C++中set/unordered_set 自定义比较规则
- set
-
- set外部比较器
- set内部比较器
- unordered_set
-
- unordered_set外部比较器
- unordered_set内部比较器
- 代码
以 Heroes 类为例进行演示 如何自定义set/unordered_set内外部比较器 ,类 Heroes定义如下:
class Heroes {
public:
Heroes(string _name, int _age) :name(_name), age(_age) {
}
private:
string name;//私有变量 name
int age;//私有变量 age
};
set
现在我们需要使用 set 容器对Heroes类的一些对象进行存储,我们知道set的底层实现是RB-Tree(红黑树),因此如何对这些对象进行排序就成了我们必须手动完成的事情了。
下面是set容器用到的参数列表:
template <class _Kty, class _Pr = less<_Kty>, class _Alloc = allocator<_Kty>>
其中提供了默认的排序规则less:
// STRUCT TEMPLATE less
template <class _Ty = void>
struct less {
_CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef _Ty _FIRST_ARGUMENT_TYPE_NAME;
_CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef _Ty _SECOND_ARGUMENT_TYPE_NAME;
_CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef bool _RESULT_TYPE_NAME;
constexpr bool operator()(const _Ty& _Left, const _Ty& _Right) const {
return _Left < _Right;
}
};
less中对 () 进行了重载,因此我们也可以仿照它定义比较器。
set外部比较器
class externalCmp{
public:
bool operator()(const Heroes& a, const Heroes& b) const{
return a.age > b.age;//set内部按照自定义规则排序
}
};
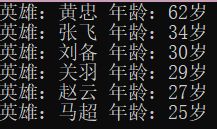
该比较是将Heroes对象按照年龄从大到小存储。
外部比较器使用示例:
//使用 外部比较器 按照既定规则排序
void set_方法1() {
set<Heroes, externalCmp> hero;
hero.insert({
"刘备",30 });
hero.insert({
"关羽", 29 });
hero.insert({
"张飞", 34 });
hero.insert({
"黄忠", 62 });
hero.insert({
"马超", 25 });
hero.insert({
"赵云", 27 });
for (auto& it : hero) {
cout << it << endl;
}
}
注意:由于Heroes类中的成员属性都设置为了私有,这里用到自己定义的类需要在Heroes类中形成为友元关系。(或者将属性改为public)
特别的,细心的小伙伴是不是发现输出的格式有点意外,没错,这里对 << 进行了重载:
//重载 << 操作符,让其直接输出 Heroes 对象信息
ostream& operator<<(ostream& O,const Heroes& os) {
O <<"英雄:" <<os.name <<" 年龄:"<< os.age<<"岁";
return O;
}
set内部比较器
在自定义类中对 < 进行重载即可。
//内部重载 < 自定义排序规则
constexpr bool operator<(const Heroes& hero)const {
return age<hero.age;
}
效果与上面的外部比较器一致,就不多加赘述了。
unordered_set
与set不同的是,unordered_set底层是以哈希表为基础的一种容器,让我们看看头文件中对它的定义:
template <class _Kty, class _Hasher = hash<_Kty>, class _Keyeq = equal_to<_Kty>, class _Alloc = allocator<_Kty>>
以上为unordered_set()的参数列表,其中后面三个均为可缺省参数,默认为我们提供了 hash<_Kty>、equal_to<_Kty>(_Kty为类模板)
hash<类型> 的作用是根据传递的参数通过哈希函数生成下标
在头文件中定义分别如下:
// STRUCT TEMPLATE hash
template <class _Kty>
struct hash
: _Conditionally_enabled_hash<_Kty,
!is_const_v<_Kty> && !is_volatile_v<_Kty> && (is_enum_v<_Kty> || is_integral_v<_Kty> || is_pointer_v<_Kty>)> {
// hash functor primary template (handles enums, integrals, and pointers)
static size_t _Do_hash(const _Kty& _Keyval) noexcept {
return _Hash_representation(_Keyval);
}
};
unordered_set外部比较器
我们可以仿照其在外部定义一个类实现hash功能:
class hash_Heroes {
public:
size_t operator()(const Heroes& hero)const {
hash<string> hs;
return hs(hero.name);//哈希值由对象的name属性决定
}
};
**equal_to<_Kty>**则定义的是如何判断两个对象是否相同。
同样我们找出其在库文件中的定义:
// STRUCT TEMPLATE equal_to
template <class _Ty = void>
struct equal_to {
_CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef _Ty _FIRST_ARGUMENT_TYPE_NAME;
_CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef _Ty _SECOND_ARGUMENT_TYPE_NAME;
_CXX17_DEPRECATE_ADAPTOR_TYPEDEFS typedef bool _RESULT_TYPE_NAME;
constexpr bool operator()(const _Ty& _Left, const _Ty& _Right) const {
return _Left == _Right;
}
};
不难发现函数中仅是对 **()**进行了重载,因此我们仿照其定义自己的判定规则:
class equal_to_Heroes {
public:
bool operator()(const Heroes& hero1, const Heroes& hero2)const {
return hero1.name == hero2.name && hero1.age== hero2.age;
}//只有当姓名与年龄均相同时破判定为相同对象
};
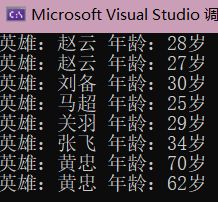
外部比较器使用示例:
//传入指定的模板参数,告诉容器如何哈希一个Heroes对象,以及如何比较两个Heroes对象是否相同
void unordered_set方法1() {
unordered_set<Heroes, hash_Heroes, equal_to_Heroes> hero3;
hero3.insert({
"刘备",30 });
hero3.insert({
"关羽", 29 });
hero3.insert({
"张飞", 34 });
hero3.insert({
"黄忠", 62 });
hero3.insert({
"马超", 25 });
hero3.insert({
"赵云", 27 });
hero3.insert({
"赵云", 28 });
hero3.insert({
"黄忠", 70 });
for (auto& it : hero3) {
cout << it << endl;
}
}
unordered_set内部比较器
这里仅对 equal_to<> 内部进行修改:重载比较运算符 == 即可:
//内部重载 == 自定义哈希集合如何判断对象为相同
const bool operator==(const Heroes& hero)const {
return name == hero.name && age == hero.age;
}
代码
#include