作者 | 春哥大魔王
来源 | Serverless 公众号
写在前面
在 SaaS 领域 Salesforce 是佼佼者,其 CRM 的概念已经扩展到了 Marketing、Sales、Service 等领域。那么 Salesforce 靠什么变成了这三个行业的解决方案呢?得益于 Salesforce 强大的 aPaaS 平台。
ISV、内部实施、客户均可以从自己的维度基于 aPaaS 平台构建自己的行业,实现业务定制,甚至是行业定制。因为在此之前只有在 Sales 方向有专门的 SaaS 产品,而 Marketing 和 Service 都是由自己的 ISV 在各自行业的解决方案。所以 Salesforce 已经从一家 SaaS 公司变成了一家 aPaaS 平台公司了。
搭建一个 aPaaS 平台是需要很长时间的,当然也可以基于一些公有云产品的 Serverless 方案实现现有系统的灵活性与扩展性,从而实现针对于不同客户的定制。
什么是 Serverless
Serverless 由两部分组成,Server 和 Less。
- 前者可以理解为其解决方案范围处在服务端;
- 后者可以译为少量的;
组合起来就是较少服务端干预的服务端解决方案。
与 Serverless 相对的是 Serverfull,比较下对应的概念可能更便于理解。
在 Serverfull 时代,研发交付流程一般有三个角色:RD,PM,QA。
RD 根据 PM 的 PRD 进行功能开发,交付到 QA 进行测试,测试完成之后发布到服务器。由运维人员规划服务器规格、数量、机房部署、节点扩缩容等,这种更多由人力处理的时代就是 Serverfull 时代。
之后进入了 DevOps 时代。这个时代运维自己开发一套运维控制台,可以让研发同学在控制台上自己进行服务观测、数据查询、运维处理等,运维同学的工作轻松了不少,这个阶段主要释放了运维同学的人力。
而到了 Serverless 时代,这套运维控制台能力越来越丰富,可以实现按配置的自动扩缩容、性能监控、DevOps 流水线等,同时侵入到研发流程侧,比如自动发布流水线、编译打包、代码质量监测、灰度发布、弹性扩缩等流程基本不需要人力处理了,这就是 Serverless 时代。
Serverless 怎么用
相信你有过这样的经历,在一个 Web 界面上,左侧写代码,右侧展示执行效果。
- 写的是代码块,代码数量不会特别大;
- 代码运行速度快;
- 支持多种编程语言;
- 可以支持不可预计的流量洪峰冲击。
以阿里云解决方案看下如何支持多语言架构:
抽象来说,前端只需要将代码片段和编程语言的标识传给 Server 端即可,等待响应结果。Server 端可以针对于不同编程语言进行 runtime 分类、预处理等工作。
Serverless 怎么做
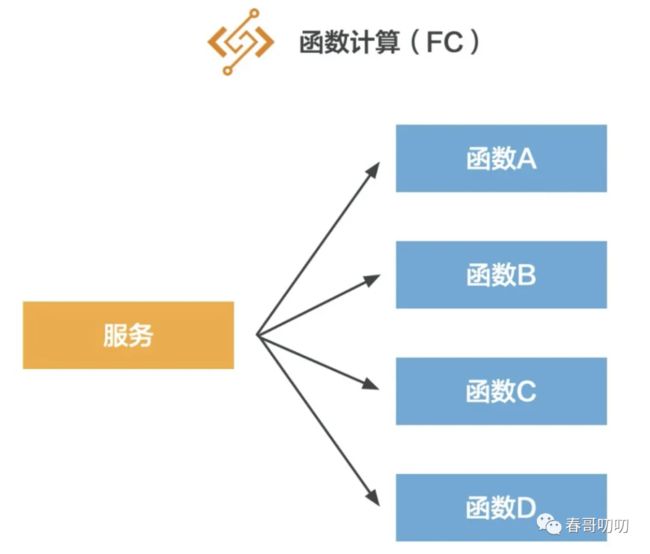
很多人把 Serverless 看做是 FC(function compute:函数计算),使用函数计算,无需业务自己搭建 IT 基础设施,只需要编码并上传代码。函数计算会按需为你准备好计算资源,弹性、可靠地运行,并提供 trace、日志查询、监控告警等治理能力。
比如:
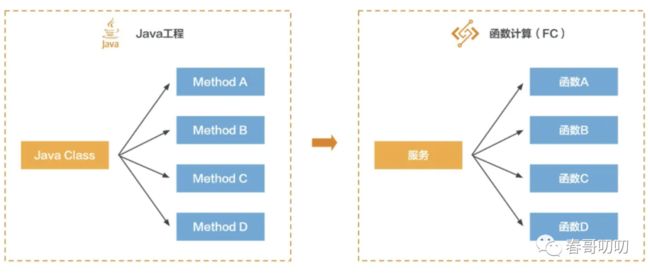
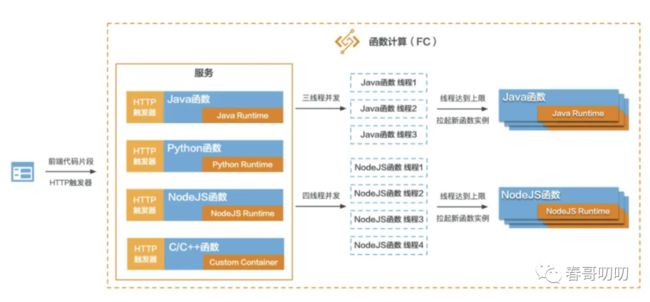
在 FC 中有服务和函数之分。一个服务可以包含多个函数。我们可以用微服务理解,我们通过 golang 或 java 搭建了一个微服务架构,而 FC 服务就是其中的类,FC 函数是类中的一个方法:
区别在于 Java 搭建的微服务只能运行 java 类代码,golang 的类只能运行 go 写的代码,而 FC 函数可以安装不同语言的 runtime,支持运行不同语言程序。
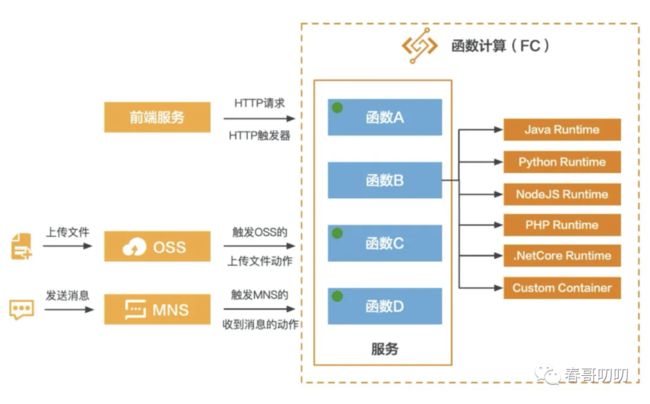
类比理解之后,我们再看下如何调用 FC 的函数,一般的 FC 解决方案里面都有一个触发器的概念。比如 HTTP 触发器、对象存储触发器、日志服务触发器、定时任务触发器、CDN 触发器、消息队列触发器等。触发器是对于 FC 函数调用的抽象收口,比如 HTTP 触发器一般都类比网关的一个 http 请求事件,或是指定对象存储路径下上传了一个图片,这些触发事件的入口都可以是触发器。
触发器产生事件之后可以调用 FC 函数,函数执行的逻辑可以是下载一张图片或是注册一个用户。
这样从触发器到 FC 函数逻辑处理就是一个 FC 的生命周期了。
那么 FC 是如何实现高可用的呢?
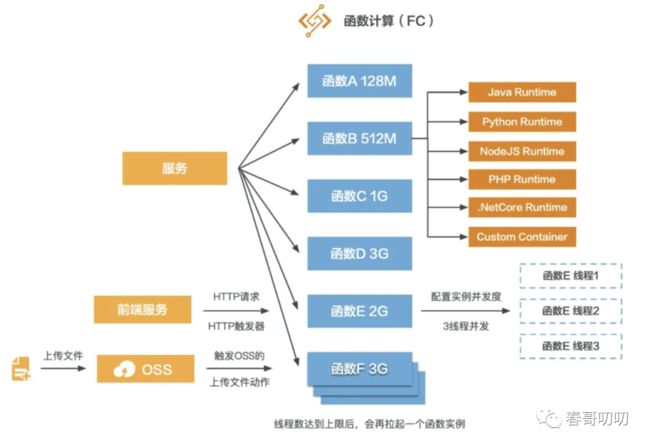
其实每个函数底层代码都是运行在一套 IaaS 平台上,使用 IaaS 资源,我们可以为每个函数设置运行代码时需要的内存配置即可,比如最小 128M,最大 3G 等。研发人员不需要关心代码运行在什么样的服务器上,不需要关心启动了多少函数实例支持当前场景,不需要关注背后的弹性扩缩问题,这些都被收敛在 FC 之后。
如图有两种高可用策略:
- 给函数设置并发实例数,比如 3 个,那么当有三个请求进来时,该函数只启动一个实例,但是会启动三个线程来运行逻辑;
- 线程达到上限后,会再拉起一个函数实例。
类似于线程池的方案。
那么 Serverless 如何提效呢?
- 效率高:如果新加了语言,只需要创建一个对应的 Runtime 的 FC 函数即可;
- 高可用:通过多线程、多实例两种方式保障高可用,且函数实例扩缩容完全由 FC 自助处理,不需要运维做任何配置;
- 成本低:在没有触发器请求时,函数实例不会被拉起,也不会计费,所以在流量低谷期间或者夜间时,FC 消耗的成本是非常低的。
如何在云平台创建一个 FC
1. 创建服务
- 首先新建一个服务名称;
- 选定服务部署的地区(背后帮助你就近部署在目标机房);
- 选择是否打开调试日志(开发过程开启,线上运行时可关闭)。
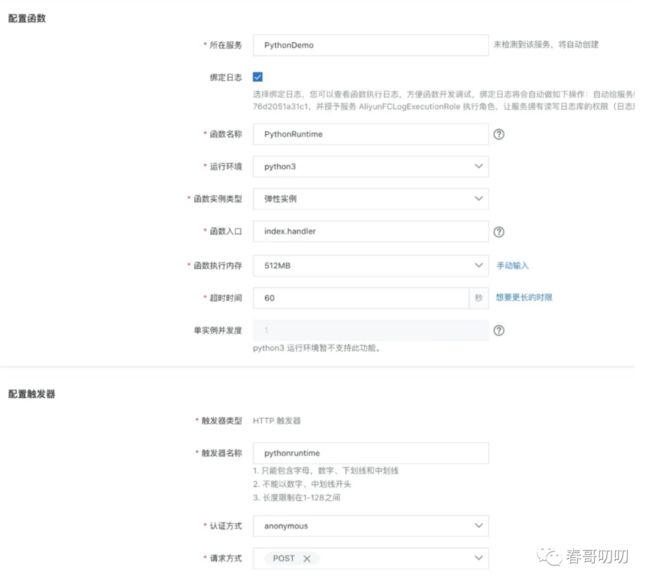
2. 创建函数
有了服务之后就可以创建函数了,比如选择基于 http 请求的函数。
- 选择函数绑定的服务;
- 设置函数名称;
- 选择 runtime 环境;
- 是否要求函数实例弹性;
- 函数入口(触发器直接调用的目标方法);
- 函数执行内存;
- 函数执行超时时间;
- 设置实例并发度。
配置触发器,比如选择了 HTTP 触发器,然后在触发器上绑定函数名称,由于是 http 访问,可以选择访问的鉴权、认证方式,以及请求方式 POST or GET。
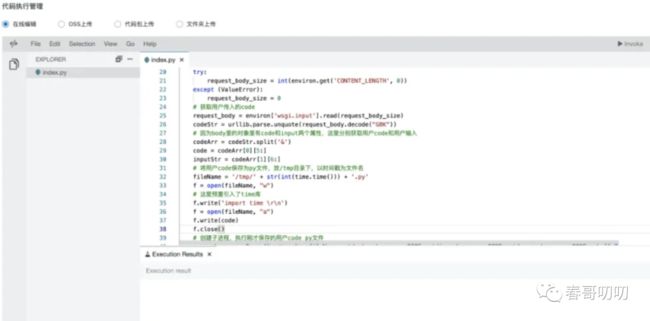
3. 代码编写
当函数创建好了之后,进入函数,可以看到描述、代码执行历史、触发器类型、日志查询页等。
如果是 HTTP 触发器,需要配置 http 触发路径。
可以看到就如前面介绍的那种,类似于类里面的一个函数,上下文请求会打到这里,直接执行。
Python 代码为例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import logging
import urllib.parse
import time
import subprocess
def handler(environ, start_response):
context = environ['fc.context']
request_uri = environ['fc.request_uri']
for k, v in environ.items():
if k.startswith('HTTP_'):
pass
try:
request_body_size = int(environ.get('CONTENT_LENGTH', 0))
except (ValueError):
request_body_size = 0
# 获取用户传入的code
request_body = environ['wsgi.input'].read(request_body_size)
codeStr = urllib.parse.unquote(request_body.decode("GBK"))
# 因为body里的对象里有code和input两个属性,这里分别获取用户code和用户输入
codeArr = codeStr.split('&')
code = codeArr[0][5:]
inputStr = codeArr[1][6:]
# 将用户code保存为py文件,放/tmp目录下,以时间戳为文件名
fileName = '/tmp/' + str(int(time.time())) + '.py'
f = open(fileName, "w")
# 这里预置引入了time库
f.write('import time \r\n')
f = open(fileName, "a")
f.write(code)
f.close()
# 创建子进程,执行刚才保存的用户code py文件
p = subprocess.Popen("python " + fileName, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, shell=True, encoding='utf-8')
# 通过标准输入传入用户的input输入
if inputStr != '' :
p.stdin.write(inputStr + "\n")
p.stdin.flush()
# 通过标准输出获取代码执行结果
r = p.stdout.read()
status = '200 OK'
response_headers = [('Content-type', 'text/plain')]
start_response(status, response_headers)
return [r.encode('UTF-8')]
流程如下:
- 前端传入代码片段,格式是字符串;
- 在 FC 函数中获取到传入的代码字符串,截取 code 内容和 input 内容;
- 将代码保存为一个 py 文件,以时间戳为文件命名,保存在 FC 函数的 /tmp 目录下,每个函数有自己独立的 /tmp 目录;
- import time 库代码;
- 通过 subprocess 创建子流程,以 shell 方式通过 py 命令执行保存在 /tmp 目录下的 py 文件;
- 最后读取执行结果返回给前端。
前端调用 FC 函数:
整个过程只需要前端将代码传入到 FC 函数里面,整个 Server 端各个环节都不需要研发与运维同学关心,体现了 Serverless 的精髓。
用 Serverless 协调工作流
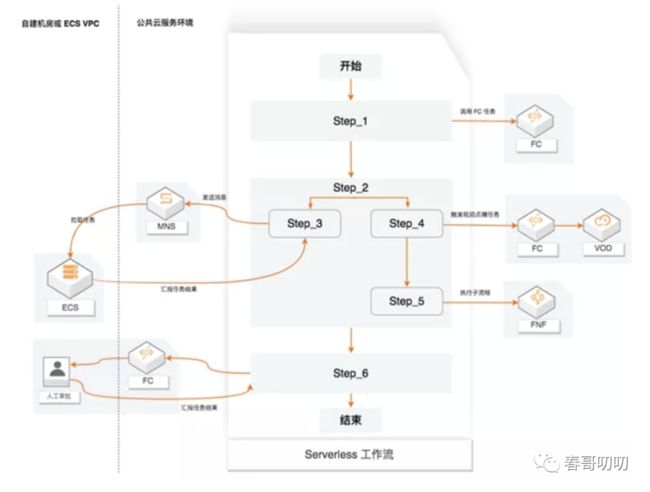
工作流可以用顺序、分支、并行等方式来编排任务执行,之后流程会按照设定好的步骤可靠地协调任务执行,跟踪每个任务的状态切换,并在必要时执行定义的重试逻辑,确保流程顺利执行。
工作流流程通过记录日志和审计方式来监视工作流的执行,便于流程的诊断与调试。
系统灵活性与扩展性的核心是服务可编排,所以我们需要做的是将现有系统内部用户希望定制的功能进行梳理、拆分、抽离、结合 FC 提供的无状态能力,将这些功能点进行编排,实现业务流程的定制。
需灵活配置工作流的业务
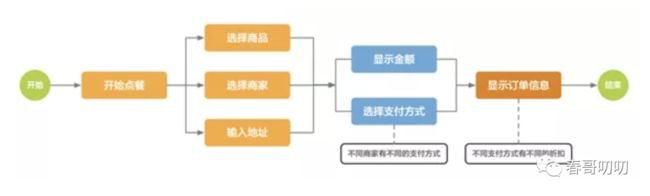
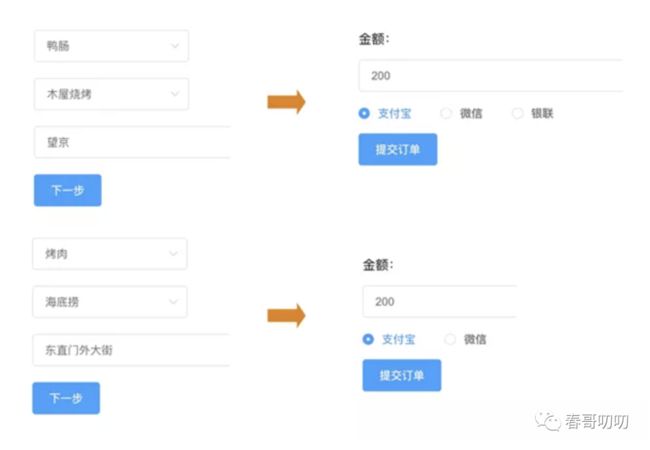
举个例子,比如餐饮场景下不同商家可以配置不同的支付方式,可以走微信支付、银联支付、支付宝支付。可以同时支持三家,也可以某一家,可以到付,也可以积分兑换等。如果没有一个好的配置化流程解决方案的话,系统中会出现大量硬编码规则判断条件,系统迭代疲于奔命,是个不可持续的过程。
有了 FC 搭建的工作流就可以很优雅地解决这种问题,比如规整流程如下:
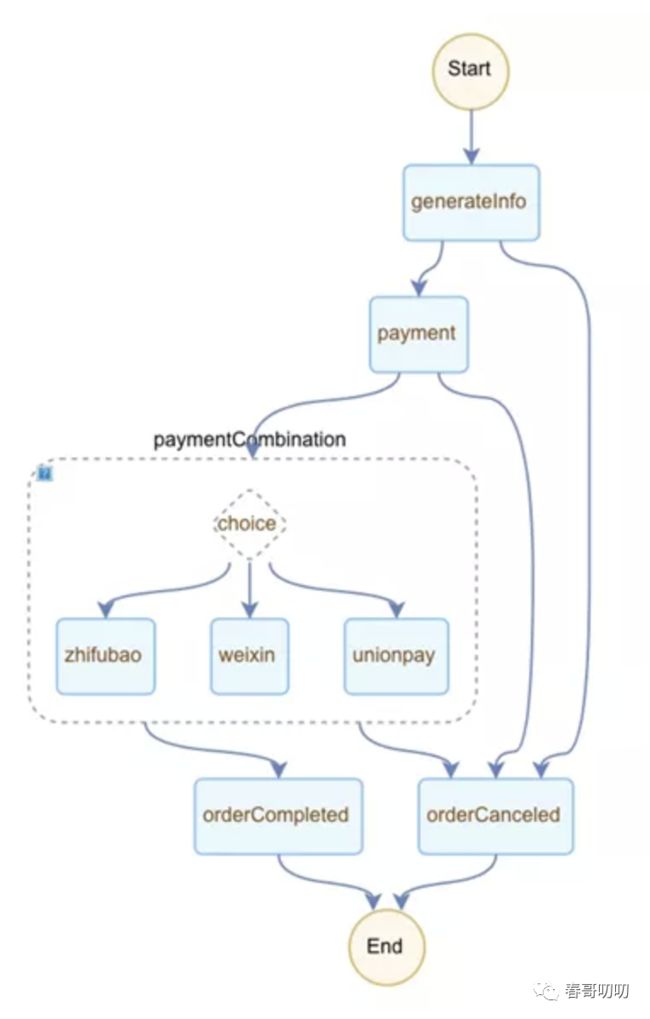
上面的流程是用户侧的流程,接下来需要转换成程序侧的流程,通过约束的 FDL 创建工作流,如图:
FDL 代码如下:
version: v1beta1
type: flow
timeoutSeconds: 3600
steps:
- type: task
name: generateInfo
timeoutSeconds: 300
resourceArn: acs:mns:::/topics/generateInfo-fnf-demo-jiyuan/messages
pattern: waitForCallback
inputMappings:
- target: taskToken
source: $context.task.token
- target: products
source: $input.products
- target: supplier
source: $input.supplier
- target: address
source: $input.address
- target: orderNum
source: $input.orderNum
- target: type
source: $context.step.name
outputMappings:
- target: paymentcombination
source: $local.paymentcombination
- target: orderNum
source: $local.orderNum
serviceParams:
MessageBody: $
Priority: 1
catch:
- errors:
- FnF.TaskTimeout
goto: orderCanceled
-type: task
name: payment
timeoutSeconds: 300
resourceArn: acs:mns:::/topics/payment-fnf-demo-jiyuan/messages
pattern: waitForCallback
inputMappings:
- target: taskToken
source: $context.task.token
- target: orderNum
source: $local.orderNum
- target: paymentcombination
source: $local.paymentcombination
- target: type
source: $context.step.name
outputMappings:
- target: paymentMethod
source: $local.paymentMethod
- target: orderNum
source: $local.orderNum
- target: price
source: $local.price
- target: taskToken
source: $input.taskToken
serviceParams:
MessageBody: $
Priority: 1
catch:
- errors:
- FnF.TaskTimeout
goto: orderCanceled
- type: choice
name: paymentCombination
inputMappings:
- target: orderNum
source: $local.orderNum
- target: paymentMethod
source: $local.paymentMethod
- target: price
source: $local.price
- target: taskToken
source: $local.taskToken
choices:
- condition: $.paymentMethod == "zhifubao"
steps:
- type: task
name: zhifubao
resourceArn: acs:fc:cn-hangzhou:your_account_id:services/FNFDemo-jiyuan/functions/zhifubao-fnf-demo
inputMappings:
- target: price
source: $input.price
- target: orderNum
source: $input.orderNum
- target: paymentMethod
source: $input.paymentMethod
- target: taskToken
source: $input.taskToken
- condition: $.paymentMethod == "weixin"
steps:
- type: task
name: weixin
resourceArn: acs:fc:cn-hangzhou:your_account_id:services/FNFDemo-jiyuan.LATEST/functions/weixin-fnf-demo
inputMappings:
- target: price
source: $input.price
- target: orderNum
source: $input.orderNum
- target: paymentMethod
source: $input.paymentMethod
- target: taskToken
source: $input.taskToken
- condition: $.paymentMethod == "unionpay"
steps:
- type: task
name: unionpay
resourceArn: acs:fc:cn-hangzhou:your_account_id:services/FNFDemo-jiyuan.LATEST/functions/union-fnf-demo
inputMappings:
- target: price
source: $input.price
- target: orderNum
source: $input.orderNum
- target: paymentMethod
source: $input.paymentMethod
- target: taskToken
source: $input.taskToken
default:
goto: orderCanceled
- type: task
name: orderCompleted
resourceArn: acs:fc:cn-hangzhou:your_account_id:services/FNFDemo-jiyuan.LATEST/functions/orderCompleted
end: true
- type: task
name: orderCanceled
resourceArn: acs:fc:cn-hangzhou:your_account_id:services/FNFDemo-jiyuan.LATEST/functions/cancerOrder
示例体现了基于 Serverless 的 FC 可实现灵活工作流。
流程如何触发的呢?
在用户选择完商品、填完地址之后,通过拉取商品、订单上下文,可以自动化触发流程了。
在微服务背景下,很多能力不是闭环在单体代码逻辑之内,很多时候是多个业务系统的连接,比如串联多个 OpenAPI 接口实现全流程:
如想使用流程引擎需要进行相关的备案鉴权:
@Configuration
public class FNFConfig {
@Bean
public IAcsClient createDefaultAcsClient(){
DefaultProfile profile = DefaultProfile.getProfile(
"cn-xxx", // 地域ID
"ak", // RAM 账号的AccessKey ID
"sk"); // RAM 账号Access Key Secret
IAcsClient client = new DefaultAcsClient(profile);
return client;
}
}
startFNF 代码里面流程如何串联起来:
- 输入要启动的流程名称,比如每次订单编号作为启动流程实例名称;
- 流程启动后的流程实例名称;
- 启动输入参数,比如业务参数,比如一个 json 里面有商品、商家、地址、订单等上下文信息。
@GetMapping("/startFNF/{fnfname}/{execuname}/{input}")
public StartExecutionResponse startFNF(@PathVariable("fnfname") String fnfName,
@PathVariable("execuname") String execuName,
@PathVariable("input") String inputStr) throws ClientException {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("fnfname", fnfName);
jsonObject.put("execuname", execuName);
jsonObject.put("input", inputStr);
return fnfService.startFNF(jsonObject);
}
再看下 fnfService.startFNF:
@Override
public StartExecutionResponse startFNF(JSONObject jsonObject) throws ClientException {
StartExecutionRequest request = new StartExecutionRequest();
String orderNum = jsonObject.getString("execuname");
request.setFlowName(jsonObject.getString("fnfname"));
request.setExecutionName(orderNum);
request.setInput(jsonObject.getString("input"));
JSONObject inputObj = jsonObject.getJSONObject("input");
Order order = new Order();
order.setOrderNum(orderNum);
order.setAddress(inputObj.getString("address"));
order.setProducts(inputObj.getString("products"));
order.setSupplier(inputObj.getString("supplier"));
orderMap.put(orderNum, order);
return iAcsClient.getAcsResponse(request);
}
- 第一部分是启动流程;
- 第二部分是创建订单对下,并模拟入库。
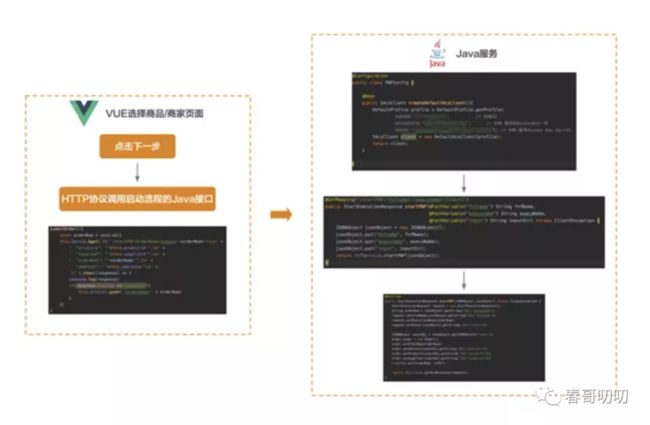
前端如何调用?
在前端当点击选择商品和商家页面中的下一步后,通过 GET 方式调用 HTTP 协议的接口 /startFNF/{fnfname}/{execuname}/{input}。和上面的 Java 方法对应。
- fnfname:要启动的流程名称;
- execuname:随机生成 uuid,作为订单的编号,也作为启动流程实例的名称;
- input:将商品、商家、订单号、地址构建为 JSON 字符串传入流程。
submitOrder(){
const orderNum = uuid.v1()
this.$axios.$get('/startFNF/OrderDemo-Jiyuan/'+orderNum+'/{\n' +
' "products": "'+this.products+'",\n' +
' "supplier": "'+this.supplier+'",\n' +
' "orderNum": "'+orderNum+'",\n' +
' "address": "'+this.address+'"\n' +
'}' ).then((response) => {
console.log(response)
if(response.message == "success"){
this.$router.push('/orderdemo/' + orderNum)
}
})
}
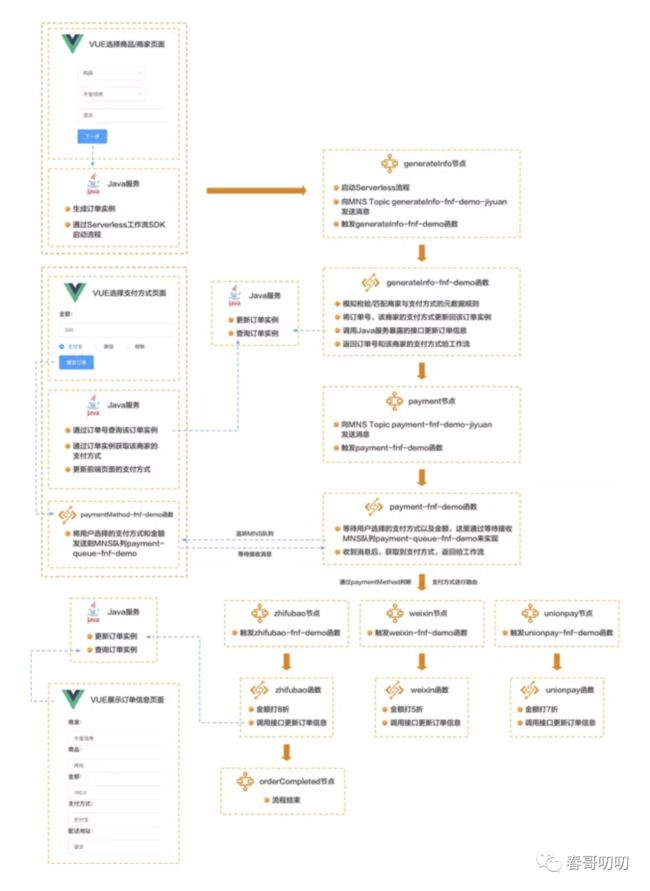
1. generateInfo 节点
先看下第一个 FDL 节点定义:
- type: task
name: generateInfo
timeoutSeconds: 300
resourceArn: acs:mns:::/topics/generateInfo-fnf-demo-jiyuan/messages
pattern: waitForCallback
inputMappings:
- target: taskToken
source: $context.task.token
- target: products
source: $input.products
- target: supplier
source: $input.supplier
- target: address
source: $input.address
- target: orderNum
source: $input.orderNum
- target: type
source: $context.step.name
outputMappings:
- target: paymentcombination
source: $local.paymentcombination
- target: orderNum
source: $local.orderNum
serviceParams:
MessageBody: $
Priority: 1
catch:
- errors:
- FnF.TaskTimeout
goto: orderCanceled
- name:节点名称;
- timeoutSeconds:超时时间,节点等待时长,超过时间后跳转到 goto 分支指向的 orderCanceled 节点;
- pattern:设置为 waitForCallback,表示需要等待确认;
- inputMappings:该节点入参;
- taskToken:Serverless 工作流自动生成的 Token;
- products:选择的商品;
- supplier:选择的商家;
- address:送餐地址;
- orderNum:订单号;
- outputMappings:该节点的出参;
- paymentcombination:该商家支持的支付方式;
- orderNum:订单号;
- catch:捕获异常,跳转到其他分支。
Serverless 工作流支持多个云服务集成,将其他服务作为任务步骤的执行单元。服务集成方式通过 FDL 表达式实现,在任务步骤中,可以使 用resourceArn 来定义集成的目标服务,使用 pattern 定义集成模式。
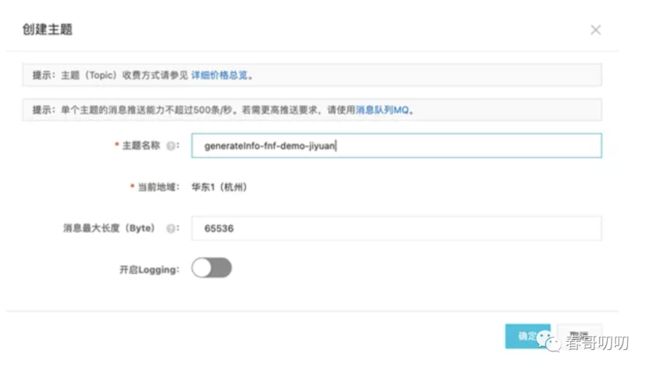
在 resourceArn 中配置 /topics/generateInfo-fnf-demo-jiyuan/messages 信息,就是集成了 MNS 消息队列服务,当 generateInfo 节点触发后会向 generateInfo-fnf-demo-jiyuanTopic 中发送一条消息。消息的正文和参数在 serviceParams 对象中 zhi'd 指定。MessageBody 是消息正文,配置 $ 表示通过输入映射 inputMappings 产生消息正文。
generateInfo-fnf-demo 函数:
向 generateInfo-fnf-demo-jiyuanTopic 中发送的这条消息包含了商品信息、商家信息、地址、订单号,表示一个下订单流程的开始,既然有发消息,那么必然有接受消息进行后续处理。在函数计算控制台,创建服务,在服务下创建名为 generateInfo-fnf-demo 的事件触发器函数,这里选择 Python Runtime:
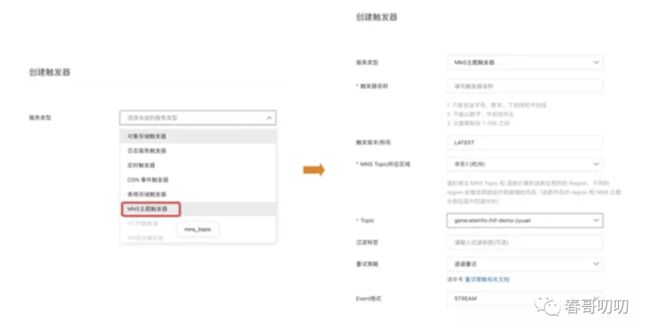
创建 MNS 触发器,选择监听 generateInfo-fnf-demo-jiyuanTopic:
打开消息服务 MNS 控制台,创建 generateInfo-fnf-demo-jiyuanTopic:
接下来写函数代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import logging
import json
import time
import requests
from aliyunsdkcore.client import AcsClient
from aliyunsdkcore.acs_exception.exceptions import ServerException
from aliyunsdkfnf.request.v20190315 import ReportTaskSucceededRequest
from aliyunsdkfnf.request.v20190315 import ReportTaskFailedRequest
def handler(event, context):
# 1. 构建Serverless工作流Client
region = "cn-hangzhou"
account_id = "XXXX"
ak_id = "XXX"
ak_secret = "XXX"
fnf_client = AcsClient(
ak_id,
ak_secret,
region
)
logger = logging.getLogger()
# 2. event内的信息即接受到Topic generateInfo-fnf-demo-jiyuan中的消息内容,将其转换为Json对象
bodyJson = json.loads(event)
logger.info("products:" + bodyJson["products"])
logger.info("supplier:" + bodyJson["supplier"])
logger.info("address:" + bodyJson["address"])
logger.info("taskToken:" + bodyJson["taskToken"])
supplier = bodyJson["supplier"]
taskToken = bodyJson["taskToken"]
orderNum = bodyJson["orderNum"]
# 3. 判断什么商家使用什么样的支付方式组合,这里的示例比较简单粗暴,正常情况下,应该使用元数据配置的方式获取
paymentcombination = ""
if supplier == "haidilao":
paymentcombination = "zhifubao,weixin"
else:
paymentcombination = "zhifubao,weixin,unionpay"
# 4. 调用Java服务暴露的接口,更新订单信息,主要是更新支付方式
url = "http://xx.xx.xx.xx:8080/setPaymentCombination/" + orderNum + "/" + paymentcombination + "/0"
x = requests.get(url)
# 5. 给予generateInfo节点响应,并返回数据,这里返回了订单号和支付方式
output = "{\"orderNum\": \"%s\", \"paymentcombination\":\"%s\" " \
"}" % (orderNum, paymentcombination)
request = ReportTaskSucceededRequest.ReportTaskSucceededRequest()
request.set_Output(output)
request.set_TaskToken(taskToken)
resp = fnf_client.do_action_with_exception(request)
return 'hello world'
代码分五部分:
构建 Serverless 工作流 Client;
event 内的信息即接受到 TopicgenerateInfo-fnf-demo-jiyuan 中的消息内容,将其转换为 Json 对象;
判断什么商家使用什么样的支付方式组合,这里的示例比较简单粗暴,正常情况下,应该使用元数据配置的方式获取。比如在系统内有商家信息的配置功能,通过在界面上配置该商家支持哪些支付方式,形成元数据配置信息,提供查询接口,在这里进行查询;
调用 Java 服务暴露的接口,更新订单信息,主要是更新支付方式;
给予 generateInfo 节点响应,并返回数据,这里返回了订单号和支付方式。因为该节点的 pattern 是 waitForCallback,所以需要等待响应结果。
generateInfo-fnf-demo 函数配置了 MNS 触发器,当 TopicgenerateInfo-fnf-demo-jiyuan 有消息后就会触发执行 generateInfo-fnf-demo 函数。
2. payment 节点
接下来是 payment 的 FDL 代码定义:
- type: task
name: payment
timeoutSeconds: 300
resourceArn: acs:mns:::/topics/payment-fnf-demo-jiyuan/messages
pattern: waitForCallback
inputMappings:
- target: taskToken
source: $context.task.token
- target: orderNum
source: $local.orderNum
- target: paymentcombination
source: $local.paymentcombination
- target: type
source: $context.step.name
outputMappings:
- target: paymentMethod
source: $local.paymentMethod
- target: orderNum
source: $local.orderNum
- target: price
source: $local.price
- target: taskToken
source: $input.taskToken
serviceParams:
MessageBody: $
Priority: 1
catch:
- errors:
- FnF.TaskTimeout
goto: orderCanceled
当流程流转到 payment 节点后,用户就可以进入到支付页面。
payment 节点会向 MNS 的 Topicpayment-fnf-demo-jiyuan 发送消息,会触发 payment-fnf-demo 函数。
payment-fnf-demo 函数:
payment-fnf-demo 函数的创建方式和 generateInfo-fnf-demo 函数类似。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import logging
import json
import os
import time
import logging
from aliyunsdkcore.client import AcsClient
from aliyunsdkcore.acs_exception.exceptions import ServerException
from aliyunsdkcore.client import AcsClient
from aliyunsdkfnf.request.v20190315 import ReportTaskSucceededRequest
from aliyunsdkfnf.request.v20190315 import ReportTaskFailedRequest
from mns.account import Account # pip install aliyun-mns
from mns.queue import *
def handler(event, context):
logger = logging.getLogger()
region = "xxx"
account_id = "xxx"
ak_id = "xxx"
ak_secret = "xxx"
mns_endpoint = "http://your_account_id.mns.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/"
queue_name = "payment-queue-fnf-demo"
my_account = Account(mns_endpoint, ak_id, ak_secret)
my_queue = my_account.get_queue(queue_name)
# my_queue.set_encoding(False)
fnf_client = AcsClient(
ak_id,
ak_secret,
region
)
eventJson = json.loads(event)
isLoop = True
while isLoop:
try:
recv_msg = my_queue.receive_message(30)
isLoop = False
# body = json.loads(recv_msg.message_body)
logger.info("recv_msg.message_body:======================" + recv_msg.message_body)
msgJson = json.loads(recv_msg.message_body)
my_queue.delete_message(recv_msg.receipt_handle)
# orderCode = int(time.time())
task_token = eventJson["taskToken"]
orderNum = eventJson["orderNum"]
output = "{\"orderNum\": \"%s\", \"paymentMethod\": \"%s\", \"price\": \"%s\" " \
"}" % (orderNum, msgJson["paymentMethod"], msgJson["price"])
request = ReportTaskSucceededRequest.ReportTaskSucceededRequest()
request.set_Output(output)
request.set_TaskToken(task_token)
resp = fnf_client.do_action_with_exception(request)
except Exception as e:
logger.info("new loop")
return 'hello world'
上面代码核心思路是等待用户在支付页面选择某个支付方式确认支付。使用了 MNS 的队列来模拟等待。循环等待接收队列 payment-queue-fnf-demo 中的消息,当收到消息后将订单号和用户选择的具体支付方式以及金额返回给 payment 节点。
前端选择支付方式页面:
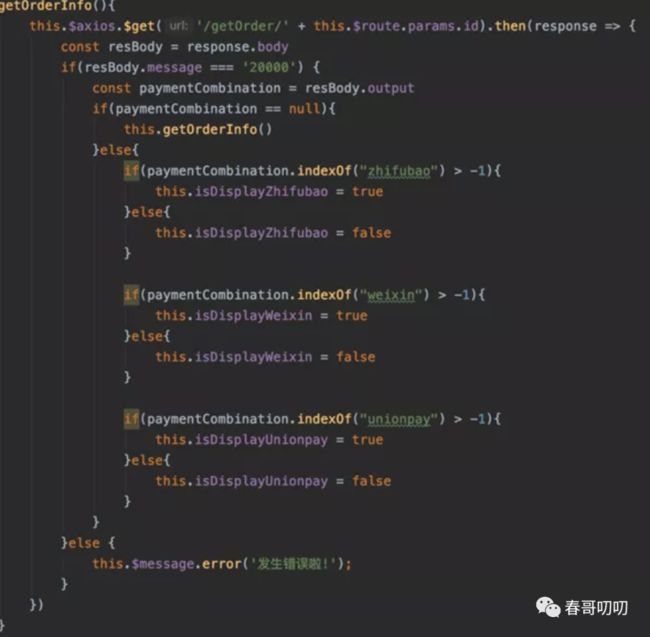
经过 generateInfo 节点后,该订单的支付方式信息已经有了,所以对于用户而言,当填完商品、商家、地址后,跳转到的页面就是该确认支付页面,并且包含了该商家支持的支付方式。
进入该页面后,会请求 Java 服务暴露的接口,获取订单信息,根据支付方式在页面上显示不同的支付方式。
代码片段如下:
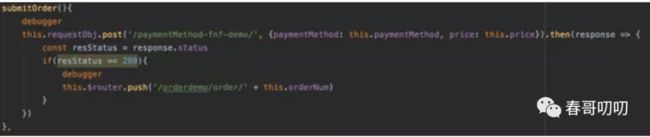
当用户选定某个支付方式点击提交订单按钮后,向 payment-queue-fnf-demo 队列发送消息,即通知 payment-fnf-demo 函数继续后续的逻辑。
使用了一个 HTTP 触发器类型的函数,用于实现向 MNS 发消息的逻辑,paymentMethod-fnf-demo 函数代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import logging
import urllib.parse
import json
from mns.account import Account # pip install aliyun-mns
from mns.queue import *
HELLO_WORLD = b'Hello world!\n'
def handler(environ, start_response):
logger = logging.getLogger()
context = environ['fc.context']
request_uri = environ['fc.request_uri']
for k, v in environ.items():
if k.startswith('HTTP_'):
# process custom request headers
pass
try:
request_body_size = int(environ.get('CONTENT_LENGTH', 0))
except (ValueError):
request_body_size = 0
request_body = environ['wsgi.input'].read(request_body_size)
paymentMethod = urllib.parse.unquote(request_body.decode("GBK"))
logger.info(paymentMethod)
paymentMethodJson = json.loads(paymentMethod)
region = "cn-xxx"
account_id = "xxx"
ak_id = "xxx"
ak_secret = "xxx"
mns_endpoint = "http://your_account_id.mns.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/"
queue_name = "payment-queue-fnf-demo"
my_account = Account(mns_endpoint, ak_id, ak_secret)
my_queue = my_account.get_queue(queue_name)
output = "{\"paymentMethod\": \"%s\", \"price\":\"%s\" " \
"}" % (paymentMethodJson["paymentMethod"], paymentMethodJson["price"])
msg = Message(output)
my_queue.send_message(msg)
status = '200 OK'
response_headers = [('Content-type', 'text/plain')]
start_response(status, response_headers)
return [HELLO_WORLD]
函数的逻辑很简单,就是向 MNS 的队列 payment-queue-fnf-demo 发送用户选择的支付方式和金额。
3. paymentCombination 节点
paymentCombination 节点是一个路由节点,通过判断某个参数路由到不同的节点,以 paymentMethod 作为判断条件:
- type: choice
name: paymentCombination
inputMappings:
- target: orderNum
source: $local.orderNum
- target: paymentMethod
source: $local.paymentMethod
- target: price
source: $local.price
- target: taskToken
source: $local.taskToken
choices:
- condition: $.paymentMethod == "zhifubao"
steps:
- type: task
name: zhifubao
resourceArn: acs:fc:cn-hangzhou:your_account_id:services/FNFDemo-jiyuan/functions/zhifubao-fnf-demo
inputMappings:
- target: price
source: $input.price
- target: orderNum
source: $input.orderNum
- target: paymentMethod
source: $input.paymentMethod
- target: taskToken
source: $input.taskToken
- condition: $.paymentMethod == "weixin"
steps:
- type: task
name: weixin
resourceArn: acs:fc:cn-hangzhou:your_account_id:services/FNFDemo-jiyuan.LATEST/functions/weixin-fnf-demo
inputMappings:
- target: price
source: $input.price
- target: orderNum
source: $input.orderNum
- target: paymentMethod
source: $input.paymentMethod
- target: taskToken
source: $input.taskToken
- condition: $.paymentMethod == "unionpay"
steps:
- type: task
name: unionpay
resourceArn: acs:fc:cn-hangzhou:your_account_id:services/FNFDemo-jiyuan.LATEST/functions/union-fnf-demo
inputMappings:
- target: price
source: $input.price
- target: orderNum
source: $input.orderNum
- target: paymentMethod
source: $input.paymentMethod
- target: taskToken
source: $input.taskToken
default:
goto: orderCanceled
流程是,用户选择支付方式后,通过消息发送给 payment-fnf-demo 函数,然后将支付方式返回,于是流转到 paymentCombination 节点通过判断支付方式流转到具体处理支付逻辑的节点和函数。
4. zhifubao 节点
看一个 zhifubao 节点:
choices:
- condition: $.paymentMethod == "zhifubao"
steps:
- type: task
name: zhifubao
resourceArn: acs:fc:cn-hangzhou:your_account_id:services/FNFDemo-jiyuan/functions/zhifubao-fnf-demo
inputMappings:
- target: price
source: $input.price
- target: orderNum
source: $input.orderNum
- target: paymentMethod
source: $input.paymentMethod
- target: taskToken
source: $input.taskToken
节点的 resourceArn 和之前两个节点的不同,这里配置的是函数计算中函数的 ARN,也就是说当流程流转到这个节点时会触发 zhifubao-fnf-demo 函数,该函数是一个事件触发函数,但不需要创建任何触发器。流程将订单金额、订单号、支付方式传给 zhifubao-fnf-demo 函数。
zhifubao-fnf-demo 函数:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import logging
import json
import requests
import urllib.parse
from aliyunsdkcore.client import AcsClient
from aliyunsdkcore.acs_exception.exceptions import ServerException
from aliyunsdkfnf.request.v20190315 import ReportTaskSucceededRequest
from aliyunsdkfnf.request.v20190315 import ReportTaskFailedRequest
def handler(event, context):
region = "cn-xxx"
account_id = "xxx"
ak_id = "xxx"
ak_secret = "xxx"
fnf_client = AcsClient(
ak_id,
ak_secret,
region
)
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.info(event)
bodyJson = json.loads(event)
price = bodyJson["price"]
taskToken = bodyJson["taskToken"]
orderNum = bodyJson["orderNum"]
paymentMethod = bodyJson["paymentMethod"]
logger.info("price:" + price)
newPrice = int(price) * 0.8
logger.info("newPrice:" + str(newPrice))
url = "http://xx.xx.xx.xx:8080/setPaymentCombination/" + orderNum + "/" + paymentMethod + "/" + str(newPrice)
x = requests.get(url)
return {"Status":"ok"}
代码逻辑很简单,接收到金额后,将金额打 8 折,然后将价格更新回订单。其他支付方式的节点和函数如法炮制,变更实现逻辑就可以。在这个示例中,微信支付打了 5 折,银联支付打 7 折。
完整流程
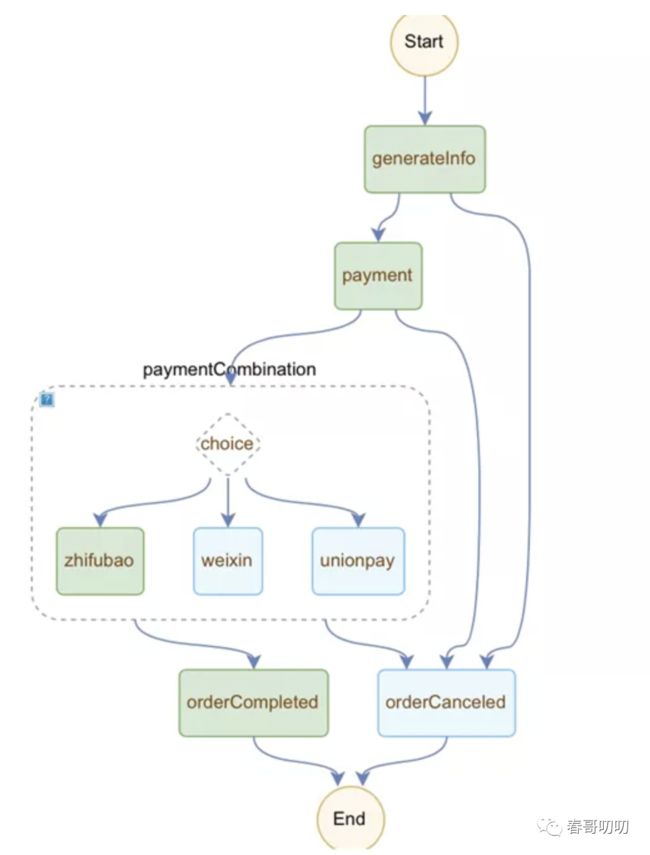
流程中的 orderCompleted 和 orderCanceled 节点没做什么逻辑,流程如下:
从 Serverless 工作流中看到的节点流转是这样的:
写在后面
以上是一个基于 Serverless 的 FC 实现的工作流,模拟构建了一个订单模块,规则包括:
- 配置商家和支付方式的元数据规则;
- 确认支付页面的元数据规则。
在实际项目中,需要将可定制的部分抽象为元数据描述,需要有配置界面供运营或商家定制支付方式也就是元数据规则,然后前后端页面基于元数据信息展示相应的内容。
如果之后需要接入新的支付方式,只需要在 paymentCombination 路由节点中确定好路由规则,之后增加对应的支付方式函数即可,通过增加元数据配置项,就可以在页面展示新加的支付方式,并路由到新的支付函数中。
经过整篇文章相信很多人对于 Serverless 的定义,以及如何基于现有的公有云系统的 Serverless 功能实现商业能力已经有了一定的了解,甚至基于此有实力的公司可以自研一套 Serverless 平台。当然思想是相同的,其实文中很多逻辑与理论不止适用于 Serverless,就是我们日常基于微服务的平台化/中台化解决方案,都可以从中获取设计营养在工作中应用。