手写简易版vue-router
关注 前端开发博客,回复“加群”
加入我们一起学习,天天进步
作者:wangkaiwd
https://github.com/wangkaiwd/simple-vue-router
vue-router是开发vue项目中必不可少的依赖,为了能更好的理解其实现原理,而源码阅读起来又过于复杂和枯燥,笔者这里实现一个简易版本的vue-rouer,帮助自己来更好的理解源码。
其功能如下:
通过
Vue插件形式使用支持
hash模式支持嵌套路由
router-view组件router-link组件路由守卫
基本使用
基础
demo单独新建了一个分支 ,方便学习和查看
在实现自己的router之前,我们先使用官方的包来书写一个基础demo,之后我们会以这个demo为需求,一步步实现我们自己的vue-router。
demo的代码逻辑如下:
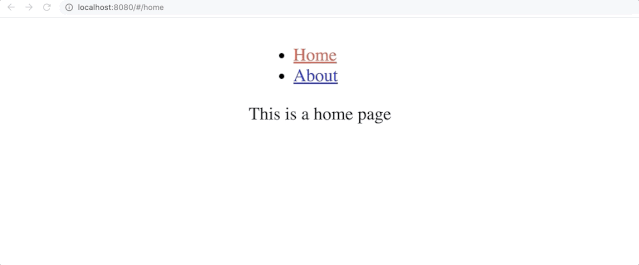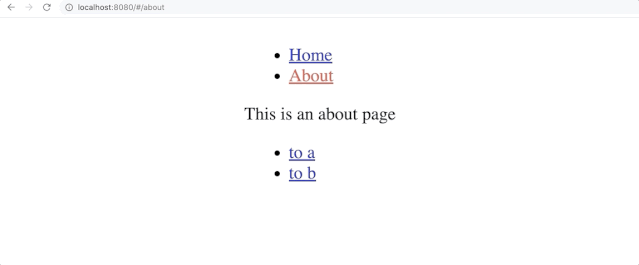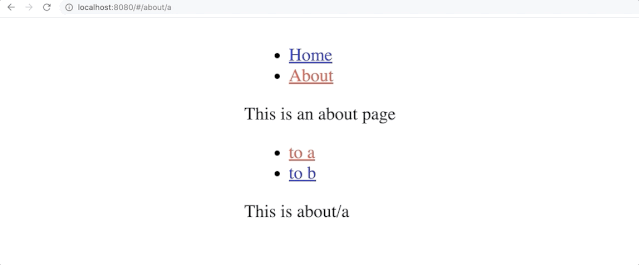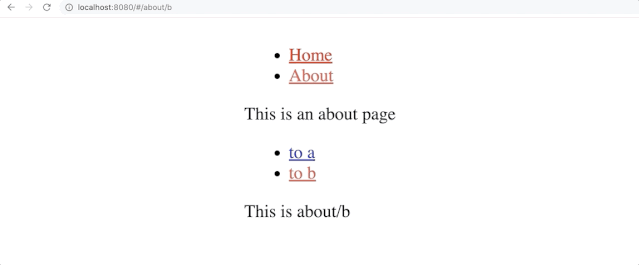
App页面中拥有Home和About俩个链接点击
Home会跳转到Home页面点击
About会跳转到About页面而
About又有to a和to b俩个链接,分别跳转到a和b页面
下面开始使用我们自己写的vue-router来实现上边展示的功能。
intall方法
vue-router使用方式如下:
import Vue from 'vue';
import VueRouter from '../my-router';
import Home from '../views/Home.vue';
import About from '@/views/About';
Vue.use(VueRouter);
const routes = [
{
path: '/home',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
component: About
}
];
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
});
export default router;
之后会在main.js中将router作为配置项传入:
import Vue from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
import router from './router';
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
由用法我们可以知道vue-router是一个类,并且它有一个静态方法install:
import install from '@/my-router/install';
class VueRouter {
constructor (options) {
}
init(app) {
}
}
VueRouter.install = install;
export default VueRouter;
install方法中会为所有组件添加$router以及$route属性,并且会全局注册router-view以及router-link组件。我们在install.js中来单独书写install的逻辑:
import RouterView from '@/my-router/components/view';
import RouterLink from '@/my-router/components/link';
const install = (Vue) => {
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
const { router } = this.$options;
// mount $router property for all components
if (router) {
// 用_rootRouter来存储根实例
this._rootRouter = this;
// 为根实例添加$router属性
this.$router = router;
// 在实例上定义响应式属性,但是这个API可能会发生变化,所以Vue并没有在文档中提供
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '$route', this.$router.history.current);
// 初始化路由
router.init(this);
} else {
this._rootRouter = this.$parent && this.$parent._rootRouter;
if (this._rootRouter) {
this.$router = this._rootRouter.$router;
// 在为$route赋值时,会重新指向新的地址,导致子组件的$route不再更新
// this.$route = this._rootRouter.$route;
Object.defineProperty(this, '$route', {
get () {
return this._rootRouter.$route;
}
});
}
}
}
});
Vue.component('RouterView', RouterView);
Vue.component('RouterLink', RouterLink);
};
在install方法中做了如下几件事:
为所有组件的实例添加
_rootRouter,值为根实例,方便获取根实例上的属性和方法在根实例执行
beforeCreate钩子时执行VueRouter实例的init方法为所有组件的实例添加
$router属性,值为VueRouter实例为所有组件添加
$route属性,值为当前的路由信息(之后会介绍它的由来)
hashchange事件
vue-router在hash模式下可以利用hash值的切换来渲染对应的组件,原理其实是利用页面地址hash值发生改变不会刷新页面,并且会触发hashchange事件。
在history目录下,新建hash.js来存放hash值变化,组件进行切换的逻辑:
import { getHash } from '@/my-router/util';
import { createRoute } from '@/my-router/create-matcher';
const ensureSlash = () => {
if (!location.hash) {
location.hash = '/';
}
};
class HashHistory {
constructor (router) {
this.router = router;
// 绑定this指向
this.onHashchange = this.onHashchange.bind(this);
// 默认hash值为'/'
ensureSlash();
}
listenEvent () {
window.addEventListener('hashchange', this.onHashchange);
}
onHashchange () {
}
}
export default HashHistory;
在VueRouter实例执行init方法时,监听hashchange事件:
class VueRouter {
constructor (options) {
this.history = new HashHistory(this);
}
init (app) {
// 第一次渲染时也需要手动执行一次onHashchange方法
this.history.onHashchange();
this.history.listenEvent();
}
}
在onHashchange方法中,需要根据当前页面地址的hash值来找到其对应的路由信息:
class HashHistory {
// some code ...
onHashchange () {
const path = getHash();
const route = this.router.match(path);
}
}
匹配路由信息
为了找到当前的路由信息,HashHistory中调用了VueRouter的match方法。match方法放到了create-matcher.js中来实现:
// create-matcher.js
export const createRoute = (route, path) => {
const matched = [];
// 递归route的所有父路由,生成matched数组,并和path一起返回,作为当前的路由信息
while (route) {
matched.unshift(route);
route = route.parent;
}
return {
path,
matched
};
};
function createMatcher (routes) {
const pathMap = createRouteMap(routes);
// need to get all matched route, then find current routes by matched and router-view
const match = (path) => {
const route = pathMap[path];
return createRoute(route, path);
};
return {
match
};
}
// create-route-map.js
function addRouteRecord (routes, pathMap, parent) {
routes.forEach(route => {
const { path, children, ...rest } = route;
// 拼接子路由path
const normalizedPath = parent ? parent.path + '/' + path : path;
// 将parent也放入到属性中,方便之后生成matched数组
pathMap[normalizedPath] = { ...rest, path: normalizedPath, parent };
if (children) {
// 继续遍历子路由
addRouteRecord(children, pathMap, route);
}
});
}
const createRouteMap = (routes, pathMap = {}) => {
addRouteRecord(routes, pathMap);
return pathMap;
};
createMatcher会通过createRouteMap生成hash值和路由的映射关系:
const pathMap = {
'/about': {
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
children: [
// ...
],
parent: undefined
}
// ...
}
这样我们可以很方便的通过hash值来获取路由信息。
最终我们调用match方法得到的路由信息结构如下:
{
"path": "/about/a",
"matched": [
{
"path": "/about",
"name": "About",
"component": About,
"children": [
{
"path": "a",
"name": "AboutA",
"component": A
},
{
"path": "b",
"name": "AboutB",
"component": B
}
]
},
// ...
]
}
需要注意的是对象中的matched属性,它里面存放的是当前hash匹配的所有路由信息组成的数组。在实现嵌套路由时会用到matched数组,因为嵌套路由本质上是router-view组件的嵌套,所以可以根据router-view在组件中的深度在matched中找到对应的匹配项,然后进行展示。
现在我们回到hashHistory的onHashchange方法,它会调用VueRouter实例的match方法,代码如下:
class VueRouter {
constructor (options) {
this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes);
this.history = new HashHistory(this);
}
init (app) {
this.history.onHashchange();
this.history.listenEvent();
}
match (path) {
return this.matcher.match(path);
}
}
在hashHistory中将其赋值给实例中的current属性:
class HashHistory {
constructor (router) {
// pass instance of VueRoute class, can call methods and properties of instance directly
this.router = router;
// 当前的路由信息,在current更新后,由于其不具有响应性,所以尽管值更新了,但是不会触发页面渲染
// 需要将其定义为响应式的数据
this.current = createRoute(null, '/');
this.onHashchange = this.onHashchange.bind(this);
ensureSlash();
}
listenEvent () {
window.addEventListener('hashchange', this.onHashchange);
}
onHashchange () {
const path = getHash();
const route = this.router.match(path);
this.current = route
}
}
为了方便用户访问当前路由信息,并且让其具有响应性,会通过Vue.util.defineReactive来为vue的根实例提供响应性的$route属性,并在每次页面初始化以及路径更新时更新$route:
class HashHistory {
constructor (router) {
// pass instance of VueRoute class, can call methods and properties of instance directly
this.router = router;
// 当前的路由信息,在current更新后,由于其不具有响应性,所以尽管值更新了,但是不会触发页面渲染
// 需要将其定义为响应式的数据
this.current = createRoute(null, '/');
this.onHashchange = this.onHashchange.bind(this);
}
// some code ...
onHashchange () {
const path = getHash();
const route = this.router.match(path);
// 将当前路由赋值给根实例,app会在router.init方法中进行初始化
this.router.app.$route = this.current = route
}
}
在install方法中为根实例定义$route属性,并将所有子组件实例的$route属性赋值为根实例的$route属性:
const install = (Vue) => {
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
const { router } = this.$options;
// mount $router property for all components
if (router) {
this._rootRouter = this;
this.$router = router;
// 定义响应性$route属性
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '$route', this.$router.history.current);
router.init(this);
} else {
this._rootRouter = this.$parent && this.$parent._rootRouter;
if (this._rootRouter) {
this.$router = this._rootRouter.$router;
// 这样直接赋值会导致引用刷新而无法改变$route
// this.$route = this._rootRouter.$route;
// 获取根组件实例的$route属性,其具有响应性
Object.defineProperty(this, '$route', {
get () {
return this._rootRouter.$route;
}
});
}
}
}
});
};
到这里,我们已经可以在地址切换时获取到对应的路由信息,接下来我们实现router-view来展示对应的组件。
实现router-view组件
router-view组件需要展示当前匹配的hash所对应的component,这里采用函数式组件来实现:
export default {
name: 'RouterView',
render (h) {
// 记录组件的深度,默认为0
let depth = 0;
const route = this.$parent.$route;
let parent = this.$parent;
// 递归查找父组件,如果父组件是RouterView组件,深度++
// 最终的深度即为路由的嵌套层数
while (parent) {
if (parent.$options.name === 'RouterView') {
depth++;
}
parent = parent.$parent;
}
// 根据深度从matched中找到对应的记录
const record = route.matched[depth];
if (record) { // /about会匹配About页面,会渲染About中的router-view,此时record为undefined
return h(record.component);
} else {
return h();
}
}
};
这里必须要为组件指定name属性,方便进行递归查找,进行深度标识。
到这里,我们为路由信息中添加的matched数组,终于派上了用场,其与router-view组件的深度depth进行巧妙结合,最终展示出了所有匹配到的路由组件。
实现router-link组件
router-link主要支持以下几个功能:
进行路由跳转
通过传入的
tag渲染不同标签为当前激活的
router-link添加router-link-active类名
在页面中vue-router也支持通过router-link来进行路由跳转,其实现比较简单:
export default {
props: {
to: {
type: String,
},
tag: {
type: String,
default: () => 'a'
}
},
computed: {
active () {
return this.$route.matched.map(item => item.path).includes(this.to);
}
},
methods: {
onClick () {
this.$router.push(this.to);
}
},
render () {
return (
{this.$slots.default}
);
}
};
router-link可以接受tag来渲染不同的标签,默认会渲染a标签。当点击router-link的时候,其内部会调用VueRouter实例的push方法:
class VueRouter {
// some code ...
push (path) {
location.hash = path;
}
// some code ...
}
// some code ...
push方法会切换页面的hash,当hash发生变化后,就会触发hashchange事件,执行事件处理函数onHashchange,重新通过path匹配对应的路由信息。
在代码中我们通过计算属性active来计算当前的router-link是否激活,需要注意的是当子路由激活时父路由也会激活。如果matched的path属性组成的数组中包含this.to,说明该router-link被激活。用户可以通过router-link-active类来设置激活样式。
路由beforeEach钩子
在日常开发中,经常会用到beforeEach全局前置守卫,让我们在进入页面之前执行一些逻辑:
// some code ....
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
});
// 在每次进入页面之前,都会先执行所有的beforeEach中的回调函数
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
console.log(1);
setTimeout(() => {
// 调用下一个回调函数
next();
}, 1000);
});
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
console.log(2);
next();
});
在每次进入页面之前,vue-router会先执行beforeEach中的回调函数,并且只有当用户调用回调函数中传入的next函数后,才会执行之后的beforeEach中的回调。
当所有beforeEach中的回调执行完毕后,调用next函数会更新路由信息,然后通过router-view来显示对应的组件。其实现如下:
// my-router/index.js
class VueRouter {
constructor (options) {
// some code ...
this.beforeEachs = [];
}
// cache in global, execute before get matched route record
beforeEach (fn) {
this.beforeEachs.push(fn);
}
}
// my-router/history/hash.js
class HashHistory {
// some code ...
onHashchange () {
const path = getHash();
const route = this.router.match(path);
// 当用户手动调用next时,会执行下一个beforeEach钩子,在所有的钩子执行完毕后,会更新当前路由信息
const next = (index) => {
const { beforeEachs } = this.router;
if (index === beforeEachs.length) {
//update route after executed all beforeEach hook
this.router.app.$route = this.current = route;
return;
}
const hook = beforeEachs[index];
hook(route, this.current, () => next(index + 1));
};
next(0);
}
}
上述代码的执行流程如下:
将
beforeEach中传入的函数放到全局的数组beforeEachs中在根据路径匹配最新的路由信息时,先执行
beforeEachs中存储的函数根据一个递增的
index来读取beforeEachs中的函数,执行时传入新的路由信息route、旧的路由信息this.current,以及需要用户调用的回调函数当用户调用回调后,
index+1继续执行next函数,进而执行beforeEachs中的下一个函数当执行完
beforeEachs中的所有函数后,为$route赋值最新的路由信息
庆祝一下????,这里我们已经完成了文章开头定下的所有目标!
结语
希望在读完文章之后,能让读者对vue-router的底层实现有更深入的了解,明白日常使用的API是怎么来的,从而更加熟练的使用vue-router。
最后,如果文章有帮到你的话,希望能点赞鼓励一下作者????。
最后
公众号后台回复:vue router,获取源码地址。
![]()