stl 关联容器
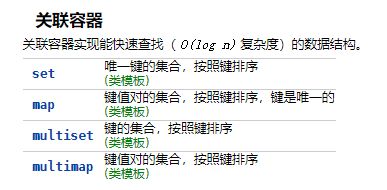
set,multiset
特性
- 以rb\_tree为底层结构,因此有自动排序的特性,而且key与value合一
- set/multiset 提供遍历操作及迭代器
- 不能通过迭代器改变原始值,因为使用的是rb\_tree的const iteration
- set key必须独一,其insert用的是rb\_tree的insert\_unique,multiset key可以重复,insert\_equal
- set,multiset的所有操作,都转由tree来做未尝不是一个adapter
/** gcc/libstdc++-v3/include/bits/stl_set.h 中,完整的同文件大概有800行的样子,看的烦的一批,其实核心东西没多少
* @brief A standard container made up of unique keys, which can be
* retrieved in logarithmic time.
*
* @ingroup associative_containers
*
* @tparam _Key Type of key objects.
* @tparam _Compare Comparison function object type, defaults to less<_Key>.
* @tparam _Alloc Allocator type, defaults to allocator<_Key>.
*
* Meets the requirements of a container, a
* reversible container, and an
* associative container (using unique keys).
*
* Sets support bidirectional iterators.
*
* The private tree data is declared exactly the same way for set and
* multiset; the distinction is made entirely in how the tree functions are
* called (*_unique versus *_equal, same as the standard).
*/
template,
typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Key> >
class set
{
public:
// typedefs:
//@{
/// Public typedefs.
typedef _Key key_type;
typedef _Key value_type;
typedef _Compare key_compare;
typedef _Compare value_compare;
typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
//@}
private:
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template
rebind<_Key>::other _Key_alloc_type;
typedef _Rb_tree,
key_compare, _Key_alloc_type> _Rep_type;
_Rep_type _M_t; // Red-black tree representing set.
typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Key_alloc_type> _Alloc_traits;
public:
//@{
/// Iterator-related typedefs.
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::pointer pointer;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::const_pointer const_pointer;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::reference reference;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::const_reference const_reference;
// _GLIBCXX_RESOLVE_LIB_DEFECTS
// DR 103. set::iterator is required to be modifiable,
// but this allows modification of keys.
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_iterator const_iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_reverse_iterator reverse_iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_reverse_iterator const_reverse_iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::size_type size_type;
typedef typename _Rep_type::difference_type difference_type;
//@}
/**
* @brief Attempts to insert an element into the %set.
* @param __x Element to be inserted.
* @return A pair, of which the first element is an iterator that points
* to the possibly inserted element, and the second is a bool
* that is true if the element was actually inserted.
*
* This function attempts to insert an element into the %set. A %set
* relies on unique keys and thus an element is only inserted if it is
* not already present in the %set.
*
* Insertion requires logarithmic time.
*/
std::pair
insert(const value_type& __x)
{
std::pair __p =
_M_t._M_insert_unique(__x);
return std::pair(__p.first, __p.second);
}
/**
* @brief Tries to locate an element in a %set.
* @param __x Element to be located.
* @return Iterator pointing to sought-after element, or end() if not
* found.
*
* This function takes a key and tries to locate the element with which
* the key matches. If successful the function returns an iterator
* pointing to the sought after element. If unsuccessful it returns the
* past-the-end ( @c end() ) iterator.
*/
iterator
find(const key_type& __x)
{ return _M_t.find(__x); }
const_iterator
find(const key_type& __x) const
{ return _M_t.find(__x); }
}
/**
* @brief A standard container made up of elements, which can be retrieved
* in logarithmic time.
*
* @ingroup associative_containers
*
*
* @tparam _Key Type of key objects.
* @tparam _Compare Comparison function object type, defaults to less<_Key>.
* @tparam _Alloc Allocator type, defaults to allocator<_Key>.
*
* Meets the requirements of a container, a
* reversible container, and an
* associative container (using equivalent
* keys). For a @c multiset the key_type and value_type are Key.
*
* Multisets support bidirectional iterators.
*
* The private tree data is declared exactly the same way for set and
* multiset; the distinction is made entirely in how the tree functions are
* called (*_unique versus *_equal, same as the standard).
*/
template ,
typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Key> >
class multiset
{
#ifdef _GLIBCXX_CONCEPT_CHECKS
// concept requirements
typedef typename _Alloc::value_type _Alloc_value_type;
# if __cplusplus < 201103L
__glibcxx_class_requires(_Key, _SGIAssignableConcept)
# endif
__glibcxx_class_requires4(_Compare, bool, _Key, _Key,
_BinaryFunctionConcept)
__glibcxx_class_requires2(_Key, _Alloc_value_type, _SameTypeConcept)
#endif
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
static_assert(is_same::type, _Key>::value,
"std::multiset must have a non-const, non-volatile value_type");
# if __cplusplus > 201703L || defined __STRICT_ANSI__
static_assert(is_same::value,
"std::multiset must have the same value_type as its allocator");
# endif
#endif
public:
// typedefs:
typedef _Key key_type;
typedef _Key value_type;
typedef _Compare key_compare;
typedef _Compare value_compare;
typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
private:
/// This turns a red-black tree into a [multi]set.
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template
rebind<_Key>::other _Key_alloc_type;
typedef _Rb_tree,
key_compare, _Key_alloc_type> _Rep_type;
/// The actual tree structure.
_Rep_type _M_t;
typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Key_alloc_type> _Alloc_traits;
public:
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::pointer pointer;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::const_pointer const_pointer;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::reference reference;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::const_reference const_reference;
// _GLIBCXX_RESOLVE_LIB_DEFECTS
// DR 103. set::iterator is required to be modifiable,
// but this allows modification of keys.
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_iterator const_iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_reverse_iterator reverse_iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_reverse_iterator const_reverse_iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::size_type size_type;
typedef typename _Rep_type::difference_type difference_type;
/**
* @brief Inserts an element into the %multiset.
* @param __x Element to be inserted.
* @return An iterator that points to the inserted element.
*
* This function inserts an element into the %multiset. Contrary
* to a std::set the %multiset does not rely on unique keys and thus
* multiple copies of the same element can be inserted.
*
* Insertion requires logarithmic time.
*/
iterator
insert(const value_type& __x)
{ return _M_t._M_insert_equal(__x); }
// _GLIBCXX_RESOLVE_LIB_DEFECTS
// 214. set::find() missing const overload
//@{
/**
* @brief Tries to locate an element in a %set.
* @param __x Element to be located.
* @return Iterator pointing to sought-after element, or end() if not
* found.
*
* This function takes a key and tries to locate the element with which
* the key matches. If successful the function returns an iterator
* pointing to the sought after element. If unsuccessful it returns the
* past-the-end ( @c end() ) iterator.
*/
iterator
find(const key_type& __x)
{ return _M_t.find(__x); }
const_iterator
find(const key_type& __x) const
{ return _M_t.find(__x); }
}
map,multimap
特性
- 以rb\_tree为底层结构,因此有自动排序的特性,排序依据是key
- map/multimap 提供遍历操作及迭代器
- 不能通过迭代器改变key,但是可以用来改变data(key+data=value)
- map key必须独一,其insert用的是rb\_tree的insert\_unique,multiap key可以重复,insert\_equal
- map和multimap的所有操作,都转由tree来做,未尝不是一个adapter
- map有独特的operater[],可以用下标来访问map的data,而且If the key does not exist,a pair with that key is created using default values, which is then returned.
/**
* @brief Subscript ( @c [] ) access to %map data.
* @param __k The key for which data should be retrieved.
* @return A reference to the data of the (key,data) %pair.
*
* Allows for easy lookup with the subscript ( @c [] )
* operator. Returns data associated with the key specified in
* subscript. If the key does not exist, a pair with that key
* is created using default values, which is then returned.
*
* Lookup requires logarithmic time.
*/
/**
* @brief A standard container made up of (key,value) pairs, which can be
* retrieved based on a key, in logarithmic time.
*
* @ingroup associative_containers
*
* @tparam _Key Type of key objects.
* @tparam _Tp Type of mapped objects.
* @tparam _Compare Comparison function object type, defaults to less<_Key>.
* @tparam _Alloc Allocator type, defaults to
* allocator.
*
* Meets the requirements of a container, a
* reversible container, and an
* associative container (using unique keys).
* For a @c map the key_type is Key, the mapped_type is T, and the
* value_type is std::pair.
*
* Maps support bidirectional iterators.
*
* The private tree data is declared exactly the same way for map and
* multimap; the distinction is made entirely in how the tree functions are
* called (*_unique versus *_equal, same as the standard).
*/
template ,
typename _Alloc = std::allocator > >
class map
{
public:
typedef _Key key_type;
typedef _Tp mapped_type;
typedef std::pair value_type;
typedef _Compare key_compare;
typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
private:
#ifdef _GLIBCXX_CONCEPT_CHECKS
// concept requirements
typedef typename _Alloc::value_type _Alloc_value_type;
# if __cplusplus < 201103L
__glibcxx_class_requires(_Tp, _SGIAssignableConcept)
# endif
__glibcxx_class_requires4(_Compare, bool, _Key, _Key,
_BinaryFunctionConcept)
__glibcxx_class_requires2(value_type, _Alloc_value_type, _SameTypeConcept)
#endif
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
#if __cplusplus > 201703L || defined __STRICT_ANSI__
static_assert(is_same::value,
"std::map must have the same value_type as its allocator");
#endif
#endif
public:
class value_compare
: public std::binary_function
{
friend class map<_Key, _Tp, _Compare, _Alloc>;
protected:
_Compare comp;
value_compare(_Compare __c)
: comp(__c) { }
public:
bool operator()(const value_type& __x, const value_type& __y) const
{ return comp(__x.first, __y.first); }
};
private:
/// This turns a red-black tree into a [multi]map.
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template
rebind::other _Pair_alloc_type;
typedef _Rb_tree,
key_compare, _Pair_alloc_type> _Rep_type;
/// The actual tree structure.
_Rep_type _M_t;
typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Pair_alloc_type> _Alloc_traits;
public:
// many of these are specified differently in ISO, but the following are
// "functionally equivalent"
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::pointer pointer;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::const_pointer const_pointer;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::reference reference;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::const_reference const_reference;
typedef typename _Rep_type::iterator iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_iterator const_iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::size_type size_type;
typedef typename _Rep_type::difference_type difference_type;
typedef typename _Rep_type::reverse_iterator reverse_iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_reverse_iterator const_reverse_iterator;
...
}
/**
* @brief A standard container made up of (key,value) pairs, which can be
* retrieved based on a key, in logarithmic time.
*
* @ingroup associative_containers
*
* @tparam _Key Type of key objects.
* @tparam _Tp Type of mapped objects.
* @tparam _Compare Comparison function object type, defaults to less<_Key>.
* @tparam _Alloc Allocator type, defaults to
* allocator.
*
* Meets the requirements of a container, a
* reversible container, and an
* associative container (using equivalent
* keys). For a @c multimap the key_type is Key, the mapped_type
* is T, and the value_type is std::pair.
*
* Multimaps support bidirectional iterators.
*
* The private tree data is declared exactly the same way for map and
* multimap; the distinction is made entirely in how the tree functions are
* called (*_unique versus *_equal, same as the standard).
*/
template ,
typename _Alloc = std::allocator > >
class multimap
{
public:
typedef _Key key_type;
typedef _Tp mapped_type;
typedef std::pair value_type;
typedef _Compare key_compare;
typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
private:
#ifdef _GLIBCXX_CONCEPT_CHECKS
// concept requirements
typedef typename _Alloc::value_type _Alloc_value_type;
# if __cplusplus < 201103L
__glibcxx_class_requires(_Tp, _SGIAssignableConcept)
# endif
__glibcxx_class_requires4(_Compare, bool, _Key, _Key,
_BinaryFunctionConcept)
__glibcxx_class_requires2(value_type, _Alloc_value_type, _SameTypeConcept)
#endif
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
#if __cplusplus > 201703L || defined __STRICT_ANSI__
static_assert(is_same::value,
"std::multimap must have the same value_type as its allocator");
#endif
#endif
public:
class value_compare
: public std::binary_function
{
friend class multimap<_Key, _Tp, _Compare, _Alloc>;
protected:
_Compare comp;
value_compare(_Compare __c)
: comp(__c) { }
public:
bool operator()(const value_type& __x, const value_type& __y) const
{ return comp(__x.first, __y.first); }
};
private:
/// This turns a red-black tree into a [multi]map.
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template
rebind::other _Pair_alloc_type;
typedef _Rb_tree,
key_compare, _Pair_alloc_type> _Rep_type;
/// The actual tree structure.
_Rep_type _M_t;
typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Pair_alloc_type> _Alloc_traits;
public:
// many of these are specified differently in ISO, but the following are
// "functionally equivalent"
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::pointer pointer;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::const_pointer const_pointer;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::reference reference;
typedef typename _Alloc_traits::const_reference const_reference;
typedef typename _Rep_type::iterator iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_iterator const_iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::size_type size_type;
typedef typename _Rep_type::difference_type difference_type;
typedef typename _Rep_type::reverse_iterator reverse_iterator;
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_reverse_iterator const_reverse_iterator;
}
