springboot配置+日志+web
一、spring多模块开发优化
1.为什么需要?
idea中多模块开发,必须依赖于父亲模块,但是我们项目也必须是boot的parent,所以要在项目的父模块中管理boot的版本以来
2.怎么实现?
父级maven模块中:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-dependencies
2.0.5.RELEASE
pom
import
3.多模块的打jar包支持
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
cn.itsource.springboot.HelloApplication
repackage
如果依赖父亲是spring-boot-starter-parent,就不需要添加,在里面已经配置了
二、spring boot配置
1.引入
前面我们看到访问的端口是8080,我们想把他改为9090,可以不,当然可以。在修改之前先学习一下关于配置文件的知识
2.配置文件类型-yml
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件,配置文件名是固定的;
•application.properties -传统方式,不太优美
•application.yml-推荐使用
配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值;SpringBoot在底层都给我们自动配置好;
YAML做配置一门语言:
以前的配置文件;大多都使用的是 xxxx.xml文件还有properties;
YAML:以数据为中心,比json、xml等更适合做配置文件;
YAML:配置例子
server:
port: 8081
XML:
8081
properties:
server.port =8081
3.YML语法
3.1.基本语法
k:(空格)v:表示一对键值对(空格必须有);
以空格的缩进来控制层级关系;只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的
server:
port: 8081
path: /hello
属性和值也是大小写敏感;
3.2.值的写法
1)字面量:普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔)
k: v:字面直接来写;
字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号;
"":双引号;不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符;特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思
name: "zhangsan \n lisi":输出;zhangsan 换行 lisi
'':单引号;会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
name: ‘zhangsan \n lisi’:输出;zhangsan \n lisi
2)k: v:在下一行来写对象的属性和值的关系;注意缩进
对象还是k: v的方式
friends:
lastName: zhangsan
age: 20
3)数组(List、Set):
用- 值表示数组中的一个元素
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
4.读取配置文件
4.1.准备配置文件
server:
port: 80
student:
name: 小王
age: 20
boss: false
birth: 2017/12/12
maps: {k1: v1,k2: 12}
lists:
- zs
- ww
cat:
name: 猫科
age: 9
4.2.读取
关于两种方法的比较:
 如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
@Component
//方式2:统一配置
//默认从application.yml或properties读取
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")
@PropertySource(value={"classpath:person.properties"})
public class Student {
//取值方法一:@value(${xxx.yyy}),太繁琐
@Value("${student.name}")
private String name;
private Long age;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Map maps;
private List 读取指定配置文件:@PropertySource
@PropertySource(“classpath:指定配置文件”)
5.profile多环境支持
5.1.为什么要做多环境?
一套代码要在多种环境运行(开发,测试,上线),所以我们的配置文件要支持多种环境
5.2.多profile文件
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml
application-dev.yml
application-test.yml
默认使用application.properties的配置;
5.3.Yml多文档块模式
server:
port: 80
---
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev
5.4.激活特定环境
1、在配置文件中指定 spring.profiles.active=dev
2、命令行: 部署环境
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod;
可以直接在测试的时候,配置传入命令行参数
3、虚拟机参数; 开发环境
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
6.自动配置原理-怎么配置
解决怎么配置?
配置文件到底写什么?怎么写?
6.1.自动配置原理
1)SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能 @EnableAutoConfiguration
2)@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用:
- 利用EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入一些组件?
- 可以查看selectImports()方法的内容;
- List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);获取候选的配置
将 类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中;
每一个这样的 xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能;
3)以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理;
@Configuration //表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class) //启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;将配置文件中对应的值和HttpEncodingProperties绑定起来;并把HttpEncodingProperties加入到ioc容器中
@ConditionalOnWebApplication //Spring底层@Conditional注解(Spring注解版),根据不同的条件,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效; 判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效
@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器;
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = “spring.http.encoding”, value = “enabled”, matchIfMissing = true) //判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置 spring.http.encoding.enabled;如果不存在,判断也是成立的
//即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的;
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
//他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了
private final HttpEncodingProperties properties;
//只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Bean //给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断容器没有这个组件?
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST));
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}
根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效?
一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
4)、所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装者‘;配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
6.2.自动配置总结
精髓:
1)、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2)、我们看我们需要的功能有没有SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类;
3)、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件有,我们就不需要再来配置了)
4)、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们就可以在配置文件中指定这些属性的值;
xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;
给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;
使用SpringBoot;
1)、创建SpringBoot应用,选中我们需要的模块;
2)、SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来
3)、自己编写业务代码;
三、整合测试-springboottest
1.导入spring-boot-starter-test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
2.创建一个SpringBoot应用,并在下面创建一个Bean
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class);
}
}
@Controller
public class SpringBootController {
public void test(){
System.out.println("整合测试.....");
Date d=new Date();
System.out.println(d);
}
}
3.测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = App.class)//在哪里加载配置文件
public class TestSpringBoot {
@Autowired
private SpringBootController springBootController;
@Test
public void test(){
System.out.println(springBootController);
springBootController.test();
}
}
四、springboot日志支持
1.为什么需要日志框架?
通过日志的方式记录系统运行的过程或错误以便定位问题。
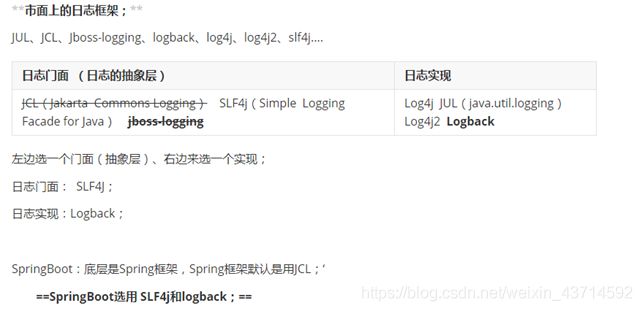
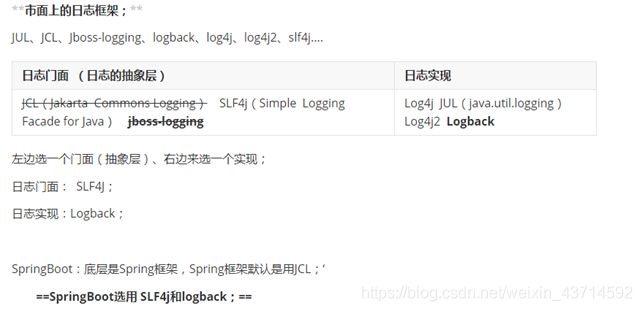
2.常见的日志框架
2.1.设计思想
1、System.out.println("");将关键数据打印在控制台;去掉?写在一个文件?
2、框架来记录系统的一些运行时信息;日志框架 ; zhanglogging.jar;log.ingo
3、高大上的几个功能?异步模式?自动归档?xxxx? zhanglogging-good.jar?
4、将以前框架卸下来?换上新的框架,重新修改之前相关的API;zhanglogging-prefect.jar;
5、JDBC---数据库驱动;
写了一个统一的接口层;日志门面(日志的一个抽象层);logging-abstract.jar;
给项目中导入具体的日志实现就行了;我们之前的日志框架都是实现的抽象层;
2.2.常见框架
3.Slf4j使用

 遗留问题
遗留问题
统一日志记录,即使是别的框架和我一起统一使用slf4j进行输出?
解决办法:
1、将系统中其他日志框架先排除出去;
2、用中间包来替换原有的日志框架;
3、我们导入slf4j其他的实现
4.springboot日志关系
1)、SpringBoot底层也是使用slf4j+logback的方式进行日志记录
2)、SpringBoot也把其他的日志都替换成了slf4j;
3)、中间替换包?
4)、如果我们要引入其他框架,一定要把这个框架的默认日志依赖移除掉。
1 springboot底层使用了slf4j来作为门面,logback是默认实现
2 其他框架日志被替换或者转换
1)排除
2)转换或替换
3)导入slf4j,logbak
上面的事情都是spring帮我们做了,只需要关心两件事件就ok
1)默认logback有哪些配置
2)切换其他日志实现 log4j2
5.logback日志使用
 日志输出格式:
日志输出格式:
%d表示日期时间,
%thread表示线程名,
%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度
%logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。
%msg:日志消息,
%n是换行符
–>
%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
修改配置
logging.level.cn.itsource=trace
#logging.path=
不指定路径在当前项目下生成springboot.log日志
可以指定完整的路径;
#logging.file=G:/springboot.log
在当前磁盘的根路径下创建spring文件夹和里面的log文件夹;使用 spring.log 作为默认文件
logging.path=/spring/log
在控制台输出的日志的格式
logging.pattern.console=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
指定文件中日志输出的格式
logging.pattern.file=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} === [%thread] === %-5level === %logger{50} ==== %msg%n
6.切换日志框架
五、SpringBoot web
1.入门-返回json
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/c01")
public class Controller01 {
//json字符串
@RequestMapping("/str")
@ResponseBody
public String jsonStr(){
return "webtest";
}
//json对象-日期特殊处理
@RequestMapping("/obj")
@ResponseBody
public Student jsonObj(){
return new Student(1L,"zs",new Date());
}
//json对象-日期特殊处理
@RequestMapping("/array")
@ResponseBody
public List jsonArray(){
return Arrays.asList(new Student(1L,"zs",new Date()),
new Student(2L,"ls",new Date()));
}
}
2.返回页面
2.1.常见的模板引擎
JSP、Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf
2.2.Thymeleaf入门
引入:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
3.0.9.RELEASE
2.2.2
使用:
@RestController
public class ThymeleafController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public ModelAndView hello(Model model){
model.addAttribute("hello","你好.....");
return new ModelAndView("test");
}
}
模板入门
成功
欢迎
![]()
3.springmvc配置
3.1.自动配置
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.10.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-developing-web-applications
3.2.静态资源配置
分析
1)所有 /webjars/** ,都去 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 找资源;==
webjars:以jar包的方式引入静态资源;
http://www.webjars.org/
http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.3.1/dist/jquery.js
在访问的时候只需要写webjars下面资源的名称即可
org.webjars.bower
jquery
3.3.1
 2)访问当前项目的任何资源,都去静态资源的文件夹找映射。
2)访问当前项目的任何资源,都去静态资源的文件夹找映射。
“classpath:/META-INF/resources/”,
“classpath:/resources/”,
“classpath:/static/”,
“classpath:/public/”
“/”:当前项目的根路径
例如:localhost:8080/abc === 去静态资源文件夹里面找abc
3)、欢迎页; 静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面;被"/**"映射;==
localhost:8080/ 找index页面
4)、所有的 **/favicon.ico 都是在静态资源文件下找;==
注意: 改模板不需要重启
3.3.扩展springmvc配置
六、springboot+mybatis
1.整合mybatis
1.1.xml及注解版的实现
第一步,导入相关依赖
mysql驱动,mybatis依赖包,mysql分页PageHelper:
mysql
mysql-connector-java
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.1.1
第二步,创建启动类,扫描mapper文件
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("cn.itcast.mapper")
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class);
}
}
第三步,编写mapper文件
注解版:
public interface UserMapper {
@Insert("insert into user (name) values (#{name})")
void add(User user);
@Select("select * from user")
List get();
}
xml版:
public interface UserMapper {
void add(User user);
List get();
}
UserMapper.xml
insert into user (name) values (#{name})
测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = App.class)//在哪里加载配置文件
public class TestMybatis {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void test(){
userService.add(new User("zs"));
}
@Test
public void get(){
List users =userService.get();
System.out.println(users);
}
}
1.2.配置事务
声明式事务:
注解式事务:
1)事务管理器
2)开启注解,就是能够识别@Transactional
3)在要控制事务的Service的或方法上面加上@Transactional
建议:类级别为只读事务,需要写事务的方法上面加写事务
SpringBoot:注解式事务
所有配置springboot都已经实现了,只需打注解@Transactional即可。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS,readOnly = true)
1.3.使用PageHelper分页
PageHelper是mybatis一个分页插件,原理就是基于mybatis拦截器,可以用它完成分页
第一步,导包
com.github.pagehelper
pagehelper
4.1.0
第二步,配置
@Configuration
public class MyBatisPageConfiguration {
@Bean
public PageHelper pageHelper() {
System.out.println("MyBatisConfiguration.pageHelper()");
PageHelper pageHelper = new PageHelper();
Properties p = new Properties();
p.setProperty("offsetAsPageNum", "true");
p.setProperty("rowBoundsWithCount", "true");
p.setProperty("reasonable", "true");
pageHelper.setProperties(p);
return pageHelper;
}
}
第三步,使用
@Override
public List get() {
PageHelper.startPage(1,2);
return userMapper.get();
}
第四步,测试
@Test
public void getPage(){
Page users =(Page)userService.get();
System.out.println("当前页"+users.getPageNum());//当前页
System.out.println("每页显示条数"+users.getPageSize());
System.out.println(users);
}
1.4.获取自增ID
insert into user (name) values (#{name})
七、springboot启动分析
1.创建SpringApplication对象
initialize(sources);
private void initialize(Object[] sources) {
//保存主配置类
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));
}
//判断当前是否一个web应用
this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment();
//从类路径下找到META-INF/spring.factories配置的所有ApplicationContextInitializer;然后保存起来
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//从类路径下找到ETA-INF/spring.factories配置的所有ApplicationListener
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//从多个配置类中找到有main方法的主配置类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
2.运行run方法
原来的spring启动步骤:
第一步,启动Tomcat
第二步,启动Spring容器 DispatcherServlet(xml) 创建一个spring容器(WebApplicationContext)
第三步,把相关的组件纳入到spring容器,Controller就在spring中生效
在xml中还配置了service,controller,mapper的扫描
springboot启动步骤:
第一步,启动一个内置Tomcat
第二步, 创建一个spring容器
第三步,这个spring容器也管理子子孙孙包下面的组件
另外,由于自动配置功能,在我们使用某个功能基本不用做任何xml配置,它以javaconfig的方式,并且给我们做了自动,由于有一个main函数的入门,可以打jar,直接java-jar进行执行,让我们部署起来非常方便