1、sed 工具简介
- sed Stream EDitor, 行编辑器
- 工具特性:sed是一种流编辑器,每次处理一行文本内容。
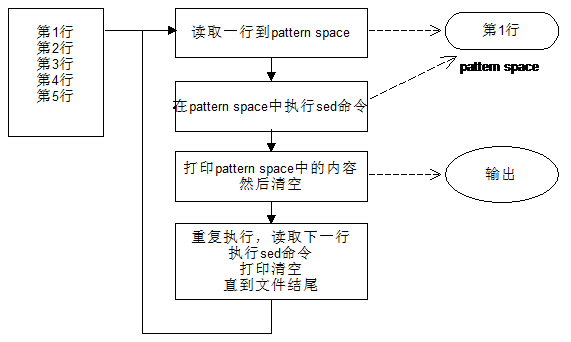
- 工作过程:将当前行储存至内存空间中,称作“模式空间”(pattern space)。在模式空间中对行进行编辑,将处理结果输出至屏幕。一般情况下,清空模式空间内容,然后读入下一行执行下一个循环,如此循环直至文本文件行尾。
- 功能:编辑一个或多个文件,简化对文件的反复操作,编写转换程序等
2、用法
sed[option]... 'script' inputfile...
常用选项:
-n:不输出模式空间内容到屏幕,即不自动打印
-e: 多点编辑
-f:/PATH/SCRIPT_FILE: 从指定文件中读取编辑脚本
-r: 支持使用扩展正则表达式
-i:文件原处编辑
-i.bak: 备份文件(后缀 .bak)并原处编辑
script:描述对文本的地址定界和编辑命令
3、地址定界
地址定界:
(1) 不给地址:对全文进行处理
(2) 单地址:
#: 指定第#行
/pattern/:被此处模式所能够匹配到的每一行
(3) 地址范围:
m,n:从第m行到第n行
m,+n:从第m行到第(m+n)行
/pat1/,/pat2/:从匹配pat1的行到匹配pat2的行
m,/pat1/:从第m行到匹配pat1的行
(4) ~:步进
1~2 奇数行:从1开始,每次步进2,即1,3,5,7···奇数列
2~2 偶数行:从2开始,每次步进2,即2,4,6,8···偶数列
4、编辑命令
d: 删除模式空间匹配的行,并立即启用下一轮循环
p:显示模式空间中的内容(仅打印符合条件的内容,本身是打印所有内容,一般是配合-n来配合使用以只显示符合条件的内容)
a \text:在指定行后面追加文本,支持使用\n实现多行追加
i \text:在行前面插入文本
c \text:替换行为单行或多行文本
w /path/somefile: 保存模式匹配的行至指定文件
r /path/somefile:读取指定文件的文本至模式空间中匹配到的行后
=: 为匹配的模式空间中的行打印行号
!:模式空间中匹配行取反处理
5、查找替换
s///:查找替换,支持使用其它分隔符,s@@@,s###
替换标记:
g: 行内全局替换
p: 显示替换成功的行
w /PATH/TO/SOMEFILE:将替换成功的行保存至文件中
6、sed执行流程图
7、举例
[root@centos6 app]#seq 11 |sed -n '1~2p' ---打印奇数行
1
3
5
7
9
11
[root@centos6 app]#seq 11 |sed -n '2~2p'
2
4
6
8
10
[root@centos6 app]#seq 5|sed 'axy'
1
xy
2
xy
3
xy
4
xy
5
xy
[root@centos6 app]#seq 5|sed 'a\ xy' ---\加不加都可以,但加上有的时候可以前面多个空格
1
xy
2
xy
3
xy
4
xy
5
xy
[root@centos6 app]#seq 5|sed '2,4axyz'
1
2
xyz
3
xyz
4
xyz
5
[root@centos6 app]#seq 5|sed '2axyz\n====\n++++' ---\n可以追加多行内容
1
2
xyz
====
++++
3
4
5
[root@centos6 ~]#sed '/^# Source/i alias yi="yum install"' .bashrc
# .bashrc
# User specific aliases and functions
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
alias rm='rm -i'
alias cp='cp -i'
alias mv='mv -i'
alias p='poweroff'
alias cdpack='cd /misc/cd/Packages/'
alias cdnet='cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/'
alias yi="yum install" ---在指定行的前面插入内容
# Source global definitions
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi
[root@centos6 ~]#sed '/^SELINUX=enforcing/cSELINUX=permissive' /etc/selinux/config ---替换
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=permissive
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
[root@centos6 ~]#seq 5|sed '2,4w /app/f1' ---保存模式空间的内容到指定文件
1
2
3
4
5
[root@centos6 ~]#cd /app
[root@centos6 app]#ls
f1 mkdvdiso.sh
[root@centos6 app]#cat f1
2
3
4
[root@centos6 app]#seq 5|sed '3r /etc/issue' ---读取文件中的内容到指定的行后
1
2
3
CentOS release 6.9 (Final)
Kernel \r on an \m
\l
\n
\t
4
5
[root@centos6 app]#sed -e '/^#/d' -e '/^$/d' /etc/fstab ---多点编辑,表示以#开头的行和空行删除
UUID=07e3094b-c50d-4568-aee5-b2f76d91c962 / ext4 defaults 1 1
UUID=4a2031c3-8595-489e-bc6d-1e2c31860c7b /app ext4 defaults 1 2
UUID=a056e3b8-7cc2-4aea-9308-9b0744741394 /boot ext4 defaults 1 2
UUID=953b7594-f906-4d3e-8a3a-a6bb79b1c900 swap swap defaults 0 0
UUID=d027885d-e32b-42e7-94aa-329130282748 /home ext4 usrquota,grpquota 0 0
tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs defaults 0 0
devpts /dev/pts devpts gid=5,mode=620 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
[root@centos6 app]#vim sed.txt
1 /^s/d
[root@centos6 app]#cat f2
bbbdddd
sdfgggg
1234445
[root@centos6 app]#sed -f sed.txt f2 ---调用文件中的脚本
bbbdddd
1234445
[root@centos6 app]#sed -n 's/ext4/xfs/p' /etc/fstab --- p表示只打印匹配成功的行
UUID=07e3094b-c50d-4568-aee5-b2f76d91c962 / xfs defaults 1 1
UUID=4a2031c3-8595-489e-bc6d-1e2c31860c7b /app xfs defaults 1 2
UUID=a056e3b8-7cc2-4aea-9308-9b0744741394 /boot xfs defaults 1 2
UUID=d027885d-e32b-42e7-94aa-329130282748 /home xfs usrquota,grpquota 0 0
[root@centos6 app]#sed -nr 's/(bash)$/\1er/pg' p1---分组和后向引用
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/basher
mysql:x:27:27:MySQL Server:/var/lib/mysql:/bin/basher
zhang:x:500:500::/home/zhang:/bin/basher
tom:x:504:505::/home/tom:/bin/basher
libai:x:510:510::/home/libai:/bin/basher
dufu:x:512:512::/home/dufu:/bin/basher
zhaoritian:x:514:514::/home/zhaoritian:/bin/basher
gentoo:x:515:501:Gentoo Distribution:/home/gentoo:/bin/basher
natasha:x:516:516::/home/natasha:/bin/basher
harry:x:517:504::/home/harry:/bin/basher
alice:x:518:518::/home/alice:/bin/basher
bash:x:519:520::/home/bash:/bin/basher
testbash:x:520:521::/home/testbash:/bin/basher
sh:x:521:522::/home/sh:/bin/basher
[root@centos6 app]#sed -nr 's/bash$/&er/pg' p1 ---可以用&代替前面匹配的内容
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/basher
mysql:x:27:27:MySQL Server:/var/lib/mysql:/bin/basher
zhang:x:500:500::/home/zhang:/bin/basher
tom:x:504:505::/home/tom:/bin/basher
libai:x:510:510::/home/libai:/bin/basher
dufu:x:512:512::/home/dufu:/bin/basher
zhaoritian:x:514:514::/home/zhaoritian:/bin/basher
gentoo:x:515:501:Gentoo Distribution:/home/gentoo:/bin/basher
natasha:x:516:516::/home/natasha:/bin/basher
harry:x:517:504::/home/harry:/bin/basher
alice:x:518:518::/home/alice:/bin/basher
bash:x:519:520::/home/bash:/bin/basher
testbash:x:520:521::/home/testbash:/bin/basher
sh:x:521:522::/home/sh:/bin/basher
[root@centos6 app]#ifconfig eth2|sed -n -e '2s/^.*addr://' -e '2s/ .*$//p' ---取出IP地址
192.168.25.179
[root@centos6 app]#ifconfig eth2|sed '2!d;s/^.*addr://;s/ .*$//' ---分号表示可以执行多次操作;2!d表示第2行不执行d命令(除了第2行都执行d命令)
192.168.25.179
8、sed 工具高级用法
- 保持空间(hold space):一段内存空间,可以从模式空间读数据也可向模式空间写数据,为sed工具提供了更加灵活的使用方法。
- sed有模式空间和保持空间,sed的所有编辑操作都在模式空间中进行编辑,编辑完如果还没有编辑结束,等下还要做编辑,可以先挪到保持空间,然后模式空间做其它处理,处理完后再把保持空间中的行再挪回来,再进行处理。保持空间是个半成品仓库
- sed的高级编辑命令
P:打印模式空间开端至\n内容,并追加到默认输出之前
h:把模式空间中的内容覆盖至保持空间中
H:把模式空间中的内容追加至保持空间中
g:从保持空间取出数据覆盖至模式空间
G:从保持空间取出内容追加至模式空间
x:把模式空间中的内容与保持空间中的内容进行互换
n: 读取匹配到的行的下一行覆盖至模式空间
N:读取匹配到的行的下一行追加至模式空间
d:删除模式空间中的行
D:删除多行模式空间中的第一行
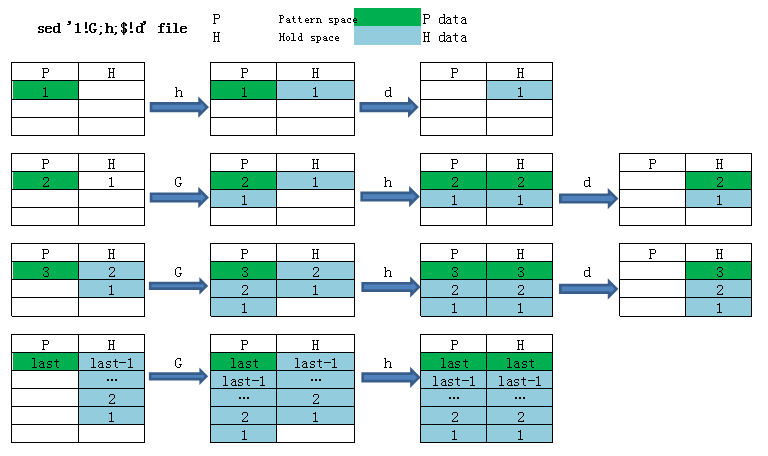
9、图解sed ‘1!G;h;$!d’ file
1!G 第一行不执行G命令,从第二行开始执行
$!d 最后一行不删除(其它行删除)
[root@localhost test]# cat file
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
[root@localhost test]# sed '1!G;h;$!d' file
3 3 3
2 2 2
1 1 1
图中P代表Pattern Space,H代表Hold Space。绿色代表pattern space中的数据,蓝色代表hold space中的数据。
10、举例
[root@localhost ~]#seq 11 | sed -n 'n;p' ---打印偶数行
2
4
6
8
10
[root@localhost ~]#seq 11 | sed '1!G;h;$!d' ---倒序输出行
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
[root@localhost ~]#seq 11 | sed 'N;D' ---打印最后一行
11
[root@localhost ~]#seq 11 | sed '$!N;$!D' --打印最后两行
10
11
[root@localhost ~]#seq 11 | sed '$!d' ---打印最后一行
11
[root@localhost ~]#seq 11 | sed 'G' ---每一行后添加一行空行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[root@localhost ~]#seq 11 | sed 'g' ---将每一行都清空为空行
sed '/^$/d;G' num ---所有空行删除,所有非空行之间添加一行空行
[root@localhost ~]#seq 11 | sed 'n;d' ---打印奇数行
1
3
5
7
9
11
[root@localhost ~]#seq 11 | sed -n '1!G;h;$p' ---倒序输出行
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1