Mysql各种锁机制
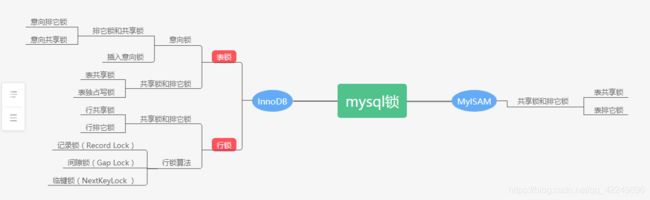
mysql锁索引树
- 一、mysql锁介绍
-
- 锁来源
- 锁种类
- 思维导图一览
- 二、MyISAM表锁:
-
- 1、读锁
-
-
- 结论1:在执行表读锁后,当前会话只能访问加锁的这个表,不能访问未加锁的表,但是非当前会话不受影响。
- 结论2:在执行表读锁后,当前会话只能进行查询操作,不能进行其它操作(update、delete等)。非当前会话可以执行其它操作,但会造成阻塞。
-
- 2、写锁:
-
-
- 结论1:当一个会话持有表读锁,其它会话可以持有表读锁,但不能持有表写锁。
- 结论2:当一个会话持有表写锁,那么该会话只能对该表进行增删改查操作。其它会话则不能对该表进行一切操作。但是不影响其它会话对别的表进行操作。
-
- 3、总结
- 二、InnoDB表锁(意向锁):
-
-
-
- 结论1:当一个会话持有某个表的行级共享锁,其它会话可以获取该表的表级共享锁,但不能获取该表的表级排它锁。
- 结论2:当一个会话持有某个表的行级排它锁,其它会话不可以获取到表级的排它锁和共享锁。
- 结论3:当一个会话持有某个表的表读锁,其它会事务可以在获取到行级读锁,但获取行级写锁会阻塞。
- 结论4:当一个会话持有某个表的表写锁锁,其它会事务都不可以在获取该表的行级读写锁。
-
- 总结
-
- 三、InnoDB行锁
-
- 1、共享锁(S锁)
-
-
- 结论1:一个会话给一个表中的某一行加共享锁,其它会话可读不可进行其它操作,直到锁释放。
- 结论2:一个会话给一个表中的某一行加共享锁,不影响该会话操作其它表,以及自身的表,这与表锁不同(表锁是当前会话给该表加表锁后,那当前会话只能操作该表中的数据,不能在进行操作其它表中的数据了)
- 结论3:当一个会话持有某行的共享锁,其它会话也可在持有某行的共享锁,但是两者同时修改这条数据的话会造成死锁。
-
- 2、排它锁(X锁)
-
-
- 结论1:当一个会话持有某行的排它锁,其它会话则不能在修改数据以及持有改行的共享锁及排它锁。会造成阻塞。
-
- 3、总结
- 四、锁的算法(行锁)
-
- 1、记录锁:
- 2、间隙锁:
- 3、临键锁
一、mysql锁介绍
锁来源
在存在并发操作的时候,必然需要一种机制来保证数据的完整性与一致性。锁就是这一技术的实现。
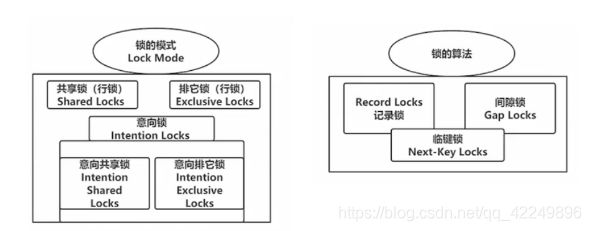
锁种类
-
根据概念分:悲观锁和乐观锁
-
根据粒度分:表锁、页锁、行锁,最常见的就是表锁和行锁。其中,
MyISAM引擎只有表锁,而InooDB既有表锁也有行锁。 -
根据功能分:共享锁、排它锁(独占锁)、意向锁等。其中,共享锁被称为S锁。排它锁称为X锁。
| 锁名称 | 特点 |
|---|---|
| 表锁 | 加锁快,不会出现死锁,锁定粒度大,发生锁冲突的概率最高,并发度最低。 |
| 行锁 | 开销大,发生锁冲突概率低。并发度高,会发生死锁。 |
| 页锁 | 开销、加锁时间、锁定粒度界于表锁和行锁之间,会出现死锁,并发度一般。 |
思维导图一览
mysql的各种锁可能会让人难以理解,理解之前务必心中要有个思维导图,哪个锁归属哪个引擎,哪个锁归属哪个锁,心中一定要有个大类和小类的区分,这样在学起来就不会太难了。
二、MyISAM表锁:
先看一下读锁和写锁的兼容性:
| 当前锁模式/是否兼容/请求锁模式 | 读锁 | 写锁 |
|---|---|---|
| 读锁 | 是 | 否 |
| 写锁 | 是 | 否 |
博主使用的mysql详细信息:
| 版本引擎等信息 | 详细描述 |
|---|---|
| mysql测试版本 | 5.6.49-log |
| 表引擎 | 其中,classromm表为MyISAM,student表为InnoDB。 |
1、读锁
语法:lock table tablename read
会话1:给classroom表加锁,就不能对student等其它表进行操作了,只能对加锁的表进行读操作。
mysql> lock table classroom read;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from classroom;
+----+---------+
| id | cname |
+----+---------+
| 1 | php班 |
| 2 | Java班 |
+----+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student;
ERROR 1100 (HY000): Table 'student' was not locked with LOCK TABLES
mysql> delete from student where id = 6;
ERROR 1100 (HY000): Table 'student' was not locked with LOCK TABLES
会话2:会话1 中给classroom表加锁,不影响会话2查询加锁的表和其它表。
mysql> select * from classroom;
+----+---------+
| id | cname |
+----+---------+
| 1 | php班 |
| 2 | Java班 |
+----+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
会话2:此时会话1虽然对classroom加表锁了,但是会话2也依然可以对classroom表加表锁。但是加上表锁后,会话2也和会话1一样只能对进行查询的操作了。
mysql> lock table classroom read;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student;
ERROR 1100 (HY000): Table 'student' was not locked with LOCK TABLES
mysql> update classroom set cid = 6 where id = 1;
ERROR 1099 (HY000): Table 'classroom' was locked with a READ lock and can't be updated
结论1:在执行表读锁后,当前会话只能访问加锁的这个表,不能访问未加锁的表,但是非当前会话不受影响。
会话1:对classroom表进行加表锁,并对id为3的数据进行删除。
mysql> lock table classroom read;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from classroom;
+----+---------+
| id | cname |
+----+---------+
| 1 | php班 |
| 2 | Java班 |
| 3 | 前端 |
+----+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> delete from classroom where id = 3;
ERROR 1099 (HY000): Table 'classroom' was locked with a READ lock and can't be updated
会话2:对classroom表中某行数据进行删除,但会造成阻塞。
mysql> delete from classroom where id = 3;
……等待
结论2:在执行表读锁后,当前会话只能进行查询操作,不能进行其它操作(update、delete等)。非当前会话可以执行其它操作,但会造成阻塞。
2、写锁:
语法:lock table tablename write
会话1:会话1持有classroom表读锁,其它会话能持有该表的读锁,但不能持有该表的写锁。
mysql> lock table classroom read;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
会话2:会话2可在持有classroom的表读锁,但不能持有表写锁,会造成阻塞。
mysql> lock table classroom read;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> lock table classroom write;
……等待
结论1:当一个会话持有表读锁,其它会话可以持有表读锁,但不能持有表写锁。
会话1:事务1给classroom加表锁,那只有事务1才能进行增删改查操作。
mysql> lock table classroom write;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from classroom;
+----+--------+------+
| id | cname | cid |
+----+--------+------+
| 1 | php班 | 7 |
| 2 | java班 | 1 |
+----+--------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
会话2:会话1加了写锁后,会话2不能在对此表进行操作,但是可以对其它表进行操作。
mysql> select * from classroom;
Ctrl-C -- sending "KILL QUERY 214" to server ...
Ctrl-C -- query aborted.
ERROR 1317 (70100): Query execution was interrupted
mysql> select * from student;
+----+--------+------+
| id | name | age |
+----+--------+------+
| 21 | 张无忌 | 32 |
| 22 | 周芷若 | 19 |
+----+--------+------+
2 rows in set (0.04 sec)
mysql> update student set age = 33 where id = 21;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.09 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from student;
+----+--------+------+
| id | name | age |
+----+--------+------+
| 21 | 张无忌 | 33 |
| 22 | 周芷若 | 19 |
+----+--------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
结论2:当一个会话持有表写锁,那么该会话只能对该表进行增删改查操作。其它会话则不能对该表进行一切操作。但是不影响其它会话对别的表进行操作。
3、总结
| \ | 表读锁 | 表写锁 |
|---|---|---|
| 当一个事务已持有表读/写锁,其它事务是否可对该表进行curd | 可查不可增删改 | 可增删该查 |
| 当一个事务已持有表读锁,其它事务能否在继续持有表读/写锁 | 能在持有表读锁 | 不能持有表写锁 |
| 当一个事务已持有表写锁,其它事务能否在继续持有表读/写锁 | 不能持有表读锁 | 不能持有表写锁 |
| 当一个事务已持有表读/写锁,那这个事务能否在对别的表进行操作 | 不能 | 不能 |
二、InnoDB表锁(意向锁):
意向锁含义(百度百科):
意向锁的含义是如果对一个结点加意向锁,则说明该结点的下层结点正在被加锁;对任一结点加锁时,必须先对它的上层结点加意向锁。
意向锁是有数据引擎自己维护的,用户无法手动干预,在加行级排它锁或共享锁之前,InooDB先会判断所在数据行的数据表中是否有对应的意向锁。
InooDB是持有行锁的,MyISAM是没有行锁的,既然有行锁,必然就要了解一下InooDB下行锁和表锁之间的那兼容性。
下面做个实验:
会话1:给student表中某一行数据加上共享锁,并未提交
mysql> select * from student;
+----+--------------+-----+
| id | name | age |
+----+--------------+-----+
| 1 | 光头强 | 21 |
| 5 | 吉吉国王 | 40 |
| 10 | 白雪公主 | 26 |
+----+--------------+-----+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 1 lock in share mode;
+----+-----------+-----+
| id | name | age |
+----+-----------+-----+
| 1 | 光头强 | 21 |
+----+-----------+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
会话2:给student表加上表级共享锁,看是否会阻塞呢?发现是能加上的。
mysql> lock table student read;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
会话2:既然表级共享锁加不上,表级排它锁是否能加上呢? 阻塞了……
mysql> lock table student write;
……
结论1:当一个会话持有某个表的行级共享锁,其它会话可以获取该表的表级共享锁,但不能获取该表的表级排它锁。
继续做第二个实验:
会话1:给student表某一行数据加上排它锁,并未提交
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 1 for update;
+----+-----------+-----+
| id | name | age |
+----+-----------+-----+
| 1 | 光头强 | 23 |
+----+-----------+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
会话2:此时窗口2去申请student表的表级共享锁。出现了阻塞。
mysql> lock table student read;
……
会话2:那去申请排它锁是否会被阻塞呢?发现也被阻塞了。
mysql> lock table student write;
……
结论2:当一个会话持有某个表的行级排它锁,其它会话不可以获取到表级的排它锁和共享锁。
以上例子,都是讲先加行锁后,在去加表锁的情况。下面翻过来试一下,在看下先加表锁在加行锁的情况。
看下第三个实验:
会话1:给student表加上表读锁。
mysql> select * from student;
+----+--------------+-----+
| id | name | age |
+----+--------------+-----+
| 1 | 光头强 | 24 |
| 5 | 吉吉国王 | 40 |
| 10 | 白雪公主 | 26 |
+----+--------------+-----+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> lock table student read;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
会话2:在去看看是否能在申请行写锁,发现已经被阻塞了。
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 1 for update;
……
会话2:那再看看是否能够申请行读锁呢?发现是可以申请的
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 1 lock in share mode;
+----+-----------+-----+
| id | name | age |
+----+-----------+-----+
| 1 | 光头强 | 24 |
+----+-----------+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
结论3:当一个会话持有某个表的表读锁,其它会事务可以在获取到行级读锁,但获取行级写锁会阻塞。
再看下第四个试验:
会话1:给student表加表读锁
mysql> select * from student;
+----+--------------+-----+
| id | name | age |
+----+--------------+-----+
| 1 | 光头强 | 24 |
| 5 | 吉吉国王 | 40 |
| 10 | 白雪公主 | 26 |
+----+--------------+-----+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> lock table student write;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
会话2:给student表加某一行数据申请行写锁,发现会被阻塞
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 1 for update;
会话2:给student表某一行数据申请行读锁,依然被阻塞。
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 1 lock in share mode;
……
结论4:当一个会话持有某个表的表写锁锁,其它会事务都不可以在获取该表的行级读写锁。
总结
那以上栗子就可以说明:
| \ | 意向共享锁(IS) | 意向排他锁(IX) |
|---|---|---|
| 表级共享锁(S) | 兼容 | 互斥 |
| 表级排他锁(X) | 互斥 | 互斥 |
明白了以上表级与行级的兼容后再去了解意向锁会更好理解。
意向锁是表锁!当我们需要给一个加表锁的时候,我们需要根据意向锁去判断表中有没有数据行被锁定,以确定是否能加成功。如果意向锁是行锁,那么我们就得遍历表中所有数据行来判断。如果意向锁是表锁,则我们直接判断一次就知道表中是否有数据行被锁定了。
注意注意注意!!!这儿有个坑,我上边的测试都是mysql5.7版本,但是在mysql5.7版本以下,加了行写锁后还能再加表读锁。版本不一样导致结果不一样,这坑研究了好几天没从网上找到答案,一度让我怀疑人生,以此谨记吧
三、InnoDB行锁
注意,InnoDB中的行锁需要在事务中运行才生效。
1、共享锁(S锁)
语法:
lock in share mode
概念:又名读锁,对某一资源加共享锁,自身可以修改或读取该资源,其它人也能继续持有该资源的共享锁,无法持有该资源的排它锁。并只能读取,不能进行其它操作。
会话1:给student表id为6的数据加上共享锁。
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 李北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
| 7 | 王上海 | 200 | 2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 6 lock in share mode;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 李北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
会话2:在去修改这条数据会一直造成阻塞,知道超时或者锁释放。
mysql> update student set name = '周北京' where id = 6;
ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
结论1:一个会话给一个表中的某一行加共享锁,其它会话可读不可进行其它操作,直到锁释放。
会话1:给student表id为6的数据加上共享锁,看看当前会话是否能在操作别的表中的数据呢?
mysql> select * from student;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 赵北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
| 7 | 王上海 | 200 | 2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 6 lock in share mode;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 赵北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from classroom;
+----+---------+
| id | cname |
+----+---------+
| 1 | php班 |
| 2 | Java班 |
+----+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> update classroom set cname = 'php一班' where id = 1;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from classroom;
+----+-----------+
| id | cname |
+----+-----------+
| 1 | php一班 |
| 2 | Java班 |
+----+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
结论2:一个会话给一个表中的某一行加共享锁,不影响该会话操作其它表,以及自身的表,这与表锁不同(表锁是当前会话给该表加表锁后,那当前会话只能操作该表中的数据,不能在进行操作其它表中的数据了)
会话1:开启事务,给student表中id为6的加上共享锁。
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 孙北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
| 7 | 王上海 | 200 | 2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 6 lock in share mode;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 孙北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
会话2:也给student表中id为6的加上共享锁。
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 孙北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
| 7 | 王上海 | 200 | 2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 6 lock in share mode;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 孙北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
会话1:去修改这条数据,会造成阻塞。
mysql> update student set name = '李北京' where id = 6;
……等待
会话2:在去修改这条数据,出现死锁。
mysql> update student set name = '李北京' where id = 6;
ERROR 1213 (40001): Deadlock found when trying to get lock; try restarting transaction
结论3:当一个会话持有某行的共享锁,其它会话也可在持有某行的共享锁,但是两者同时修改这条数据的话会造成死锁。
2、排它锁(X锁)
语法:
for update
概念:又名写锁,对某一资源加排它锁,自身可以修改或读取该资源,其它会话不能继续持有该资源的共享锁和排它锁。并只能对加锁数据进行读取,不能进行其它操作。
排他锁的申请前提 : 没有线程对该结果集中的任何行数据使用排他锁或共享锁,否则申请会阻塞
for update及lock in share mode 仅适用于 InnoDB,且必须在事务块 (BEGIN/COMMIT) 中才能生效,在进行事务操作时,通过 for update 语句,MySQL会对查询结果集中每行数据都添加排他锁,其他线程对该记录的更新与删除操作都会阻塞,排他锁包含 行锁、表锁
行排它锁可不是加上以后其它事务就不能查询该行数据,只是其它事务则不能再去给该行加其它的锁。mysql InnoDB引擎默认的修改数据语句,update,delete,insert都会自动给涉及到的数据加上排他锁,select语句默认不会加任何锁类型,不管是行共享锁还是行排它锁都能够进行查询的,因为普通查询没有任何锁机制。
会话1:给student表id为6的数据加上排它锁。
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 李北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
| 7 | 王上海 | 200 | 2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 6 for update;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 李北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
会话2:会话1加上排它锁后,会话2是否能够读取加锁数据呢?答案是可以的!
mysql> select * from student where id = 6;
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| id | name | price | cid |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
| 6 | 李北京 | 50 | 6,2 |
+----+-----------+-------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
会话2:会话1加上排它锁后,会话2是否还能在继续持有该行的排它锁呢?答案是被阻塞了。
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 6 for update;
……等待
会话2:会话1加上排它锁后,会话2是否还能在继续持有该行的共享锁呢?也会被阻塞。
mysql> select * from student where id = 6 lock in share mode;
……等待
会话2:会话1加上排它锁后,会话2是否还能够修改这条数据呢?答案是肯定不行的!会造成锁等待,直到资源释放。
mysql> update student set name = '吴北京' where id = 6;
……等待
结论1:当一个会话持有某行的排它锁,其它会话则不能在修改数据以及持有改行的共享锁及排它锁。会造成阻塞。
3、总结
| \ | 行读锁 | 行写锁 |
|---|---|---|
| 加上行读/写锁后,其它事务能删改这条数据吗 | 会阻塞 | 会阻塞 |
| 加上行读/写锁后,其它事务能读取这条数据吗 | 能 | 能 |
| 加上行读锁后,其它事务能在去持有行/读锁吗 | 能 | 不能 |
| 加上行写锁后,其它事务能在去持有行/读锁吗 | 不能 | 不能 |
四、锁的算法(行锁)
1、记录锁:
窗口1:直接锁住id为1的记录
mysql> select * from student;
+----+--------+
| id | name |
+----+--------+
| 1 | 小王 |
| 2 | 李 |
| 3 | 张 |
+----+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where id = 1 for update;
+----+--------+
| id | name |
+----+--------+
| 1 | 小王 |
+----+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
窗口2:
则不能对id为1的记录进行修加锁以及增删改操作,但是可以查出
mysql> select * from student where id = 1 for update;
ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
2、间隙锁:
间隙锁(Gap Lock)是Innodb在可重复读提交下为了解决幻读问题时引入的锁机制。
3、临键锁
临键锁,是记录锁与间隙锁的组合,它的封锁范围,既包含索引记录,又包含索引区间,解决幻读问题。