Android本地开发武器库概览
Android本地开发支持简史
Android 1.0的时代,没有提供对于C/C++开发本地Android代码的支持,尽管Android系统本身使用了大量的C++做底层开发。
第一个里程碑 - 支持jni开发so库 (Android 1.5)
Android第一次支持本地开发是在Android 1.5版本,对应Android API level 3。这一版本,有了正式的Android NDK的支持,可以通过jni写so库的方式,供Android应用来调用。
Android 1.6增加了对于OpenGL ES 1.x的支持
Android 2.0开始支持OpenGL ES 2.0
第二个里程碑 - 支持本地应用开发 (Android 2.3)
Android 2.3是一个重要的版本,这一版本增加了完全用C++写本地应用的接口。
我们看看这一版提供了什么API头文件:
- native_activity.h
- looper.h
- input.h
- keycodes.h
- sensor.h
- rect.h
- window.h
- native_window.h
- native_window_jni.h
- configuration.h
- asset_manager.h
- storage_manager.h
- obb.h
直至今天,Android 7.0,API level 24的时代,上面这些仍然构成了我们这系列教程的主要内容。
同时,Android 2.3还开始支持EGL接口。
Android 4.0开始支持OpenMAX AL库。
Android 4.3开始支持Open GL ES 3.0版
Android 6.0开始支持trace库
Android 7.0开始支持Vulkan, Camera, Choreographer和Multinework库,同时对Open GL ES 3.2的支持
本地应用和窗口
本地应用的框架
首先,写native应用需要一个本地应用的框架的支持。
Java应用需要写一个manifest.xml,我们也入乡随俗需要写一个,我们先看一个NDK sample的例子:
因为我们没有写Java代码,所以需要将android:hasCode值设为false.
可以使用NDK中的android_native_app_glue定义的类来对本地API进行封装,我们来看一下,先认识一下后面我们会介绍的几个类:
struct android_app {
// The application can place a pointer to its own state object
// here if it likes.
void* userData;
// Fill this in with the function to process main app commands (APP_CMD_*)
void (*onAppCmd)(struct android_app* app, int32_t cmd);
// Fill this in with the function to process input events. At this point
// the event has already been pre-dispatched, and it will be finished upon
// return. Return 1 if you have handled the event, 0 for any default
// dispatching.
int32_t (*onInputEvent)(struct android_app* app, AInputEvent* event);
// The ANativeActivity object instance that this app is running in.
ANativeActivity* activity;
// The current configuration the app is running in.
AConfiguration* config;
// This is the last instance's saved state, as provided at creation time.
// It is NULL if there was no state. You can use this as you need; the
// memory will remain around until you call android_app_exec_cmd() for
// APP_CMD_RESUME, at which point it will be freed and savedState set to NULL.
// These variables should only be changed when processing a APP_CMD_SAVE_STATE,
// at which point they will be initialized to NULL and you can malloc your
// state and place the information here. In that case the memory will be
// freed for you later.
void* savedState;
size_t savedStateSize;
// The ALooper associated with the app's thread.
ALooper* looper;
// When non-NULL, this is the input queue from which the app will
// receive user input events.
AInputQueue* inputQueue;
// When non-NULL, this is the window surface that the app can draw in.
ANativeWindow* window;
// Current content rectangle of the window; this is the area where the
// window's content should be placed to be seen by the user.
ARect contentRect;
// Current state of the app's activity. May be either APP_CMD_START,
// APP_CMD_RESUME, APP_CMD_PAUSE, or APP_CMD_STOP; see below.
int activityState;
// This is non-zero when the application's NativeActivity is being
// destroyed and waiting for the app thread to complete.
int destroyRequested;
// -------------------------------------------------
// Below are "private" implementation of the glue code.
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
int msgread;
int msgwrite;
pthread_t thread;
struct android_poll_source cmdPollSource;
struct android_poll_source inputPollSource;
int running;
int stateSaved;
int destroyed;
int redrawNeeded;
AInputQueue* pendingInputQueue;
ANativeWindow* pendingWindow;
ARect pendingContentRect;
};
我们看下这个结构中都用到了什么:
- ANativeActivity: 它是本地应用中对应于android.app.NativeActivity的代理类,定义于android/native_activity.h
- AConfiguration: 处理配置项。定义于android/configuration.h
- ALooper: 对应于Java中的Looper,用于处理消息队列,每个线程只能有一个. 定义于android/looper.h
- AInputQueue: 输入事件的队列,定义于android/input.h中
- ANativeWindow: 处理窗口的类,定义于android/native_window.h中
- ARect:代表一个矩形,定义于android/rect.h中
武器库鸟瞰
native应用比起Java应用来,跟Android版本的相关性更高一些。
所以,这些API都是根据平台版本号分成不同的目录的。
下面介绍的android下面的API,对应于Android源码中的frameworks/native/include/中。
在NDK中,以r13b为例,Android 7.0,也就是API 24的头文件位于:android-ndk/r13b/platforms/android-24/arch-arm64/usr/include/中。
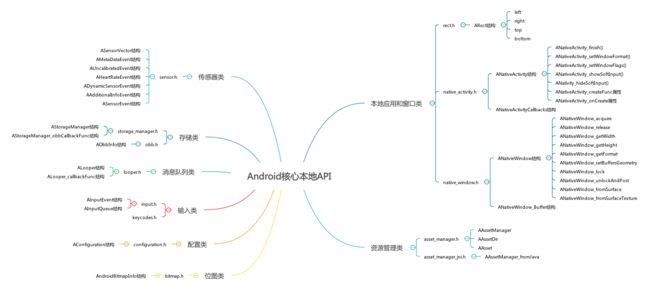
我们首先通过一张图来看看Android为我们提供了哪些API:
本地应用和本地窗口类
主要包括下面的头文件:
- android/native_activity.h
- ANativeActivity结构:对应android.app.NativeActivity
- ANativeActivityCallback结构,处理回调
- android/native_window.h
- ANativeWindow结构
- ANativeWindow_Buffer结构
- android/rect.h
- ARect结构:有left, top, right, bottom四个属性的矩阵的抽象
- android/native_window_jni.h: 辅助类
- android/window.h: 辅助类
资源管理类
- android/asset_manager.h
- AAssetManager结构
- AAssetDir结构
- AAsset结构
- android/asset_manager_jni.h
- AAssetManager_fromJava结构
位图类
- bitmap.h
- AndroidBitmapInfo结构
配置类
- configuration.h
- AConfiguration结构
输入类
- input.h
- AInputEvent结构
- AInputQueue结构
- keycodes.h:定义了键码的enum
Looper类
- android/looper.h
- ALooper结构
- ALooper_callbackFunc结构
存储类
- android/storage_manager.h
- AStorageManager结构
- AStorageManager_obbCallbackFunc结构
- android/obb.h
- AObbInfo结构
传感器类
- android/sensor.h
- ASensorVector结构
- AMetaDataEvent结构
- AUncalibratedEvent结构
- AHeartRateEvent结构
- ADynamicSensorEvent结构
- AAdditionalInfoEvent结构
- ASensorEvent结构