一、简单介绍
1.什么是UIDynamic
UIDynamic是从iOS 7开始引入的一种新技术,隶属于UIKit框架可以认为是一种物理引擎,能模拟和仿真现实生活中的物理现象如:重力、弹性碰撞等现象
2.物理引擎的价值
广泛用于游戏开发,经典成功案例是“愤怒的小鸟”,让开发人员可以在远离物理学公式的情况下,实现炫酷的物理仿真效果提高了游戏开发效率,产生更多优秀好玩的物理仿真游戏
3.知名的2D物理引擎
Box2d
Chipmunk
二、使用步骤
要想使用UIDynamic来实现物理仿真效果,大致的步骤如下:
1.创建一个物理仿真器(顺便设置仿真范围)
2.创建相应的物理仿真行为(顺便添加物理仿真元素)
3.将物理仿真行为添加到物理仿真器中开始仿真
三、相关说明
1.三个概念
- 谁要进行物理仿真?
物理仿真元素(Dynamic Item) - 执行怎样的物理仿真效果?怎样的动画效果?
物理仿真行为(Dynamic Behavior) - 让物理仿真元素执行具体的物理仿真行为
物理仿真器(Dynamic Animator)
2.物理仿真元素
注意:
不是任何对象都能做物理仿真元素
不是任何对象都能进行物理仿真
物理仿真元素要素:
任何遵守了UIDynamicItem协议的对象
UIView默认已经遵守了UIDynamicItem协议,因此任何UI控件都能做物理仿真
UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes类默认也遵守UIDynamicItem协议
3.物理仿真行为
(1)UIDynamic提供了以下几种物理仿真行为
UIGravityBehavior:重力行为
UICollisionBehavior:碰撞行为
UISnapBehavior:捕捉行为
UIPushBehavior:推动行为
UIAttachmentBehavior:附着行为
UIDynamicItemBehavior:动力元素行为
(2)物理仿真行为须知
上述所有物理仿真行为都继承自UIDynamicBehavior,所有的UIDynamicBehavior都可以独立进行组合使用多种行为时,可以实现一些比较复杂的效果
4.物理仿真器
(1)物理仿真器须知
它可以让物理仿真元素执行物理仿真行为
它是UIDynamicAnimator类型的对象
(2)UIDynamicAnimator的初始化
- (instancetype)initWithReferenceView:(UIView *)view;
view参数:是一个参照视图,表示物理仿真的范围
5.物理仿真器的说明
(1)UIDynamicAnimator的常见方法
//移除之前添加过的所有物理仿真行为
- (void)addBehavior:(UIDynamicBehavior *)behavior;
//移除之前添加过的所有物理仿真行为
- (void)removeBehavior:(UIDynamicBehavior *)behavior;
//添加1个物理仿真行为
- (void)removeAllBehaviors;
(2)UIDynamicAnimator的常见属性
//参照视图
@property (nonatomic, readonly) UIView* referenceView;
//添加到物理仿真器中的所有物理仿真行为
@property (nonatomic, readonly, copy) NSArray* behaviors;
//是否正在进行物理仿真
@property (nonatomic, readonly, getter = isRunning) BOOL running;
//代理对象(能监听物理仿真器的仿真过程,比如开始和结束)
@property (nonatomic, assign) id
四、案例介绍
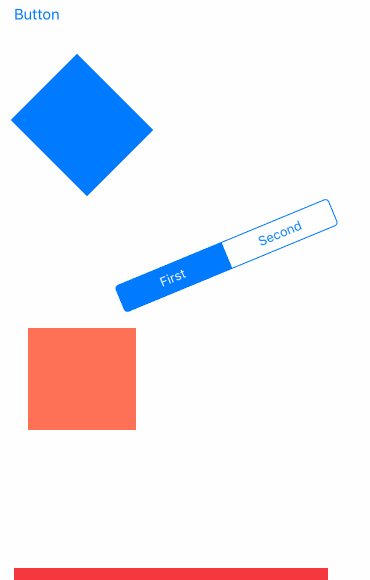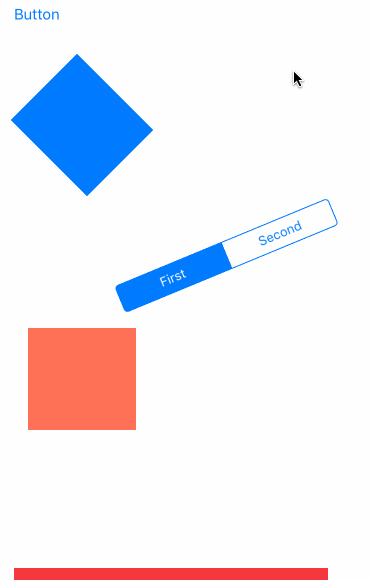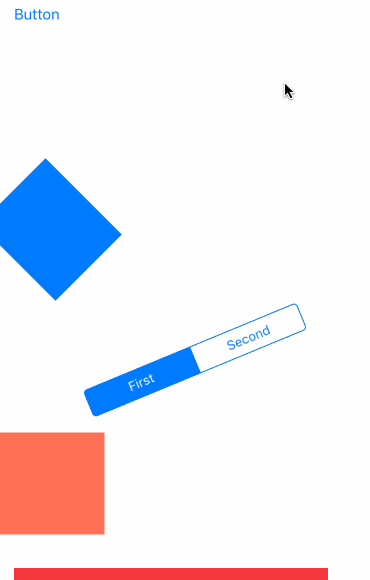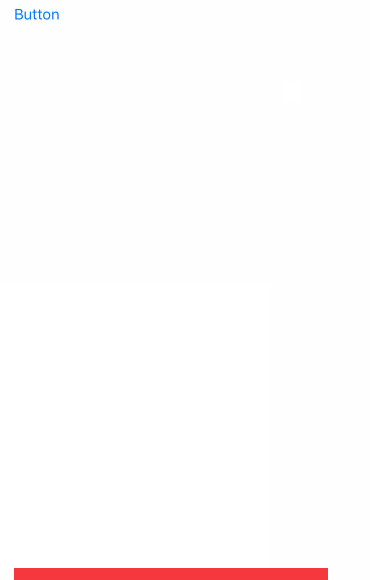
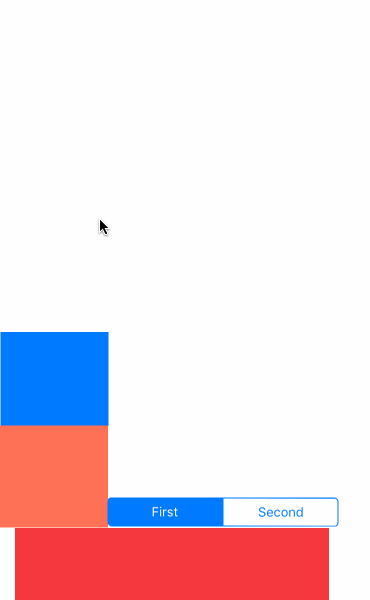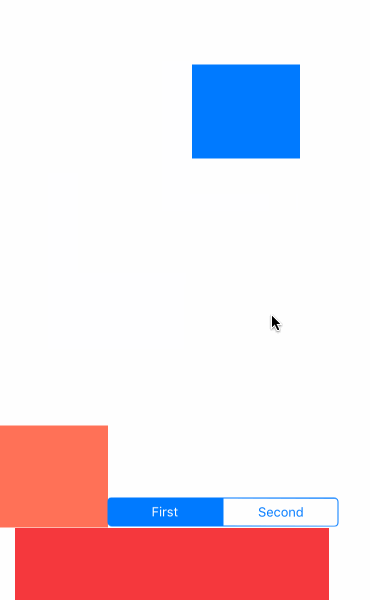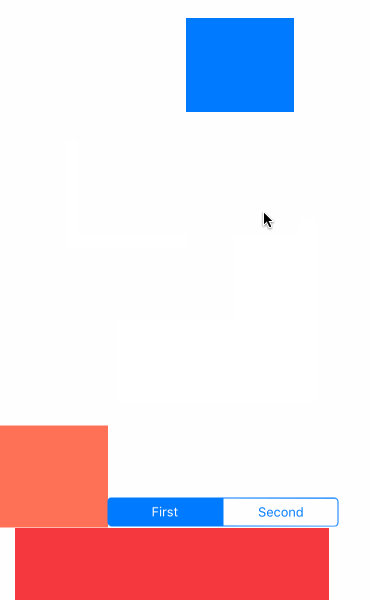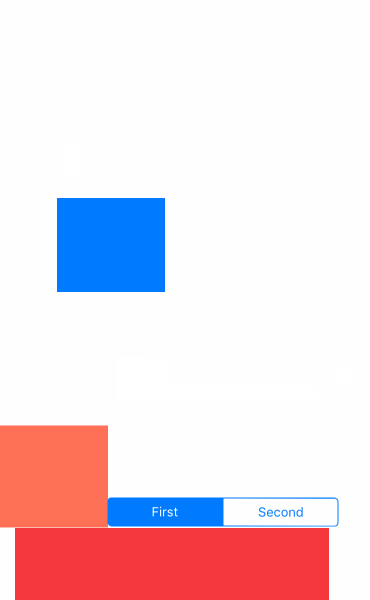
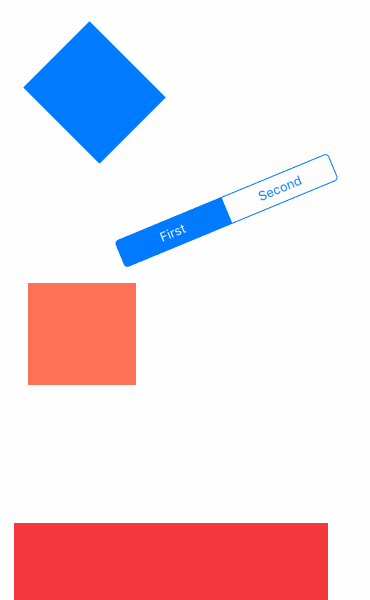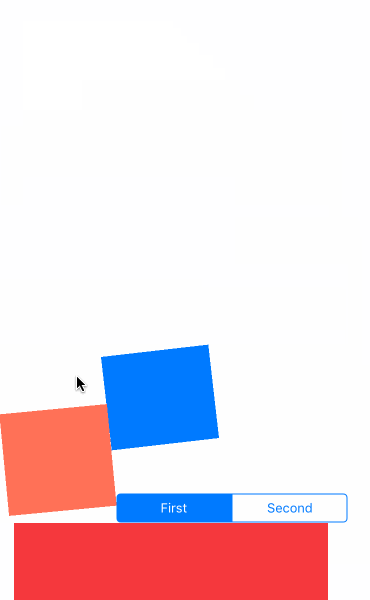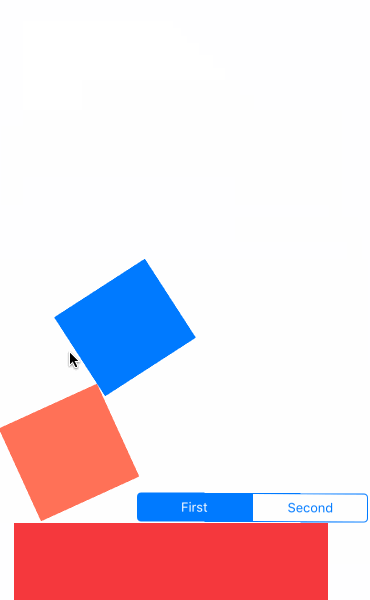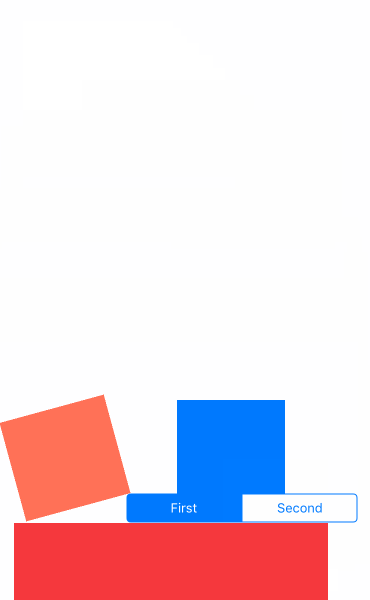
先看效果吧
- UIGravityBehavior:重力行为
- UICollisionBehavior:碰撞行为
- UISnapBehavior:捕捉行为
- UIPushBehavior:推动行为
- 复合效果
最后是代码
#import
@interface SecondViewController : UIViewController
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIView *blueView;
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIView *orangeView;
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UISegmentedControl *segmented;
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIView *redView;
@property (nonatomic,strong) UIDynamicAnimator *animator;
@end
#import "SecondViewController.h"
@interface SecondViewController ()
@property (nonatomic,strong)UISnapBehavior *snapBehavior;
@property (nonatomic,strong)UIPushBehavior *pushBehavior;
@property (nonatomic,strong)UIAttachmentBehavior *attachmentBehavior;
@end
@implementation SecondViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.blueView.transform = CGAffineTransformMakeRotation(M_PI_4);
self.segmented.transform = CGAffineTransformMakeRotation(-M_PI / 8);
if (!_pushBehavior) {
_pushBehavior = [[UIPushBehavior alloc]initWithItems:@[_blueView] mode:UIPushBehaviorModeContinuous];
}
_pushBehavior.active = YES;
_pushBehavior.pushDirection = CGVectorMake(10.0f, 10.0f);
_pushBehavior.magnitude = 1.0f;
[self.animator addBehavior:_pushBehavior];
}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent: (UIEvent *)event {
_pushBehavior.active = NO;
//创建重力行为
UIGravityBehavior *gravityBehavior = [[UIGravityBehavior alloc]init];
[gravityBehavior addItem:self.blueView];
[gravityBehavior addItem:self.orangeView];
[gravityBehavior addItem:self.segmented];
gravityBehavior.gravityDirection = CGVectorMake(-0.3f, 1.0f);
//加速度
gravityBehavior.magnitude = 3;
//创建碰撞行为
UICollisionBehavior *collisionBehavior = [[UICollisionBehavior alloc]init];
//碰撞类型为元素和边界
collisionBehavior.collisionMode = UICollisionBehaviorModeEverything;
CGFloat Y = self.view.frame.size.height - CGRectGetHeight(self.redView.frame);
CGFloat X = self.view.frame.size.width;
CGFloat height = self.view.frame.size.height;
//设置红色的View为底边界,左边框跟右边框作为边界
[collisionBehavior addBoundaryWithIdentifier:@"collision1" fromPoint:CGPointMake(0,Y) toPoint:CGPointMake(X, Y)];
[collisionBehavior addBoundaryWithIdentifier:@"collision2" fromPoint:CGPointMake(0, 0) toPoint:CGPointMake(0, height)];
[collisionBehavior addBoundaryWithIdentifier:@"collision3" fromPoint:CGPointMake(X,0) toPoint:CGPointMake(X, height)];
[collisionBehavior addItem:self.blueView];
[collisionBehavior addItem:self.segmented];
[collisionBehavior addItem:self.orangeView];
[self.animator addBehavior:collisionBehavior];
[self.animator addBehavior:gravityBehavior];
UIDynamicItemBehavior *itemBehavior = [[UIDynamicItemBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.blueView]];
[itemBehavior setElasticity:0.5];
[self.animator addBehavior:itemBehavior];
UITapGestureRecognizer *tap = [[UITapGestureRecognizer alloc]initWithTarget:self action:@selector(tapGesture:)];
[self.view addGestureRecognizer:tap];
}
- (void)tapGesture:(UITapGestureRecognizer *)gesture
{
CGPoint tapPoint = [gesture locationInView:self.view];
if (_snapBehavior) {
[self.animator removeBehavior:_snapBehavior];
_snapBehavior = nil;
}
_snapBehavior = [[UISnapBehavior alloc]initWithItem:self.blueView snapToPoint:tapPoint];
_snapBehavior.action = ^(){
NSLog(@"UISnapBehavior 在执行");
};
_snapBehavior.damping = 0.9;
[self.animator addBehavior:_snapBehavior];
}
- (UIDynamicAnimator *)animator{
if (_animator == nil) {
_animator = [[UIDynamicAnimator alloc]init];
}
return _animator;
}
- (void)panGestureRecognizer:(UIPanGestureRecognizer *)gesture
{
CGPoint location = [gesture locationInView:self.view];
CGPoint imageLocation = [gesture locationInView:self.orangeView];
switch (gesture.state) {
case UIGestureRecognizerStateBegan:
{
NSLog(@"touch position %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(location));
NSLog(@"loction in image %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(imageLocation));
[self.animator removeAllBehaviors];
UIOffset centerOffset = UIOffsetMake(imageLocation.x - CGRectGetMidX(self.orangeView.bounds), imageLocation.y - CGRectGetMidY(self.orangeView.bounds));
_attachmentBehavior = [[UIAttachmentBehavior alloc]initWithItem:self.orangeView offsetFromCenter:centerOffset attachedToAnchor:location];
_attachmentBehavior.damping = 0.5;
_attachmentBehavior.frequency = 0.8;
[self.animator addBehavior:_attachmentBehavior];
}
break;
case UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded:
{
[self.animator removeBehavior:_attachmentBehavior];
}
break;
default:
{
[_attachmentBehavior setAnchorPoint:[gesture locationInView:self.view]];
}
break;
}
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
/*
#pragma mark - Navigation
// In a storyboard-based application, you will often want to do a little preparation before navigation
- (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender {
// Get the new view controller using [segue destinationViewController].
// Pass the selected object to the new view controller.
}
*/
@end
UIKit动力学的部分介绍完了.
最开始项目中只是用到了重力跟碰撞行为,参考学习了:UIDynamic 详细用法 中的案例.然后自己又展开了解了下UIKit动力学的知识,把捕捉行为,推动行为加了进去,做个完善.整理了一下.就是这样.