PriorityQueue
一个基于优先级堆的无界优先级队列。
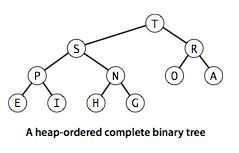
二叉堆
可视化操作:二叉堆
二叉堆(The binary heap)数据结构能够有效的支持基本的优先队列操作。key存储在一个数组中,其中每个key大于(或等于)指定的两个位置及以上的key
如果key节点比两个key子节点(如果有)大或等于表示这个二叉树是堆有序的。(子节点间无序)
位置
二叉堆使用完全二叉树在数组中实现,堆中节点的位置可以用数组下标很方便的表示。其中k表示数组下标
- 数组下标1开始
一个节点的父节点:k/2 向下取整
一个节点的两个子节点:左子节点2*k 右子节点2*k+1。
- 数组下标0开始
父节点:(k-1)/2 向下取整
左子节点:2*k+1
右子节点:2*(k+1) 即 (2*k+1)+1
最后一个父节点(只有存在子节点):(size/2)-1
PriorityQueue为下标0开始
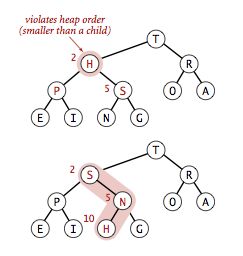
上浮(siftUp)
当一个key被添加到有序的二叉堆时,即插入到数组最后,此时会破坏堆的有序性,需要交换key使堆有序。假设使用最大优先队列即父节点大于或等于子节点
过程很简单,即比较key与父节点p位置为(k-1)/2的大小:(针对最大优先队列,如果是最小优先,颠倒符号即可)
- 如果key>p就交换两者的位置并与新的父节点继续比较
- 如果key<=p排序完成
下面是PriorityQueue的源码,注意是使用 最小堆,即自然顺序natural ordering
// 使用指定位置k的节点x向上使堆有序
private static void siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] es) {
Comparable key = (Comparable) x;
// 找到key在堆中的位置 当key的位置k是根节点位置0时终止
while (k > 0) {
// k位置的父节点位置
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = es[parent];
// 如果key比父节点大或相等时 此时堆有序 最小堆
if (key.compareTo((T) e) >= 0)
break;
// 将父节点e移动到子节点位置k上。此时会导致父子节点都为同一个值原来的父节点,子节点被覆盖
es[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
// 将key放到父节点位置k。
es[k] = key;
}
下沉(siftDown)
在堆中移除后,与二叉树的删除使用左右子树的最值子节点替换类似,对移除位置使用堆数组最后位置元素替换到移除位置上,然后重新平衡二叉堆。
假设使用最大优先队列即父节点大于或等于子节点
当数组最后一个元素被替换到删除位置时,这个叶子节点元素key必定小于删除位置的父节点p,所以需要与较大的子节点child比较
- 如果节点key < 较大的子节点child,交换key与child的位置,并继续与新的较大子节点比较
- 如果节点key >= 较大的子节点child,完成当前堆有序
如果节点key交换到了叶子节点k 下面是PriorityQueue的源码(最小优先队列为例,如果是最大优先队列需要交换符号) 在向下筛选时,叶子节点不需要再向下比较筛选,所以比较完最后一个父节点size/2 -1后 二叉堆有序的关键在于堆数组的元素的位置,在使堆有序的时候经常要使用父子节点和最后一个父节点的位置 构造器需要对堆数组和可能指定的比较器comparator初始化,还有如果使用集合初始化PriorityQueue时需要考虑集合是否有序。 下面使用两个典型的构造器说明,其他的构造器调用或调用相同的方法 通过集合初始化涉及到的私有方法实现: 注意 下面使用一个有序集合构造为优先队列的示例说明 有序数组本就堆有序 下面是模拟堆数组第一次出队的步骤: PriorityQueue的扩容比较简单,当数组较小时(<64)扩大为数组的两倍,否则将扩大50% 注意 移除第一个(最小)元素。使用最后一个元素替代位置0并下沉有序 移除任意位置的元素i。 判断i是否为最后一个元素,是则置为null即可 将最后一个元素l覆盖移除位置i,元素l的大小与i的父子节点不确定,不能简单的仅siftDown就认为堆有序 注意 返回该元素遍历,由于移除的关系,最后元素i已经不会被获取,所以提前返回该元素 注意 PriorityQueue的迭代器不保证顺序遍历 ,在需要顺序遍历时请使用 迭代器是在堆数组中一个个遍历,无法保证优先队列的顺序; 由于个别元素的特殊性,在删除元素时替换元素上浮,导致已经遍历的位置替换为新元素,所以这样的元素均放置在一个deque中,priorityqueue遍历完成后再遍历deque,无法保证顺序// 将指定元素在堆中位置为k的向下使堆有序
private static ((size/2)-1 < size/2),退出循环实现
构造器
一般初始化
/**
* Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the specified initial capacity
* that orders its elements according to the specified comparator.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity for this priority queue
* @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this
* priority queue. If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable
* natural ordering} of the elements will be used.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code initialCapacity} is
* less than 1
*/
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity,
Comparator comparator) {
// Note: This restriction of at least one is not actually needed,
// but continues for 1.5 compatibility
//至少容量为1是为了兼容性
if (initialCapacity < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.comparator = comparator;
}
集合初始化
/**
* Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} containing the elements in the
* specified collection. If the specified collection is an instance of
* a {@link SortedSet} or is another {@code PriorityQueue}, this
* priority queue will be ordered according to the same ordering.
* Otherwise, this priority queue will be ordered according to the
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} of its elements.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed
* into this priority queue
* @throws ClassCastException if elements of the specified collection
* cannot be compared to one another according to the priority
* queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any
* of its elements are null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public PriorityQueue(Collection c) {
// 如果是SortedSet
if (c instanceof SortedSet) {
SortedSet ss = (SortedSet) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator) ss.comparator();
// 从集合中初始化到堆数组中 检查集合元素是否存在null 由于本身是有序的 queue[0]一定是最值 不需要使堆完全有序
initElementsFromCollection(ss);
}
// 如果是优先队列
else if (c instanceof PriorityQueue) {
PriorityQueue pq = (PriorityQueue) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator) pq.comparator();
// 直接使用PriorityQueue.toArray的数组 堆完整有序
initFromPriorityQueue(pq);
}
else {
this.comparator = null;
// 将指定的集合添加到priorityqueue中并使堆有序
initFromCollection(c);
}
}
// 从指定集合Collection中 初始化堆数组 此时堆数组无序
private void initElementsFromCollection(Collection c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
// If c.toArray incorrectly doesn't return Object[], copy it.
// 保证底层数组queue为Object[]类型
if (a.getClass() != Object[].class)
a = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length, Object[].class);
int len = a.length;
// 如果有比较器 扫描容器数组中元素不含null元素
if (len == 1 || this.comparator != null)
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
if (a[i] == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.queue = a;
this.size = a.length;
}
/**
* Initializes queue array with elements from the given Collection.
*
* @param c the collection
*/
// 将指定的集合添加到priorityqueue中并使堆有序
private void initFromCollection(Collection c) {
// 将集合元素初始化到优先队列queue中
initElementsFromCollection(c);
// 使堆有序
heapify();
}
// 如果是PriorityQueue就直接使用toArray的数组 否则调用initFromCollection
private void initFromPriorityQueue(PriorityQueue c) {
if (c.getClass() == PriorityQueue.class) {
this.queue = c.toArray();
this.size = c.size();
} else {
initFromCollection(c);
}
}
static void constructoraddAllTest() {
SortedSet经过集合构造器的堆数组: [1, 3, 6, 7, 9, 12, 15]
1 <--出队
3 6
7 9 12 15 <--到堆顶替换
--------------------------------
15 <--用数组最后元素替换
3 6
7 9 12
--------------------------------
3
15 6 <--下沉 取子节点中小的交换
7 9 12
--------------------------------
3
7 6
15 9 12 <--完成下沉
--------------------------------
一次出队后堆数组: [3, 7, 6, 15, 9, 12, null]
扩容
/**
* Increases the capacity of the array.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// 旧数组容量
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
// 如果数组过小(<64)就扩大两倍,否则扩大一半50%
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
// 如果增加50%后超过最大容量,没有溢出就使用int最大或最大容量值
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// 复制到新数组长度为newCapaciry
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
添加
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
*
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be
* compared with elements currently in this priority queue
* according to the priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
// 扩容
if (i >= queue.length)
// i + 1用于判断是否溢出,当容量达到int和vm的限制时才有影响。i+1不会用于扩容容量size
grow(i + 1);
// 插入数组已有元素最后然后向上有序,i为最新位置
siftUp(i, e);
size = i + 1;
return true;
}
移除
public E poll() {
final Object[] es;
final E result;
// 如果数组第一个元素不为null
if ((result = (E) ((es = queue)[0])) != null) {
modCount++;
final int n;
// 最后一个元素
final E x = (E) es[(n = --size)];
es[n] = null;
// 还存在元素,使堆有序
if (n > 0) {
// 将位置0的元素下沉使堆有序
final Comparator cmp;
if ((cmp = comparator) == null)
siftDownComparable(0, x, es, n);
else
siftDownUsingComparator(0, x, es, n, cmp);
}
}
return result;
}
i的子节点<=l<=i的父节点 /**
* Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue,
* if it is present. More formally, removes an element {@code e} such
* that {@code o.equals(e)}, if this queue contains one or more such
* elements. Returns {@code true} if and only if this queue contained
* the specified element (or equivalently, if this queue changed as a
* result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this queue, if present
* @return {@code true} if this queue changed as a result of the call
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
int i = indexOf(o);
if (i == -1)
return false;
else {
removeAt(i);
return true;
}
}
/**
* Removes the ith element from queue.
*
* Normally this method leaves the elements at up to i-1,
* inclusive, untouched. Under these circumstances, it returns
* null. Occasionally, in order to maintain the heap invariant,
* it must swap a later element of the list with one earlier than
* i. Under these circumstances, this method returns the element
* that was previously at the end of the list and is now at some
* position before i. This fact is used by iterator.remove so as to
* avoid missing traversing elements.
*/
E removeAt(int i) {
// assert i >= 0 && i < size;
final Object[] es = queue;
modCount++;
int s = --size;
if (s == i) // removed last element
es[i] = null;
// 非最后一个元素
else {
// 最后一个元素
E moved = (E) es[s];
// 删除最后一位元素
es[s] = null;
// 将最后一个元素覆盖被移除的位置i并下沉
siftDown(i, moved);
// 无法下沉,未修改堆结构
if (es[i] == moved) {
// 上浮操作
siftUp(i, moved);
// 上浮成功,返回该对象,用于iterator遍历,forget me not
if (es[i] != moved)
return moved;
}
}
// 正常情况下都返回null,仅当迭代时被修改返回
return null;
}
removeAt返回moved对象,表示移除时最后一个元素被替换移除位置时被siftUp成功的元素,对于迭代器来说是致命的,无法保证元素正确被遍历,未遍历的元素(最后一个)已经被移动到已经遍历过的位置。 1
6 3
删除12--> 12 15 7 4 <--最后元素用于替换
-------------------------------
1
6 3
需要上浮--> 4 15 7
-------------------------------
1
4 3
完成 6 15 7
-------------------------------
获取
// 返回但不移除 队头元素
public E peek() {
return (E) queue[0];
}
迭代器
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this queue. The iterator
* does not return the elements in any particular order.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this queue
*/
public Iterator
Arrays.sort(pq.toArray())
并行迭代器Spliterator
参考