3.14 Java AQS原理解析
3.14 AQS
AQS是Java中AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的简称,AQS实在是太有名了,以至于它的全称经常被遗忘,先看看AQS是什么。
Provides a framework for implementing blocking locks and related synchronizers (semaphores, events, etc) that rely on first-in-first-out (FIFO) wait queues. This class is designed to be a useful basis for most kinds of synchronizers that rely on a single atomic {@code int} value to represent state.1
AQS通过一个先进先出的等待队列提供了一个实现锁和相应同步的框架。AQS依靠一个原子型数值表示状态来搭建同步操作的基础。
3.14.1 AQS继承关系
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS)继承了AbstractOwnableSynchronizer(AOS),先来看下AOS是个啥。
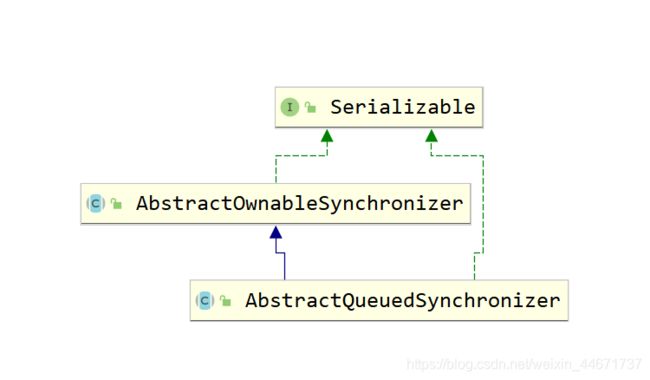
3.14.2 AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
AOS只有一个私有的exclusiveOwnerThread线程属性,表示当前运行的独占的线程,它的子类只能通过受保护的get和set方法访问该属性。
public abstract class AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3737899427754241961L;
protected AbstractOwnableSynchronizer() {
}
private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread;
protected final void setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread thread) {
exclusiveOwnerThread = thread;
}
protected final Thread getExclusiveOwnerThread() {
return exclusiveOwnerThread;
}
}
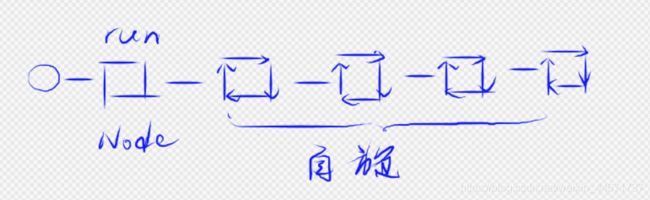
3.14.3 AQS CLH队列
CLH队列是一种自旋锁队列,自旋锁队列是什么含义呢?当头部节点线程在运行的时候,它的后续节点线程都处于一种自旋的状态。
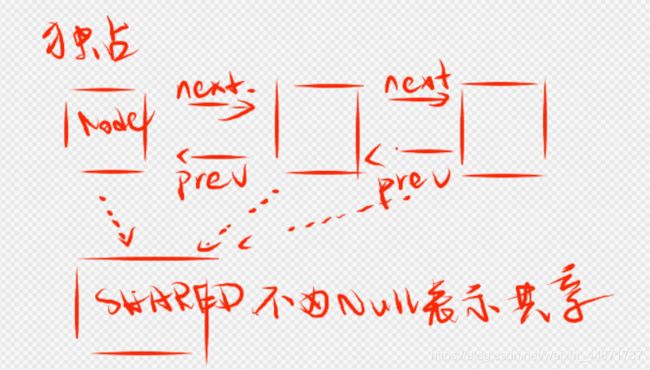
CLH队列Node源码,其实内部很简单,一个双向链表,每个节点有一个线程和表示该线程的状态的waitStatus。还有惟一一个非volatile修饰的nextWaiter属性,当该属性Node为该类属性SHARED节点时,表示共享,这个SHARED节点上的线程都是可共享的,不存在排他性,所以不需要用volatile关键词修饰。
static final class Node {
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
/** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled */
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
/** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
/** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */
static final int CONDITION = -2;
/**
* waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should
* unconditionally propagate
*/
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
volatile int waitStatus;
* head only as a result of successful acquire. A
* cancelled thread never succeeds in acquiring, and a thread only
* cancels itself, not any other node.
*/
volatile Node prev;
volatile Node next;
volatile Thread thread;
Node nextWaiter;
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
Node() {
// Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker
}
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) {
// Used by addWaiter
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) {
// Used by Condition
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
3.14.4 AQS组成
双向链表,一个指向头部,一个指向尾部,再加一个state表示属性。
/**
* Head of the wait queue, lazily initialized. Except for
* initialization, it is modified only via method setHead. Note:
* If head exists, its waitStatus is guaranteed not to be
* CANCELLED.
*/
private transient volatile Node head;
/**
* Tail of the wait queue, lazily initialized. Modified only via
* method enq to add new wait node.
*/
private transient volatile Node tail;
/**
* The synchronization state.
*/
private volatile int state;
3.14.5 源码方法解析
添加新Node进入CLH队列(尾插法),添加新节点到尾部。
private Node enq(final Node node) {
//循环直到尾节点不为null,添加到尾部
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) {
// Must initialize
//当前head为null比较并更新成新Node,是Unsafe提供的方法,可以看出头Node不存线程。
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
addWaiter方法
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
//当尾节点不为null,直接入队列
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
//当尾节点为null,循环先构建head节点然后入队列
enq(node);
return node;
}
acquireQueued方法
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//tryAcquire(arg)抽象方法,子类具体实现
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
//成功,新的头节点
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
3.14.6 小结
AQS中还有很多方法没有提到,实在是肝不动了,AQS作为Java源码中最难的一块笔者在写这点的时候也是很担心写错,虽然看了很多遍,但很多细节还是不了解,本来在写锁之前就该先说AQS,不过AQS确实太难了,先知道锁再去看AQS反而更容易理解。
JAVA源码AQS解释 ↩︎