在 Java8 中,HashMap 由数组+链表+红黑树组成的。扩容时,数组容量翻倍,数组中每一个桶中的多个节点(链结构或树结构)都需要 rehash 迁移到新的数组中去。
本文通过阅读 HashMap 的 resize 方法了解其扩容原理,对桶节点的迁移算法进行单元测试,画图以方便理解。
1. 扩容的时机
- HashMap 中 put 入第一个元素,初始化数组 table。
- HashMap 中的元素数量大于阈值 threshold。
threshold = capacity * load factor。
当 size > threshold 时,触发 rehash。
2. 扩容的源码
HashMap 中的 resize 方法主要包含两部分逻辑:
- 初始化数组 table,并设置阈值。
- 数组容量翻倍,将元素迁移到新数组。
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node[] resize() {
Node[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) { // 第一次进来,table为null,oldCap为0,不会进入这里
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { // 扩容前的数组大小如果已经达到最大(2^30)了
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 取整型最大值(2^31-1),这样以后就不会扩容了
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && // oldCap翻倍得到newCap
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold // 第一次进来,如果手动设置了初始容量initialCapacity,这里为true,则将threshold作为初始容量
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults // 如果没有手动设置initialCapacity,则设为默认值16
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) { // 第一次进来,这里必为true,重新计算 threshold = capacity * Load factor
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node[] newTab = (Node[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) { // 对oldTab中所有元素进行rehash。由于每次扩容是2次幂的扩展(指数组长度/桶数量扩为原来2倍),所以,元素的位置要么是在原位置,要么是在原位置再移动2次幂的位置
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { // 数组j位置的元素不为空,需要该位置上的所有元素进行rehash
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null) // 桶中只有一个元素,则直接rehash
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode) // 桶中是树结构
((TreeNode)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order // 桶中是链表结构(JDK1.7中旧链表迁移新链表的时候,用的是头插法,如果在新表的数组索引位置相同,则链表元素会倒置;但是JDK1.8不会倒置,用的是双指针)
Node loHead = null, loTail = null; // low位链表,其桶位置不变,head和tail分别代表首尾指针
Node hiHead = null, hiTail = null; // high位链表,其桶位于追加后的新数组中
Node next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { // 是0的话索引没变,是1的话索引变成“原索引+oldCap”
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e; // 总是指向头结点
else
loTail.next = e; // 该操作有可能会改变原链表结构
loTail = e; // 总是指向下一个节点,直到尾节点
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead; // 原索引
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; // 原索引+oldCap
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
} 在 Java8 中,HashMap 中的桶可能是链表结构,也可能是树结构。
从网上找来一张图,直观展示 HashMap 结构:
如果是链结构
将旧链表拆分成两条新的链表,通过 e.hash & oldCap 来计算新链表在扩容后的数组中的新下标。
当 e.hash & oldCap = 0,则节点在新数组中的索引值与旧索引值相同。
当 e.hash & oldCap = 1,则节点在新数组中的索引值为旧索引值+旧数组容量。
对 e.hash & oldCap 公式的推导见上一篇文章 《HashMap中的取模和扩容公式推导》
如果是树结构
HashMap 对树结构的定义如下:
static final class TreeNode extends LinkedHashMap.Entry {
TreeNode parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
} 需要明确的是:TreeNode 既是一个红黑树结构,也是一个双链表结构。
判断节点 e instanceof TreeNode 为 true,则调用 HashMap.TreeNode#split 方法对树进行拆分,而拆分主要用的是 TreeNode 的链表属性。
拆分代码如下:
final void split(HashMap map, Node[] tab, int index, int bit) {
TreeNode b = this;
// Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving order
TreeNode loHead = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0; // 用于决定红黑树是否要转回链表
for (TreeNode e = b, next; e != null; e = next) { // 对节点e进行遍历(首先明确:TreeNode既是一个红黑树结构,也是一个双链表结构)
next = (TreeNode)e.next;
e.next = null; // 把e的下一个节点赋值给next后,断开e与e.next节点
if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) { // 原索引
if ((e.prev = loTail) == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
++lc;
}
else { // 原索引 + oldCap
if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
++hc;
}
}
if (loHead != null) {
if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map); // 转为链结构
else {
tab[index] = loHead;
if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified)
loHead.treeify(tab); // 转换成树结构
}
}
if (hiHead != null) {
if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map);
else {
tab[index + bit] = hiHead;
if (loHead != null)
hiHead.treeify(tab);
}
}
} 3. 链表迁移算法
Java8 中如何迁移桶中的链表呢?
这里构建一个链表 A->B->C 来进行调试,应用 HashMap 中的扩容算法,扩容的时候,会将该链表拆分成两个新的链表。
单元测试代码如下:
/**
* 旧链表数据迁移至新链表
* 本例中,桶的数量由1扩容为2.
*
* @author Sumkor https://segmentfault.com/blog/sumkor
* @since 2021/2/28
*/
@Test
public void resizeLink() {
int oldCap = 1;
int newCap = 2;
Node[] oldTable = new Node[oldCap];
Node[] newTable = new Node[newCap];
// A -> B -> C
Node firstLinkNode03 = new Node(new Integer(3).hashCode(), 3, "C", null);
Node firstLinkNode02 = new Node(new Integer(2).hashCode(), 2, "B", firstLinkNode03);
Node firstLinkNode01 = new Node(new Integer(1).hashCode(), 1, "A", firstLinkNode02);
oldTable[0] = firstLinkNode01;
// print
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.println("原链表:");
printTable(oldTable);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
/**
* HashMap中resize迁移算法
* @see HashMap#resize()
*/
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node loHead = null, loTail = null; // low位链表,其桶位置不变,head和tail分别代表首尾指针
Node hiHead = null, hiTail = null; // high位链表,其桶位于追加后的新数组中
Node e = oldTable[j];// 将要处理的元素
Node next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { // 是0的话索引没变,是1的话索引变成“原索引+oldCap”
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e; // 总是指向头结点
else
loTail.next = e; // 把loTail.next指向e。
loTail = e;
} else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e; // 把hiTail.next指向e。若hiTail.next原先并不指向e,该操作会改变oldTable[j]上的旧链表结构
hiTail = e; // 把hiTail指向e所指向的节点
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null; // 这一步是必须的,loTail.next有可能还其他节点,需要设为null
newTable[j] = loHead; // 原索引
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTable[j + oldCap] = hiHead; // 原索引+oldCap
}
}
System.out.println("新链表:");
printTable(newTable);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}其中,采用 HashMap 中的 Node 结构作为链表节点:
/**
* HashMap 中的 Node 结构
*/
static class Node implements Map.Entry {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry) o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
} 对数组 table 上的链表结构进行打印:
/**
* HashMap 中的 Node 结构,打印
*/
private void printTable(Node[] table) {
for (int i = 0; i < table.length; i++) {
Node tmpNode = table[i];// 用于打印,不改变table的结构
while (tmpNode != null) {
System.out.print(tmpNode + " -> ");
tmpNode = tmpNode.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}执行结果
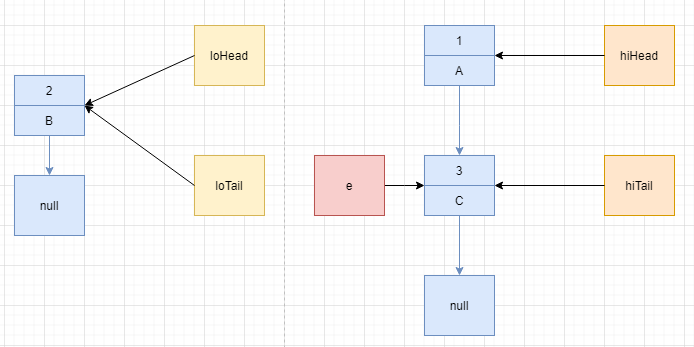
--------------------------
原链表:
1=A -> 2=B -> 3=C ->
--------------------------
新链表:
2=B ->
1=A -> 3=C ->
--------------------------注意到,迁移之后,节点 C 依旧排在节点 A 之后,而不是反过来。
在 Java8 中,HashMap 插入元素使用尾插法,扩容时使用了首尾指针保证了链表元素顺序不会倒置,从而解决了 Java7 扩容时产生的环问题。
执行过程图示
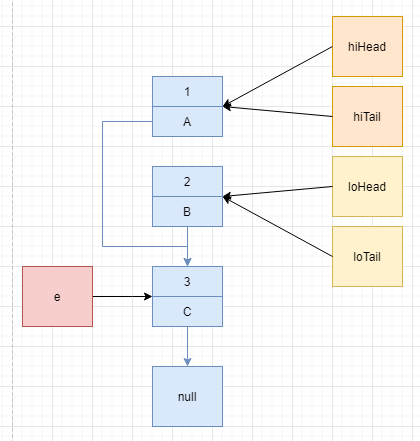
第一、二次循环之后,高低位链表指针如下:
第三次循环,由于 hiTail != null,因此执行 hiTail.next = e,注意此时 B 依旧指向 C。
接着执行 hiTail = e,把 hiTail 指向 e 所在节点。
最后执行 loTail.next = null 和 hiTail.next = null,把尾指针都指向 null。