1 概述
本文演示了如何在Spring Boot中将Redis作为缓存使用,具体的内容包括:
- 环境搭建
- 项目搭建
- 测试
2 环境
RedisMySQLMyBatis Plus
3 Redis安装
Redis安装非常简单,以笔者的Manjaro为例,直接paru安装:
paru -S redisUbuntu、CentOS之类的都提供了软件包安装:
sudo apt install redis
sudo yum install redis如果想从源码编译安装:
wget http://download.redis.io/redis-stable.tar.gz
tar xvzf redis-stable.tar.gz
cd redis-stable
makeWindows以及其他系统的安装可以参考此处。
4 新建项目
新建项目,加入如下依赖:
Maven:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.4.2
Gradle:
implementation("com.baomidou:mybatis-plus-boot-starter:3.4.2")
implementation("mysql:mysql-connector-java:8.0.23")项目结构:
5 配置类
MyBatis Plus+Redis配置类:
@Configuration
@MapperScan("com.example.demo.dao")
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
}@Configuration
@AutoConfigureAfter(RedisAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(LettuceConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
return template;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration configuration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.serializeKeysWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer())
).serializeValuesWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer())
);
return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory).cacheDefaults(configuration).build();
}
} 重点说一下Redis配置类,这个类主要生成两个Bean:
RedisTemplate:简化Redis操作的数据访问类CacheManager:Spring的中央缓存管理器
其中RedisTemplate是一个模板类,第一个参数的类型是该template使用的键的类型,通常是String,第二个参数的类型是该template使用的值的类型,通常为Object或Seriazable。
setKeySerializer和setValueSerializer分别设置键值的序列化器。键一般为String类型,可以使用自带的StringRedisSerializer。对于值,可以使用自带的GenericJackson2RedisSerializer。
CacheManager的配置类似,就不重新说了。
6 实体类
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}7 持久层
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper {
} 8 业务层
@org.springframework.stereotype.Service
@Transactional
@RequiredArgsConstructor(onConstructor = @__(@Autowired))
public class Service {
private final UserMapper mapper;
@CachePut(value = "user",key = "#user.id")
public User save(User user){
User oldUser = mapper.selectById(user.getId());
if(oldUser == null){
mapper.insert(user);
return user;
}
if(mapper.updateById(user) == 1)
return user;
return oldUser;
}
@CacheEvict(value = "user",key = "#id")
public boolean delete(Integer id){
return mapper.deleteById(id) == 1;
}
@Cacheable(value = "user",key = "#id")
public User select(Integer id){
return mapper.selectById(id);
}
@Cacheable(value="allUser",key = "#root.target+#root.methodName")
//root.target是目标类,这里是com.example.demo.Service,root.methodName是方法名,这里是selectAll
public List selectAll(){
return mapper.selectList(null);
}
} 注解说明如下:
@CachePut:执行方法体再将返回值缓存,一般用于更新数据@CacheEvict:删除缓存,一般用于删除数据@Cacheable:查询缓存,如果有缓存就直接返回,没有缓存的话执行方法体并将返回值存入缓存,一般用于查询数据
三个注解都涉及到了key以及value属性,实际上,真正的存入Redis的key是两者的组合,比如:
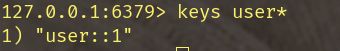
@Cacheable(value="user",key="#id")则存入的Redis中的key为:
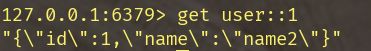
而存入对应的值为方法返回值序列化后的结果,比如如果返回值为User,则会被序列化为:
9 配置文件
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username: root
password: 123456
redis:
database: 0
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
logging:
level:
com.example.demo: debugspring.redis.database指定数据库的索引,默认为0,host与port分别指定主机(默认本地)以及端口(默认6379)。
也就是说,简单配置的话可以完全省略Redis相关配置,仅指定数据库连接url、用户名以及密码:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username: root
password: 123456
logging:
level:
com.example.demo: debug10 启动Redis
10.1 启动Redis服务器
Redis服务器启动需要一个配置文件,默认位置为/etc/redis.conf(源码编译安装的话在源文件夹内),建议先复制一份:
cp /etc/redis.conf ~/Desktop/默认的配置文件为单机Redis配置,端口6379,redis-server可以直接运行:
sudo redis-server redis.conf10.2 连接服务器
连接可以通过自带的redis-cli命令:
redis-cli -h localhost -p 6379默认情况下可以直接使用
redis-cli连接。
基本操作:
keys *:查询所有键get key:查询key所对应的值flushall:清空所有键
11 测试
@SpringBootTest
@RequiredArgsConstructor(onConstructor = @__(@Autowired))
class DemoApplicationTests {
private final Service service;
@Test
void select() {
service.select(1);
service.select(1);
}
@Test
void selectAll(){
service.selectAll();
service.selectAll();
}
@Test
void delete(){
service.delete(1);
}
@Test
void save(){
User user = new User(1,"name1");
service.save(user);
service.select(user.getId());
user.setName("name2");
service.save(user);
service.select(user.getId());
}
}执行其中的select,会发现MyBatis Plus只有一次select的输出,证明缓存生效了:
而把缓存注解去掉后,会有两次select输出:
其它测试方法就不截图了,原理类似。
12 附录:Kotlin中的一些细节
12.1 String数组
其实@Cacheable/@CacheEvict/@CachePut中的value都是String [],在Java中可以直接写上value,在Kotlin中需要[value]。
12.2 @class
序列化到Redis时,实体类会被加上一个@class字段:
这个标识供Jackson反序列化时使用,笔者一开始的实体类实现是:
data class User(var id:Int?=null, var name:String="")但是序列化后不携带@class字段:
在反序列化时直接报错:
Could not read JSON: Missing type id when trying to resolve subtype of [simple type, class java.lang.Object]: missing type id property '@class'
at [Source: (byte[])"{"id":1,"name":"name2"}"; line: 1, column: 23]; nested exception is com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.exc.InvalidTypeIdException: Missing type id when trying to resolve subtype of [simple type, class java.lang.Object]: missing type id property '@class'
at [Source: (byte[])"{"id":1,"name":"name2"}"; line: 1, column: 23]解决方法有两个:
- 手动添加
@class字段 - 将实体类设为
open
12.2.1 手动添加@class
准确来说并不是手动添加,而是让注解添加,需要添加一个类注解@JsonTypeInfo:
@JsonTypeInfo(use = JsonTypeInfo.Id.CLASS)
data class User(var id:Int?=null, var name:String="")该注解的use用于指定类型标识码,该值只能为JsonTypeInfo.Id.CLASS。
12.2.2 将实体类设置为open
在Java中,实体类没有任何额外配置,Redis序列化/反序列化一样没有问题,是因为值序列化器GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer,该类会自动添加一个@class字段,因此不会出现上面的问题。
但是在Kotlin中,类默认不是open的,也就是无法添加@class字段,因此便会反序列化失败,解决方案是将实体类设置为open:
open class User(var id:Int?=null, var name:String="")但是缺点是不能使用data class了。
13 参考源码
Java版:
Kotlin版: