android studio与ideal后台进行交互_Android通过Web与后台数据库交互
2021.1.27 更新
已更新新版本博客,更新内容与原文章相比有点多,因此新开了一篇博客,链接在下方:
氷泠:Android+Java Web+MySQL实现登录注册zhuanlan.zhihu.com1 背景
开发一个App与后台数据库交互,基于MySQL+原生JDBC+Tomcat,没有使用DBUtils或JDBC框架,纯粹底层JDBC实现。
这几天踩了很多坑,说得夸张点真是踩到没有知觉,希望能帮助读者少踩坑...
2 开发环境
Windows10- 服务器
CentOS 7 Android Studio 3.5.1IntelliJ IDEA 2019.02MySQL 8.0.17Tomcat 9.0.26
3 准备环境
主要是安装MySQL与Tomcat,已经安装的可以略过。
3.1 安装MySQL
这个是目前比较新的MySQL版本。
服务器系统是CentOS。
其他系统安装看这里:
- Win10
- Ubuntu
- Fedroa
- ReaHat
CentOS使用yum安装即可。
3.1.1 下载并安装MySQL
sudo yum localinstall https://repo.mysql.com//mysql80-community-release-el7-1.noarch.rpm
sudo yum install mysql-community-server3.1.2 启动服务并查看初始化密码
sudo service mysqld start
sudo grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log3.1.3 修改密码
首先使用root登录:
mysql -u root -p输入上一步看到的密码,接着使用alter修改密码:
alter mysql.user 'root'@'localhost' identified by 'password';注意新版本的MySQL不能使用太弱的密码,比如:
出现这种提示的话则说明密码太弱了,请使用一个更高强度的密码。
3.1.4 允许外部访问
use mysql;
update user set host='%' where user='root';这个可以根据自己的需要去修改,host='%'表明允许所有的ip登录,也可以设置特定的ip,若使用host='%'的话建议新建一个用户配置相应的权限。
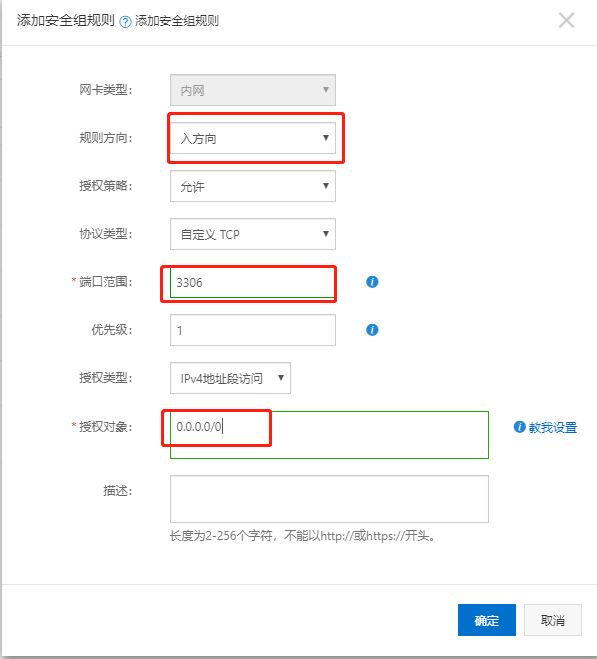
3.1.5 配置防火墙(可选)
一般来说需要在对应的云厂商的防火墙配置中开启响应端口,如图:
其中授权对象可以根据自己的需要更改,0.0.0.0/0表示允许所有的ip。
3.2 安装Tomcat
3.2.1 下载并上传到服务器
先去官网下载,下载后上传文件到服务器:
笔者使用的是scp命令,使用不熟练的可以戳这里看看:
scp apache-tomcat-xxxx.tar.gz [email protected]:/改成自己的用户名和ip。
3.2.2 解压
ssh连接到服务器,接着移动到/usr/local并解压:
mkdir /usr/local/tomcat
mv apache-tomcat-xxxx.tar.gz /usr/local/tomcat
tar -xzvf apache-tomcat-xxx.tar.gz3.2.3 修改默认端口(可选)
修改conf/server.xml文件,一般只需修改
中的8080端口,修改这个端口即可。
需要的话自行更改。
3.2.4 启动
运行bin目录下的startup.sh:
cd bin
./startup.sh3.2.5 测试
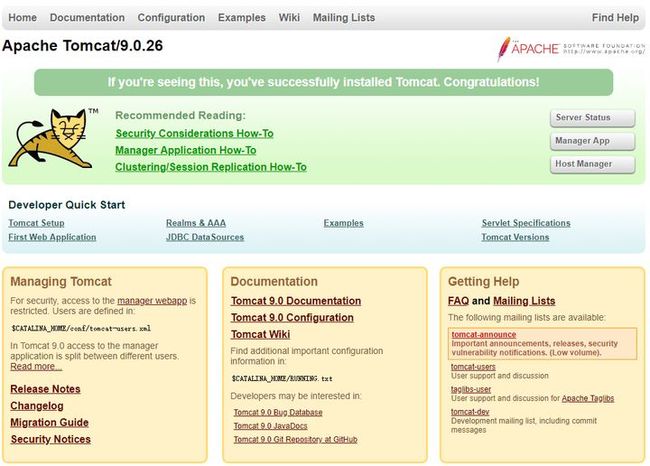
浏览器输入:
服务器IP:端口若出现:
则表示成功。
3.2.6 开机启动(可选)
建议配置开机启动,修改/etc/rc.local文件,添加:
sh /usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh这个根据自己的Tomcat安装路径修改,指定bin下的startup.sh。
4 建库建表
创建用户表,这里简化操作就不创建新用户不授权了。
这是一个在本地用root登录的示例,请根据实际情况创建并授权用户。
4.1 用户表
CREATE DATABASE userinfo;
USE userinfo;
CREATE TABLE user
(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name CHAR(30) NULL,
password CHAR(30) NULL
);4.2 导入
mysql -u root -p < user.sql这样准备工作就做好了,下面正式开始进行敲代码阶段。
5 后端部分
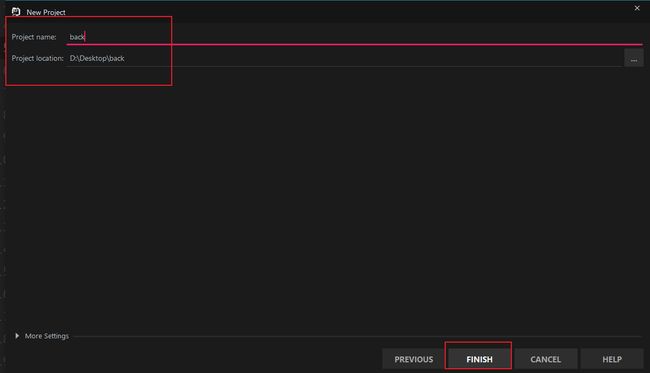
5.1 创建项目
选择Web Application:
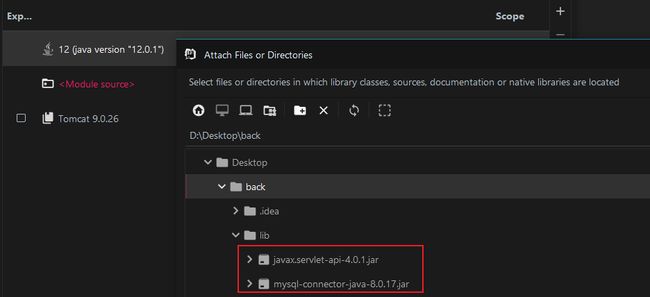
5.2 添加依赖库
创建一个叫lib的目录:
添加两个JAR包(文末提供下载链接):
mysql-connector-java-8.0.17.jarjavax.servlet-api-4.0.1.jar
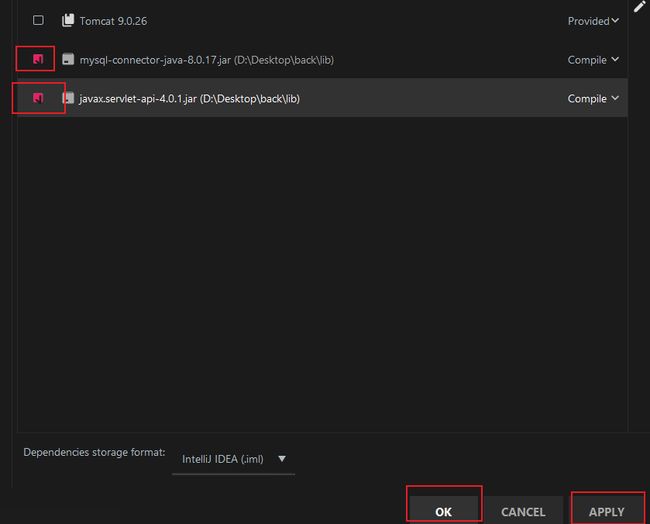
打开Project Structure:
Modules --> + --> JARs or directories:
选择刚才新建的lib下的两个JAR包:
勾选并apply:
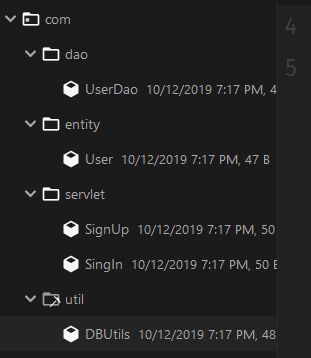
5.3 创建包与类
总共4个包:
com.servlet:用于处理来自前端的请求,包含SignUp.java、SignIn.javacom.util:主要功能是数据库连接,包含DBUtils.javacom.entity:实体类,包含User.javacom.dao:操作用户类的类,包含UserDao.java
5.4 DBUtils
连接数据库的类,纯粹的底层JDBC实现,注意驱动版本。
public class DBUtils {
private static Connection connection = null;
public static Connection getConnection()
{
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/数据库名字";
String usename = "账号";
String password = "密码";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,usename,password);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
return connection;
}
public static void closeConnection()
{
if(connection != null)
{
try {
connection.close();
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}主要就是获取连接与关闭连接两个函数。
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/数据库名字";
String usename = "账号";
String password = "密码";这几行根据自己的用户名,密码,服务器ip和库名修改。
注意,MySQL 8.0以上使用的注册驱动的语句是:
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");旧版的是:
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");5.5 User
User类比较简单,就是就三个字段与Getter+Setter。
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;
//三个Getter与三个Setter
//...
}5.6 UserDao
public class UserDao {
public boolean query(User user)
{
Connection connection = DBUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from user where name = ? and password = ?";
try {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,user.getName());
preparedStatement.setString(2,user.getPassword());
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
return resultSet.next();
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
finally {
DBUtils.closeConnection();
}
}
public boolean add(User user)
{
Connection connection = DBUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into user(name,password) values(?,?)";
try {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,user.getName());
preparedStatement.setString(2,user.getPassword());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
return preparedStatement.getUpdateCount() != 0;
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
finally {
DBUtils.closeConnection();
}
}
}主要就是查询与添加操作,查询操作中存在该用户就返回true,否则返回false。
添加操作中使用executeUpdate()与getUpdateCount() != 0。
注意不能直接使用
return preparedStatement.execute();去代替
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
return preparedStatement.getUpdateCount() != 0;咋一看好像没有什么问题,那天晚上笔者测试的时候问题可大了,Android那边显示注册失败,但是数据库这边的却insert进去了。。。
~~啊这。。。~~
好吧,还是函数的问题。
- 一般来说
select使用executeQuery(),executeQuery()返回ResultSet,表示结果集,保存了select语句的执行结果,配合next()使用 delete,insert,update使用executeUpdate(),executeUpdate()返回的是一个整数,表示受影响的行数,即delete,insert,update修改的行数,对于drop,create操作返回0create,drop使用execute(),execute()的返回值是这样的,如果第一个结果是ResultSet对象,则返回true,如果第一个结果是更新计数或者没有结果则返回false
所以在这个例子中
return preparedStatement.execute();肯定返回false,所以才会数据库这边insert进去,但前端显示注册失败(这个问题笔者找了是真的久。。。)
5.7 SignIn+SignUp
servlet包中:
SingIn类用于处理登录,调用JDBC查看数据库是否有对应的用户SignUp类用于处理注册,把User添加到数据库中
SignIn.java如下:
@WebServlet("/SignIn")
public class SingIn extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException,ServletException
{
this.doPost(httpServletRequest,httpServletResponse);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException, ServletException
{
httpServletRequest.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
httpServletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
httpServletResponse.setContentType("text/plain;charset=utf-8");//设置相应类型为html,编码为utf-8
String name = httpServletRequest.getParameter("name");
String password = httpServletRequest.getParameter("password");
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User user = new User();
user.setName(name);
user.setPassword(password);
if(!userDao.query(user))//若查询失败
{
httpServletResponse.sendError(204,"query failed.");//设置204错误码与出错信息
}
}
}首先是@WebServlet注解,表示这是一个名字叫SignIn的Servlet,可用于实现Servlet与URL的映射,如果不在这里添加这个注解,则需要在WEB-INF目录下的web.xml添加一个
@WebServlet("/SignIn")接着设置响应类型与编码:
httpServletResponse.setContentType("text/plain;charset=utf-8");//设置相应类型为html,编码为utf-8HttpServletRequest.getParameter(String name)方法表示根据name获取相应的参数:
String name = httpServletRequest.getParameter("name");
String password = httpServletRequest.getParameter("password");下面是SignUp.java:
@WebServlet("/SignUp")
public class SignUp extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException,ServletException
{
this.doPost(httpServletRequest,httpServletResponse);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException,ServletException
{
httpServletRequest.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
httpServletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");//设定编码防止中文乱码
httpServletResponse.setContentType("text/plain;charset=utf-8");//设置相应类型为html,编码为utf-8
String name = httpServletRequest.getParameter("name");//根据name获取参数
String password = httpServletRequest.getParameter("password");//根据password获取参数
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
User user = new User();
user.setName(name);
user.setPassword(password);
if(!userDao.add(user)) //若添加失败
{
httpServletResponse.sendError(204,"add failed.");//设置204错误码与出错信息
}
}
}5.8 添加Servlet到web.xml
SignIn
com.servlet.SingIn
SignUp
com.servlet.SignUp
要把刚才创建的Servlet添加进web.xml,在
Servlet的名字,建议与类名一致Servlet类的位置
如果在Servlet类中没有添加@WebServlet("/xxxx")注解,则需要在web.xml中添加:
SignIn
/SignIn
其中
5.9 Hello.html测试文件
最后添加一个叫Hello.html的测试文件。
Welcome
Hello web.