <= 15 or mouse_x % 40 >= 25) and (mouse_y % 40 <= 15 or mouse_y % 40 >= 25):
game_x = int((mouse_x + 15) // 40) - 1
game_y = int((mouse_y + 15) // 40) - 1
else: # 鼠标点击的位置不正确
return
self.g.move_1step(True, game_x, game_y)
# 2. 根据操作结果进行一轮游戏循环
res, self.flash_pieces = self.g.game_result(show=True) # 判断游戏结果
if res != 0: # 如果游戏结果为“已经结束”,则显示游戏内容,并退出主循环
self.repaint(0, 0, 650, 650)
self.game_restart(res)
return
self.g.ai_move_1step() # 电脑下一步
res, self.flash_pieces = self.g.game_result(show=True)
if res != 0:
self.repaint(0, 0, 650, 650)
self.game_restart(res)
return
self.repaint(0, 0, 650, 650) # 在游戏还没有结束的情况下,显示游戏内容,并继续下一轮循环
@run_with_exc
def end_flash(self):
# 游戏结束时的闪烁操作
if self.flash_cnt <= 5:
# 执行闪烁
self.flash_cnt += 1
self.repaint()
else:
# 闪烁完毕,执行重新开始的操作
self.end_timer.stop()
# 1. 显示游戏结束的信息
if self.res == 1:
QMessageBox.about(self, '游戏结束', '玩家获胜!')
elif self.res == 2:
QMessageBox.about(self, '游戏结束', '电脑获胜!')
elif self.res == 3:
QMessageBox.about(self, '游戏结束', '平局!')
else:
raise ValueError('当前游戏结束的标志位为' + self.res + '. 而游戏结束的标志位必须为1, 2 或 3')
# 2. 游戏重新开始的操作
self.res = 0
self.operate_status = 0
self.flash_cnt = 0
self.g = Gomoku() # 重新初始化游戏内容
self.repaint(0, 0, 650, 650) # 重新绘制游戏界面
def game_restart(self, res):
"""游戏出现开始"""
self.res = res # 标记谁获胜了
self.operate_status = 1 # 游戏结束时的闪烁过程中,不可操作
self.end_timer.start(300) # 开始结束时闪烁的计时器
corner_widget.py
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPainter, QPen
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QWidget
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
class CornerWidget(QWidget):
def __init__(self, parent):
super().__init__(parent=parent)
self.setFixedSize(30, 30)
def paintEvent(self, e):
qp = QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
pen = QPen(Qt.red, 3, Qt.SolidLine)
qp.setPen(pen)
qp.drawLine(0, 8, 0, 0)
qp.drawLine(0, 0, 8, 0)
qp.drawLine(22, 0, 28, 0)
qp.drawLine(28, 0, 28, 8)
qp.drawLine(28, 22, 28, 28)
qp.drawLine(28, 28, 20, 28)
qp.drawLine(8, 28, 0, 28)
qp.drawLine(0, 28, 0, 22)
game.py
class Gomoku:
def __init__(self):
self.g_map = [[0 for y in range(15)] for x in range(15)] # 当前的棋盘
self.cur_step = 0 # 步数
def move_1step(self, input_by_window=False, pos_x=None, pos_y=None):
"""
玩家落子
:param input_by_window: 是否从图形界面输入
:param pos_x: 从图形界面输入时,输入的x坐标为多少
:param pos_y: 从图形界面输入时,输入的y坐标为多少
"""
while True:
try:
if not input_by_window:
pos_x = int(input('x: ')) # 接受玩家的输入人
pos_y = int(input('y: '))
if 0 <= pos_x <= 14 and 0 <= pos_y <= 14: # 判断这个格子能否落子
if self.g_map[pos_x][pos_y] == 0:
self.g_map[pos_x][pos_y] = 1
self.cur_step += 1
return
except ValueError: # 玩家输入不正确的情况(例如输入了‘A’)
continue
def game_result(self, show=False):
"""判断游戏的结局。0为游戏进行中,1为玩家获胜,2为电脑获胜,3为平局"""
# 1. 判断是否横向连续五子
for x in range(11):
for y in range(15):
if self.g_map[x][y] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 1][y] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 2][y] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 3][y] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 4][y] == 1:
if show:
return 1, [(x0, y) for x0 in range(x, x + 5)]
else:
return 1
if self.g_map[x][y] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 1][y] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 2][y] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 3][y] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 4][y] == 2:
if show:
return 2, [(x0, y) for x0 in range(x, x + 5)]
else:
return 2
# 2. 判断是否纵向连续五子
for x in range(15):
for y in range(11):
if self.g_map[x][y] == 1 and self.g_map[x][y + 1] == 1 and self.g_map[x][y + 2] == 1 and self.g_map[x][y + 3] == 1 and self.g_map[x][y + 4] == 1:
if show:
return 1, [(x, y0) for y0 in range(y, y + 5)]
else:
return 1
if self.g_map[x][y] == 2 and self.g_map[x][y + 1] == 2 and self.g_map[x][y + 2] == 2 and self.g_map[x][y + 3] == 2 and self.g_map[x][y + 4] == 2:
if show:
return 2, [(x, y0) for y0 in range(y, y + 5)]
else:
return 2
# 3. 判断是否有左上-右下的连续五子
for x in range(11):
for y in range(11):
if self.g_map[x][y] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 1][y + 1] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 2][y + 2] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 3][y + 3] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 4][y + 4] == 1:
if show:
return 1, [(x + t, y + t) for t in range(5)]
else:
return 1
if self.g_map[x][y] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 1][y + 1] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 2][y + 2] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 3][y + 3] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 4][y + 4] == 2:
if show:
return 2, [(x + t, y + t) for t in range(5)]
else:
return 2
# 4. 判断是否有右上-左下的连续五子
for x in range(11):
for y in range(11):
if self.g_map[x + 4][y] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 3][y + 1] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 2][y + 2] == 1 and self.g_map[x + 1][y + 3] == 1 and self.g_map[x][y + 4] == 1:
if show:
return 1, [(x + t, y + 4 - t) for t in range(5)]
else:
return 1
if self.g_map[x + 4][y] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 3][y + 1] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 2][y + 2] == 2 and self.g_map[x + 1][y + 3] == 2 and self.g_map[x][y + 4] == 2:
if show:
return 2, [(x + t, y + 4 - t) for t in range(5)]
else:
return 2
# 5. 判断是否为平局
for x in range(15):
for y in range(15):
if self.g_map[x][y] == 0: # 棋盘中还有剩余的格子,不能判断为平局
if show:
return 0, [(-1, -1)]
else:
return 0
if show:
return 3, [(-1, -1)]
else:
return 3
def ai_move_1step(self):
"""电脑落子"""
for x in range(15):
for y in range(15):
if self.g_map[x][y] == 0:
self.g_map[x][y] = 2
self.cur_step += 1
return
def show(self, res):
"""显示游戏内容"""
for y in range(15):
for x in range(15):
if self.g_map[x][y] == 0:
print(' ', end='')
elif self.g_map[x][y] == 1:
print('〇', end='')
elif self.g_map[x][y] == 2:
print('×', end='')
if x != 14:
print('-', end='')
print('\n', end='')
for x in range(15):
print('| ', end='')
print('\n', end='')
if res == 1:
print('玩家获胜!')
elif res == 2:
print('电脑获胜!')
elif res == 3:
print('平局!')
def play(self):
while True:
self.move_1step() # 玩家下一步
res = self.game_result() # 判断游戏结果
if res != 0: # 如果游戏结果为“已经结束”,则显示游戏内容,并退出主循环
self.show(res)
return
self.ai_move_1step() # 电脑下一步
res = self.game_result()
if res != 0:
self.show(res)
return
self.show(0) # 在游戏还没有结束的情况下,显示游戏内容,并继续下一轮循环
main.py
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication
from window import GomokuWindow
from game import Gomoku
import sys
def main():
# g = Gomoku()
# g.play()
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = GomokuWindow()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
运行main.py就可以领略智障版的风采了,包你百战百胜哦!
升级AI版:
升级AI版使用了C++版的AI脚本,源码和文件都在这里,感兴趣的可以下载学习。
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1lR1yjbjuhDCp68nr-4OkcA
提取码:lbp3