2016年第七届蓝桥杯c c++B组
此为博主为记录刷题过程的代码,修正并且都是正确答案,如果你需要具体解析,请在下方留言,我将会在赛后修改回答你的问题!
2016年第七届蓝桥杯c /c++ B组
- 煤球数目
-
- 题目描述
- 代码
- 生日蜡烛
-
- 题目描述
- 代码
- 凑算式
-
- 题目描述
- 代码
- 快速排序
-
- 题目描述
- 答案
- 抽签
-
- 题目描述
- 答案
- 方格填数
-
- 题目描述
- 代码
- 剪邮票
-
- 题目描述
- 代码
- 四平方和
-
- 题目描述
- 代码
- 交换瓶子
-
- 题目描述
- 最大比例
-
- 题目描述
- 代码
煤球数目
题目描述
有一堆煤球,堆成三角棱锥形。具体:
第一层放1个,
第二层3个(排列成三角形),
第三层6个(排列成三角形),
第四层10个(排列成三角形),
…
如果一共有100层,共有多少个煤球?
请填表示煤球总数目的数字。
注意:你提交的应该是一个整数,不要填写任何多余的内容或说明性文字。
答案: 171700
代码
#include生日蜡烛
题目描述
某君从某年开始每年都举办一次生日party,并且每次都要吹熄与年龄相同根数的蜡烛。
现在算起来,他一共吹熄了236根蜡烛。
请问,他从多少岁开始过生日party的?
请填写他开始过生日party的年龄数。
注意:你提交的应该是一个整数,不要填写任何多余的内容或说明性文字。
答案:26
代码
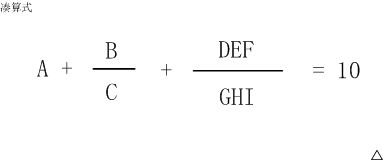
#include凑算式
题目描述
这个算式中A~I代表1~9的数字,不同的字母代表不同的数字。
比如:
6+8/3+952/714 就是一种解法,
5+3/1+972/486 是另一种解法。
这个算式一共有多少种解法?
注意:你提交应该是个整数,不要填写任何多余的内容或说明性文字。
答案:29
代码
#include快速排序
题目描述
排序在各种场合经常被用到。
快速排序是十分常用的高效率的算法。
其思想是:先选一个“标尺”,
用它把整个队列过一遍筛子,
以保证:其左边的元素都不大于它,其右边的元素都不小于它。
这样,排序问题就被分割为两个子区间。
再分别对子区间排序就可以了。
下面的代码是一种实现,请分析并填写划线部分缺少的代码。
#include 注意:只填写缺少的内容,不要书写任何题面已有代码或说明性文字。
答案
swap(a, p, j);
抽签
题目描述
X星球要派出一个5人组成的观察团前往W星。
其中:
A国最多可以派出4人。
B国最多可以派出2人。
C国最多可以派出2人。
…
那么最终派往W星的观察团会有多少种国别的不同组合呢?
下面的程序解决了这个问题。
数组a[] 中既是每个国家可以派出的最多的名额。
程序执行结果为:
DEFFF
CEFFF
CDFFF
CDEFF
CCFFF
CCEFF
CCDFF
CCDEF
BEFFF
BDFFF
BDEFF
BCFFF
BCEFF
BCDFF
BCDEF
…
(以下省略,总共101行)
#include 仔细阅读代码,填写划线部分缺少的内容。
注意:不要填写任何已有内容或说明性文字。
答案
f(a, k + 1, m - i, b);
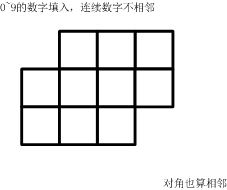
方格填数
题目描述
填入0~9的数字。要求:连续的两个数字不能相邻。
(左右、上下、对角都算相邻)
一共有多少种可能的填数方案?
请填写表示方案数目的整数。
注意:你提交的应该是一个整数,不要填写任何多余的内容或说明性文字。
答案: 1580
代码
#include剪邮票
题目描述
有12张连在一起的12生肖的邮票。
现在你要从中剪下5张来,要求必须是连着的。
(仅仅连接一个角不算相连)
比如,
请你计算,一共有多少种不同的剪取方法。
请填写表示方案数目的整数。
注意:你提交的应该是一个整数,不要填写任何多余的内容或说明性文字。
答案:116
代码
#include四平方和
题目描述
四平方和定理,又称为拉格朗日定理:
每个正整数都可以表示为至多4个正整数的平方和。
如果把0包括进去,就正好可以表示为4个数的平方和。
比如:
5 = 0^2 + 0^2 + 1^2 + 2^2
7 = 1^2 + 1^2 + 1^2 + 2^2
(^符号表示乘方的意思)
对于一个给定的正整数,可能存在多种平方和的表示法。
要求你对4个数排序:
0 <= a <= b <= c <= d
并对所有的可能表示法按 a,b,c,d 为联合主键升序排列,最后输出第一个表示法
程序输入为一个正整数N (N<5000000)
要求输出4个非负整数,按从小到大排序,中间用空格分开
例如,输入:
5
则程序应该输出:
0 0 1 2
再例如,输入:
12
则程序应该输出:
0 2 2 2
再例如,输入:
773535
则程序应该输出:
1 1 267 838
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗 < 256M
CPU消耗 < 3000ms
请严格按要求输出,不要画蛇添足地打印类似:“请您输入…” 的多余内容。
所有代码放在同一个源文件中,调试通过后,拷贝提交该源码。
注意: main函数需要返回0
注意: 只使用ANSI C/ANSI C++ 标准,不要调用依赖于编译环境或操作系统的特殊函数。
注意: 所有依赖的函数必须明确地在源文件中 #include , 不能通过工程设置而省略常用头文件。
提交时,注意选择所期望的编译器类型。
代码
#include交换瓶子
题目描述
有N个瓶子,编号 1 ~ N,放在架子上。
比如有5个瓶子:
2 1 3 5 4
要求每次拿起2个瓶子,交换它们的位置。
经过若干次后,使得瓶子的序号为:
1 2 3 4 5
对于这么简单的情况,显然,至少需要交换2次就可以复位。
如果瓶子更多呢?你可以通过编程来解决。
输入格式为两行:
第一行: 一个正整数N(N<10000), 表示瓶子的数目
第二行:N个正整数,用空格分开,表示瓶子目前的排列情况。
输出数据为一行一个正整数,表示至少交换多少次,才能完成排序。
例如,输入:
5
3 1 2 5 4
程序应该输出:
3
再例如,输入:
5
5 4 3 2 1
程序应该输出:
2
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗 < 256M
CPU消耗 < 1000ms
请严格按要求输出,不要画蛇添足地打印类似:“请您输入…” 的多余内容。
所有代码放在同一个源文件中,调试通过后,拷贝提交该源码。
注意: main函数需要返回0
注意: 只使用ANSI C/ANSI C++ 标准,不要调用依赖于编译环境或操作系统的特殊函数。
注意: 所有依赖的函数必须明确地在源文件中 #include , 不能通过工程设置而省略常用头文件。
提交时,注意选择所期望的编译器类型。
#include最大比例
题目描述
X星球的某个大奖赛设了M级奖励。每个级别的奖金是一个正整数。
并且,相邻的两个级别间的比例是个固定值。
也就是说:所有级别的奖金数构成了一个等比数列。比如:
16,24,36,54
其等比值为:3/2
现在,我们随机调查了一些获奖者的奖金数。
请你据此推算可能的最大的等比值。
输入格式:
第一行为数字 N (0
要求输出:
一个形如A/B的分数,要求A、B互质。表示可能的最大比例系数
测试数据保证了输入格式正确,并且最大比例是存在的。
例如,输入:
3
1250 200 32
程序应该输出:
25/4
再例如,输入:
4
3125 32 32 200
程序应该输出:
5/2
再例如,输入:
3
549755813888 524288 2
程序应该输出:
4/1
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗 < 256M
CPU消耗 < 3000ms
请严格按要求输出,不要画蛇添足地打印类似:“请您输入…” 的多余内容。
所有代码放在同一个源文件中,调试通过后,拷贝提交该源码。
注意: main函数需要返回0
注意: 只使用ANSI C/ANSI C++ 标准,不要调用依赖于编译环境或操作系统的特殊函数。
注意: 所有依赖的函数必须明确地在源文件中 #include , 不能通过工程设置而省略常用头文件。
提交时,注意选择所期望的编译器类型。
代码
#include