In Linux/Unix, the common premise is that everything is a file.
bin:
binaries, 存放二进制可执行文件
sbin:
super user binaries, 存放二进制可执行文件,只有 root 才能访问
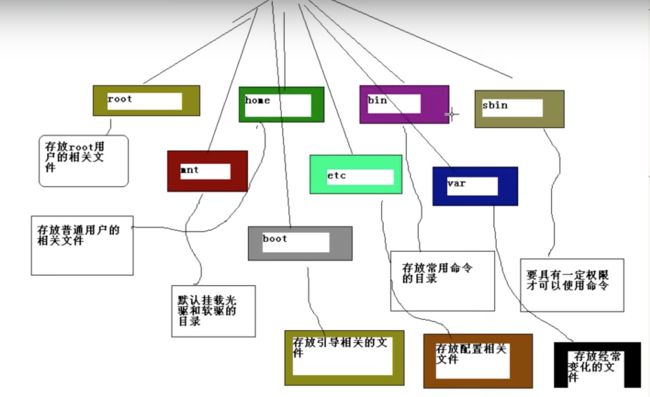
Linux File System Hierarchy
If you look at the Linux file hierarchy, you find the following :
/bin - Common binaries
/sbin - Binaries used for system administration are placed here.
/boot - Static files of the boot loader. Usually it contain the Linux kernel, Grub boot loader files and so on.
/dev - Device files such as your CD drive, hard disk, and any other physical device.
/home - User HOME directories are found here. In unices like FreeBSD, the HOME directories are found in /usr/home. And in Solaris it is in /export. So quite a big difference here.
/lib - Essential shared libraries and kernel modules.
/mnt - Temporary mount point useful for when you insert your USB stick and it gets mounted under /mnt. Though in Ubuntu and the likes, it is usually mounted under /media.
/var - Variable data, such as logs, news, mail spool files and so on which is constantly being modified by various programs running on your system.
/tmp - Temporary files are placed here by default.
/usr - The secondary hierarchy which contain its own bin and sbin sub-directories.
/etc - Usually contain the configuration files for all the programs that run on your Linux/Unix system.
/opt - Third party application packages which does not conform to the standard Linux file hierarchy can be installed here.
/srv - Contains data for services provided by the system.
And of course there is the /proc directory which does not actually reside on the disk.