三种搜索求解八数码 问题的效率对比
- 问题描述
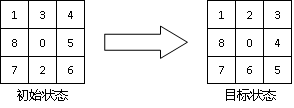
以宽度优先搜索、深度优先搜索以及A*算法求解八数码问题。每一种算法都设置相同的初始状态和目标状态,针对搜索策略,求得问题的解,并比较搜索算法的性能。
针对下列两种八数码对算法进行对比
(1)
(2)
- 基本原理
- 图搜索算法介绍
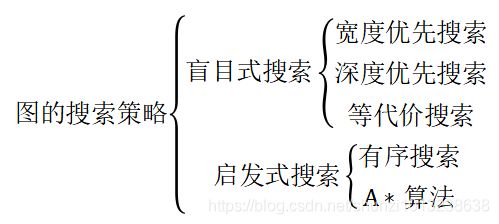
图搜索控制策略是指在图中寻找相应路径的方法。图中的每个节点对应一个状态,每条连线对应一个操作符。图的搜索策略主要有以下几种:
图的搜索策略
各个搜索算法的特点如下:
盲目搜索:没有启发信息的一种搜索形式,不需要重排open表,效率低,耗费过多的计算空间与时间,一般只适用于求解比较简单的问题。
启发式搜索:通过启发式函数来传递启发信息,需要重排open表、每一步能选择最有希望的节点进行扩展、效率高。
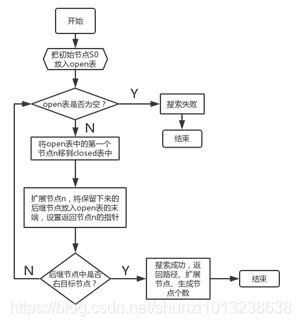
图的搜索过程主要如下:
(1)把初始节点S0放入OPEN表,并建立目前只包含S0的图,记为G。
(2)检查OPEN表是否为空,若为空则问题无解,退出。
(3)把OPEN表的第一个节点取出放入CLOSED表,记该节点为n。
(4)考察n是否为目标节点.如是,则问题得解,退出。
(5)扩展节点n,生成一组子节点.把其中不是节点n先辈的那些节点记作集合M,并把这些节点最为节点n的子节点加入G中。
(6)针对M中子节点的不同情况,分别进行处理。
1.对于那些未曾在G中出现过的M成员设置一个指向父节点(即n)的指针,并把它们放入OPEN表。
2.对于那些先前已在G中出现过的M成员,确定是否需要修改它指向父节点的指针。
3.对于那些先前已在G中出现并且已经扩展了的M成员,确定是否需要修改其后继节点指向父节点的指针。
(7)按某种搜索策略对OPEN表中的节点进行排序。
(8)转第(2)步。
图搜索过程中open表用于记录还没有扩展的节点,存放刚生成的节点。Closed表用于记录扩展过的节点。且每个表示状态的节点结构中必须有指向父节点的指针,以便寻找最后的路径。
- 宽度优先搜索
以数字零为研究对象,由此可知在每一步移动中,数字零的移动方向可能有左、上、下、右四个方向。在扩展节点时需要判断数字零是否能往这四个方向移动。通过分析可知,若该节点是通过其父节点中数字零向左(上、下、右)移动得到的,则在扩展该节点时数字零不能向右(下、上、左)移动,即通过该节点扩展出来节点是否保留的条件是扩展出来的节点是否与其父节点的父节点相同,若不相同则保留,否则舍去。
然后判断每次扩展出来的节点中是否右目标节点,若有则停止扩展、输出路径,否则将扩展的节点加入到open表的末端。
- 深度优先搜索
深度优先搜索在节点扩展时的方法与宽度优先搜索一样。唯一不同的是扩展出来的节点中若没有目标节点则把这些节点加入到open表的始端。
为了防止扩展出来更多无用的节点,设置一个扩展最大深度maxdepth。若超过此深度则舍弃扩展出来的节点。
- 启发式搜索(A*算法)
A*算法在扩展节点时的方法与宽度、深度优先搜索算法一致。唯一不同的是根据启发函数的信息对open表进行重排,这样做大大减少了对无用节点的扩展。
对open表进行重排即是按照估价函数H(n)的值从小到大的顺序重新排列open表中每个节点的顺序。这样可以保证每一次扩展的节点都是open表中最有希望的节点。
- 实验算法流程
1.宽度优先搜索
图1 宽度优先搜索算法流程图
2.深度优先搜索
图2 深度优先搜索算法流程图
3.启发式搜索(A*算法)
图3 A*算法流程图
- 实验结果
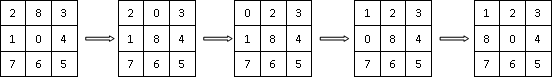
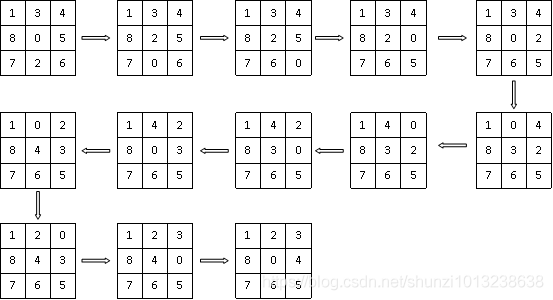
(1)三种算法对第一种八数码最终返回的路径图都如下图4所示:
图4 路径图
如图5所示,可得每种算法得到的扩展节点个数。其中A*算法所用的估价函数为节点n中不在目标状态中相应位置的数码个数。
| 算法 |
BFS |
DFS |
A* |
| 扩展节点 |
16 |
9 |
5 |
| 生成节点 |
26 |
17 |
11 |
对比结果可知,当从初始状态到目标状态所能达到的最短距离较小时,三种算法均能找到这条最短路径,其中启发式搜索能够大大减少无用节点的扩展
(2)BFS、A*算法对第二种八数码最终返回的路径图如下图5所示:
图5 路径图
DFS算法对第二种八数码最终返回的路径图如下图6所示:
图6 路径图
如图5图6所示,可得每种算法得到的扩展节点个数。
| 算法 |
BFS |
DFS |
A* |
| 扩展节点 |
69 |
3920 |
7 |
| 生成节点 |
132 |
7134 |
15 |
对比结果可知,当从初始状态到目标状态所能达到的最短距离较大时,BFS、A*算法能够找到这条最短路径,而DFS算法没有找到这条最短路径,并造成较大的资源浪费,A*算法仍然是最节省资源的搜索方法。
- 核心代码展示
import numpy as np
end = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [8, 0, 4], [7, 6, 5]]) # 最终节点
# 宽度优先搜索求解八数码问题
class BFS:
def __init__(self, arr, parent=None):
self.arr = arr
self.end = end
self.parent = parent
# 按顺序定义四个移动的方向
self.directions = ['left', 'up', 'right', 'down']
self.space = 0
# 打印路线
def showLine(self):
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
print(self.arr[i, j], end=' ')
print("\n")
print('------>')
return
# 获取零所在的位置
def getZeroPos(self):
row, col = np.where(self.arr == self.space)
return row, col
# 扩展节点
def generateSubstates(self):
subStates = []
flag = 0 # flag用来判断该节点是否有后继节点
row, col = self.getZeroPos()
for direction in self.directions:
if 'left' == direction and col > 0:
# 判断零是否能向左移动
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row, col - 1] = s[row, col - 1], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
# 判断扩展出来的新节点是否与其父节点的父节点相同
# 若不相同则扩展,否则不扩展
news = BFS(s, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
news = BFS(s, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
if 'up' == direction and row > 0:
# 判断零是否能向上移动
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row - 1, col] = s[row - 1, col], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
news = BFS(s, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
news = BFS(s, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
if 'down' == direction and row < 2:
# 判断零是否能下左移动
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row + 1, col] = s[row + 1, col], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
news = BFS(s, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
news = BFS(s, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
if 'right' == direction and col < 2:
# 判断零是否能向右移动
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row, col + 1] = s[row, col + 1], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
news = BFS(s, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
news = BFS(s, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
return subStates, flag
# 搜索路径
def search(self):
opentable = [] # open表
closedtable = [] # closed表
opentable.append(self) # 将起始节点加入open表
generatednodes = 0
expendednodes = 0 # 生成节点个数、扩展节点个数
while len(opentable):
n = opentable.pop(0)
closedtable.append(n)
subStates, flag = n.generateSubstates() # 节点n扩展出来的子节点
generatednodes = generatednodes + len(subStates)
if flag:
expendednodes += 1
path = []
for s in subStates:
if (s.arr == s.end).all():
# 判断该子节点是否为目标节点
# 若是则返回路径
path.append(s)
while s.parent and s.parent != s0:
path.append(s.parent)
s = s.parent
path.reverse()
return path, generatednodes, expendednodes
opentable.extend(subStates)
return None, None, None
# 深度优先搜索求解八数码问题
class DFS:
def __init__(self, arr, depth, parent=None):
self.arr = arr
self.end = end
self.parent = parent
self.maxdepth = 15
self.directions = ['left', 'up', 'down', 'right']
self.space = 0
self.depth = depth
def getZeroPos(self):
row, col = np.where(self.arr == self.space)
return row, col
def showLine(self):
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
print(self.arr[i, j], end=' ')
print("\n")
print('------>')
return
def generateSubstates(self):
subStates = []
flag = 0
row, col = self.getZeroPos()
for direction in self.directions:
if 'left' == direction and col > 0:
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row, col - 1] = s[row, col - 1], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
news = DFS(s, self.depth + 1, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
news = DFS(s, self.depth + 1, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
if 'up' == direction and row > 0:
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row - 1, col] = s[row - 1, col], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
news = DFS(s, self.depth + 1, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
news = DFS(s, self.depth + 1, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
if 'down' == direction and row < 2:
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row + 1, col] = s[row + 1, col], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
news = DFS(s, self.depth + 1, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
news = DFS(s, self.depth + 1, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
if 'right' == direction and col < 2:
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row, col + 1] = s[row, col + 1], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
news = DFS(s, self.depth + 1, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
news = DFS(s, self.depth + 1, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
return subStates, flag
def search(self):
opentable = []
closedtable = []
opentable.append(self)
generatednodes = 0;
expendednodes = 0
while len(opentable):
n = opentable.pop(0)
closedtable.append(n)
subStates, flag = n.generateSubstates()
generatednodes = generatednodes + len(subStates)
if flag:
expendednodes += 1
path = []
for s in subStates:
if (s.arr == s.end).all():
path.append(s)
while s.parent and s.parent != s0:
path.append(s.parent)
s = s.parent
path.reverse()
return path, generatednodes, expendednodes
if s.depth < s.maxdepth:
# 判断是否超过最大搜索深度
# 若没有则将扩展的子节点加入open表头
subStates.reverse()
for node in subStates:
opentable.insert(0, node)
return None, None, None
# A*算法解决八数码难题
class Astar:
def __init__(self, arr, depth, f, parent=None):
self.arr = arr
self.end = end
self.depth = depth
self.parent = parent
self.space = 0
self.f = f # 估价函数的值
self.flag = 1
self.directions = ['left', 'up', 'right', 'down']
def h1(self, node):
# 第一种估价函数表示为节点n中不在目标状态中相应位置的数码个数
arr1 = node - Astar.end
h = len(arr1[arr1 != 0])
return h
def h2(self, node):
# 第二种估价函数表示为节点n的每一数码与其目标位置的距离总和
h = 0
for i in range(0, 9):
row1, col1 = self.getZeroPos(node, i)
row2, col2 = self.getZeroPos(self.end, i)
dis = abs(row1 - row2) + abs(col1 - col2)
h = h + dis
return h
def getZeroPos(self, node, space=0):
row, col = np.where(node == space)
return row, col
def showLine(self):
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
print(self.arr[i, j], end=' ')
print("\n")
print('------>')
return
@staticmethod
def sortOpentable(opentable):
# 对open表按估价函数f值的大小进行重排
i = len(opentable) - 1
while i > 0:
for j in range(0, i):
if opentable[j].f > opentable[j + 1].f:
opentable[j], opentable[j + 1] = opentable[j + 1], opentable[j]
i -= 1
return opentable
def generateSubstates(self):
subStates = [];
flag = 0
row, col = self.getZeroPos(self.arr)
for direction in self.directions:
if 'left' == direction and col > 0:
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row, col - 1] = s[row, col - 1], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
if self.flag == '1':
# 计算该节点的评估函数值
f = self.depth + self.h1(s) + 1
else:
f = self.depth + self.h2(s) + 1
news = Astar(s, self.depth + 1, f, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
if self.flag == '1':
f = self.depth + self.h1(s) + 1
else:
f = self.depth + self.h2(s) + 1
news = Astar(s, self.depth + 1, f, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
if 'up' == direction and row > 0:
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row - 1, col] = s[row - 1, col], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
if self.flag == '1':
f = self.depth + self.h1(s) + 1
else:
f = self.depth + self.h2(s) + 1
news = Astar(s, self.depth + 1, f, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
if self.flag == '1':
f = self.depth + self.h1(s) + 1
else:
f = self.depth + self.h2(s) + 1
news = Astar(s, self.depth + 1, f, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
if 'down' == direction and row < 2:
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row + 1, col] = s[row + 1, col], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
if self.flag == '1':
f = self.depth + self.h1(s) + 1
else:
f = self.depth + self.h2(s) + 1
news = Astar(s, self.depth + 1, f, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
if self.flag == '1':
f = self.depth + self.h1(s) + 1
else:
f = self.depth + self.h2(s) + 1
news = Astar(s, self.depth + 1, f, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
if 'right' == direction and col < 2:
s = self.arr.copy()
s[row, col], s[row, col + 1] = s[row, col + 1], s[row, col]
if self.parent != None:
arr2 = s - self.parent.arr
if len(arr2[arr2 == 0]) < 9:
if self.flag == '1':
f = self.depth + self.h1(s) + 1
else:
f = self.depth + self.h2(s) + 1
news = Astar(s, self.depth + 1, f, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
else:
if self.flag == '1':
f = self.depth + self.h1(s) + 1
else:
f = self.depth + self.h2(s) + 1
news = Astar(s, self.depth + 1, f, parent=self)
subStates.append(news)
flag += 1
return subStates, flag
def search(self):
opentable = []
closedtable = []
opentable.append(self)
generatednodes = 0
expendednodes = 0
while len(opentable):
n = opentable.pop(0)
closedtable.append(n)
subStates, flag = n.generateSubstates()
generatednodes = generatednodes + len(subStates)
if flag:
expendednodes += 1
path = []
for s in subStates:
if (s.arr == s.end).all():
print("%d" % generatednodes)
path.append(s)
while s.parent and s.parent != s0:
path.append(s.parent)
s = s.parent
path.reverse()
return path, generatednodes, expendednodes
opentable.extend(subStates)
opentable = self.sortOpentable(opentable)
return None, None, None
if __name__ == "__main__":
start = np.array([[1, 3, 4], [8, 0, 5], [7, 2, 6]]) # 起始节点
s0 = BFS(start)
bfs = BFS(start)
path, generatednodes, expendednodes = bfs.search()
for node in path:
node.showLine()
print("BFS生成的节点个数为:%d" % generatednodes)
print("BFS扩展的节点个数为:%d" % expendednodes)
s0 = DFS(start, 1)
bfs = DFS(start, 1)
path, generatednodes, expendednodes = bfs.search()
for node in path:
node.showLine()
print("DFS生成的节点个数为:%d" % generatednodes)
print("DFS扩展的节点个数为:%d" % expendednodes)
s0 = Astar(start, 0, 5)
AStar = Astar(start, 0, 5)
path, generatednodes, expendednodes = AStar.search()
for node in path:
node.showLine()
print("A*生成的节点个数为:%d" % generatednodes)
print("A*扩展的节点个数为:%d" % expendednodes)