linux--线程(3续)
目录
- 线程同步
-
- 条件变量
- 同步概念与竞态条件
- 条件变量函数
- 为什么pthread_cond_wait 需要互斥量?
- 生产者消费者模型
-
- 为何要使用生产者消费者模型
- 生产者消费者模型优点
- 基于BlockingQueue的生产者消费者模型
-
- BlockingQueue
线程同步
同步
同步:在保证数据安全的情况下(一般使用加锁实现),让多个执行流按照特定的顺序j进行临界资源的访问
为什么要同步?
多线程协同高效完成某些事情
- 互斥锁不同,条件变量是用来等待而不是用来上锁的。条件变量用来自动阻塞一个线程,直到某特殊情况发生为止。通常条件变量和互斥锁同时使用。条件变量分为两部分: 条件和变量。条件本身是由互斥量保护的。线程在改变条件状态前先要锁住互斥量。条件变量使我们可以睡眠等待某种条件出现。条件变量是利用线程间共享的全局变量进行同步的一种机制,主要包括两个动作:一个线程等待"条件变量的条件成立"而挂起;另一个线程使"条件成立"(给出条件成立信号)。条件的检测是在互斥锁的保护下进行的。如果一个条件为假,一个线程自动阻塞,并释放等待状态改变的互斥锁。如果另一个线程改变了条件,它发信号给关联的条件变量,唤醒一个或多个等待它的线程,重新获得互斥锁,重新评价条件。如果两进程共享可读写的内存,条件变量可以被用来实现这两进程间的线程同步。
条件变量
- 当一个线程互斥地访问某个变量时,它可能发现在其它线程改变状态之前,它什么也做不了。
- 例如一个线程访问队列时,发现队列为空,它只能等待,只到其它线程将一个节点添加到队列中。这种情况就需要用到条件变量。
同步概念与竞态条件
- 同步:在保证数据安全的前提下,让线程能够按照某种特定的顺序访问临界资源,从而有效避免饥饿问题,叫做同步
- 竞态条件:因为时序问题,而导致程序异常,我们称之为竞态条件。在线程场景下,这种问题也不难理解
条件变量函数
初始化
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
参数:
cond:要初始化的条件变量
attr:NULL
销毁
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond)
等待条件满足
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t restrict cond,pthread_mutex_trestrict mutex); 参数: cond:要在这个条件变量上等待 mutex:互斥量,后面详细解释
唤醒等待
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond); int
pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
2#include<unistd.h>
4 using namespace std;
5 pthread_mutex_t lock;
6 pthread_cond_t cond;
7
8 void *run1(void *args){
9 const char*name=(char*)args;
10 while(1){
11 pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&lock);
12 cout<<name<<"开始活动"<<endl;
13 }
14 }
15 void *run2(void*args){
16 const char*name=(char*)args;
17 while(1){
18 sleep(3);
19 pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
20 cout<<name<<"唤醒了"<<endl;
21 }
22 }
23 int main(){
24 pthread_mutex_init(&lock,NULL);
25 pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
26 pthread_t t1,t2;
27 pthread_create(&t1,NULL,run1,(void*)"pthread 1");
28 pthread_create(&t2,NULL,run2,(void*)"pthread 2");
29 pthread_join(t1,NULL);
30 pthread_join(t2,NULL);
31 pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
32 pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
33 return 0;
34 }
- 线程二唤醒等待,线程一检验信号是否满足满足就执行
cond
一个线程要在cond上等,一个要把通知消息发到cond
struct cond{
int value;//当前的值是否是成立的
wait_queue *head;//等待队列,都在等一个条件成立
}
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<pthread.h>
3 #include<unistd.h>
4 using namespace std;
5 pthread_mutex_t lock;
6 pthread_cond_t cond;
7
8 void *run1(void *args){
9 const char*name=(char*)args;
10 while(1){
11 pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&lock);
12 cout<<name<<"开始活动"<<endl;
13 }
14 }
15 void *run(void*args){
16 const char*name=(char*)args;
17 while(1){
18 sleep(3);
19 pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
20 cout<<name<<"唤醒了"<<endl;
21 }
22 }
23 int main(){
24 pthread_mutex_init(&lock,NULL);
25 pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
26 pthread_t t1,t2,t3,t4;
27 pthread_create(&t1,NULL,run,(void*)"pthread");
28 pthread_create(&t2,NULL,run1,(void*)"pthread 1");
29 pthread_create(&t3,NULL,run1,(void*)"pthread 2");
30 pthread_create(&t4,NULL,run1,(void*)"pthread 3");
31 pthread_join(t1,NULL);
32 pthread_join(t2,NULL);
33 pthread_join(t3,NULL);
34 pthread_join(t4,NULL);
35 pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
36 pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
37 return 0;
38 }
39
- 当多个线程在等待队列中,如果满足一个条件,就会执行,它们的顺序也是固定的。
为什么pthread_cond_wait 需要互斥量?
生产者消费者模型
为何要使用生产者消费者模型
- 生产者消费者模式就是通过一个容器来解决生产者和消费者的强耦合问题。生产者和消费者彼此之间不直接通讯,而通过阻塞队列来进行通讯,所以生产者生产完数据之后不用等待消费者处理,直接扔给阻塞队列,消费者不找生产者要数据,而是直接从阻塞队列里取,阻塞队列就相当于一个缓冲区,平衡了生产者和消费者的处理能力。这个阻塞队列就是用来给生产者和消费者解耦的。
生产者消费者模型优点
解耦 支持并发 支持忙闲不均
基于BlockingQueue的生产者消费者模型
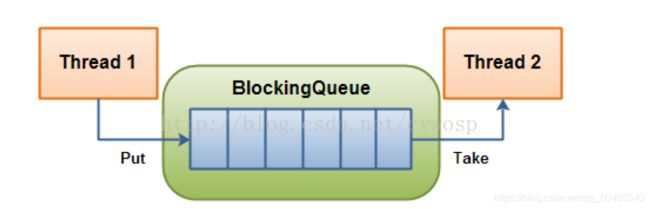
BlockingQueue
- 在多线程编程中阻塞队列(Blocking Queue)是一种常用于实现生产者和消费者模型的数据结构。其与普通的队列区别在于,当队列为空时,从队列获取元素的操作将会被阻塞,直到队列中被放入了元素;当队列满时,往队列里存放元素的操作也会被阻塞,直到有元素被从队列中取出(以上的操作都是基于不同的线程来说的,线程在对阻塞队列进程操作时会被阻塞)
BlockQueue.hpp
1 #ifndef _Queue_Block_H_
2 #define _Queue_Block_H_
3 #include<iostream>
4 #include<queue>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6 #include<pthread.h>
7 //using namespace std;
8 class blockqueue{
9 private:
10 std:: queue<int> q;
11 pthread_mutex_t lock;
12 size_t cap;
13 pthread_cond_t c_cond;//将来消费者,在该条件下等待
14 pthread_cond_t s_cond;//生产者在该条件下等待
15 public:
16 bool isfull(){
17 return q.size()>=cap;
18
19 }
20 bool iselpty(){
21 return q.size()<=cap&&0<=q.size();
22 }
23 void lockqueue(){
24 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
25 }
26 void unlockqueue(){
27 pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
28 }
29 void wakeupcon(){
30 std:: cout<<"生产者唤醒"<<std::endl;
31 pthread_cond_signal(&c_cond);
32 }
33
34
35 void wakepruct(){
36 std::cout<<"消费者唤醒"<<std::endl;
37 pthread_cond_signal(&s_cond);
38 }
39 void produstwait(){
40 std::cout<<"消费者等待"<<std::endl;
41 pthread_cond_wait(&s_cond,&lock);
42 }
43 void conaite(){
44 std::cout<<"生产者等待"<<std::endl;
45 pthread_cond_wait(&c_cond,&lock);
46 }
47 public:
48 blockqueue(int _cap){
49 cap=_cap;
50 pthread_mutex_init(&lock,NULL);
51 pthread_cond_init(&c_cond,NULL);
52 pthread_cond_init(&s_cond,NULL);
53 }
54 void in(int &in){
55 lockqueue();
56 if(isfull()){
57 wakepruct();
58 conaite();
59 }
60 q.push(in);
61 unlockqueue();
62 }
63 void out(int &out){
64 lockqueue();
65 if(iselpty()){
66 wakeupcon();
67 produstwait();
68 }
69 out=q.front();
70 q.pop();
71 unlockqueue();
72
73 }
74 ~blockqueue(){
75 pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
76 pthread_cond_destroy(&c_cond);
77 pthread_cond_destroy(&s_cond);
78 }
79 };
80 #endif
~
~
sst.cpp
1 #include"BlockQueue.hpp"
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 using namespace std;
4 void *run(void *args){
5 blockqueue *bq=(blockqueue*)args;
6 while(1){
7 int data=rand()%10+1;
8 bq->in(data);
9 cout<<"生产数据为:"<<data<<endl;
10 }
11 }
12 void *run1(void *args){
13 blockqueue * bq=(blockqueue*)args;
14 while(1){
15 int a=0;
16 bq->out(a);
17 cout<<"拿到数据为"<<a<<endl;
18 sleep(2);
19 }
20
21 }
22 int main(){
23 //www cout<<"hellow"<
24 blockqueue *bq=new blockqueue(5);
25 pthread_t t1,t2;
26 pthread_create(&t1,NULL,run,(void*)bq);
27 pthread_create(&t2,NULL,run1,(void*)bq);
28 pthread_join(t1,NULL);
29 pthread_join(t2,NULL);
30 }
1,为什么要等待?
2,你怎么知道条件不满足?
3,你要判断,就必须保证进入临界区的?
4,持有锁进入!!
5,wait时,必须释放锁。所以,调用该函数时lock会自动释放
当条件满足时进入临界区时就必须加锁。让线程重新持有该锁。
- 基于生产者消费者模型的多线程任务分配:
1 #ifndef _Queue_Block_H_
2 #define _Queue_Block_H_
3 #include<iostream>
4 #include<queue>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6 #include<pthread.h>
7 //using namespace std;
8 class Task{
9 private:
10 int a;
11 int b;
12 public:
13 Task(){
}
14 Task(int _a,int _b){
15 a=_a;
16 b=_b;
17 }
18 int add(){
19 return a+b;
20 }
21 };
22 class blockqueue{
23 private:
24 std:: queue<Task> q;
25 pthread_mutex_t lock;
26 size_t cap;
27 pthread_cond_t c_cond;//将来消费者,在该条件下等待
28 pthread_cond_t s_cond;//生产者在该条件下等待
29 public:
30 bool isfull(){
31 return q.size()>=cap;
32
33 }
34 bool iselpty(){
35 return q.empty();
36 }
37 void lockqueue(){
38 pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
39 }
40 void unlockqueue(){
41 pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
42 }
43 void wakeupcon(){
44 std:: cout<<"生产者唤醒"<<std::endl;
45 pthread_cond_signal(&c_cond);
46 }
47
48
49 void wakepruct(){
50 std::cout<<"消费者唤醒"<<std::endl;
51 pthread_cond_signal(&s_cond);
52 }
53 void produstwait(){
54 std::cout<<"消费者等待"<<std::endl;
55 pthread_cond_wait(&s_cond,&lock);
56 }
57 void conaite(){
58 std::cout<<"生产者等待"<<std::endl;
59 pthread_cond_wait(&c_cond,&lock);
60 }
61 public:
62 blockqueue(int _cap){
63 cap=_cap;
64 pthread_mutex_init(&lock,NULL);
65 pthread_cond_init(&c_cond,NULL);
66 pthread_cond_init(&s_cond,NULL);
67 }
68 void in(Task s){
69 lockqueue();
70 if(isfull()){
71 wakepruct();
72 conaite();
73 }
74 q.push(s);
75 unlockqueue();
76 }
77 void out(Task t){
78 lockqueue();
79 if(iselpty()){
80 wakeupcon();
81 produstwait();
82 }
83 t=q.front();
84 q.pop();
85 unlockqueue();
86
87 }
88 ~blockqueue(){
89 pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
90 pthread_cond_destroy(&c_cond);
91 pthread_cond_destroy(&s_cond);
92 }
93 };
94 #endif
~
~
~
~
1 #include"BlockQueue.hpp"
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 using namespace std;
4 void *run(void *args){
5 sleep(1);
6 blockqueue *bq=(blockqueue*)args;
7 while(1){
8 int x=rand()%10+1;
9 int y=rand()%5+1;
10 Task T(x,y);
11
12 bq->in(T);
13 cout<<"生产数据为:"<<x<<"+"<<y<<endl;
14 sleep(1);
15 }
16 }
17 void *run1(void *args){
18 blockqueue * bq=(blockqueue*)args;
19 while(1){
20 Task t;
21 bq->out(t);
22 cout<<"拿到数据为"<<t.add()<<endl;
23 //sleep(1);
24 }
25
26 }
27 int main(){
28 //www cout<<"hellow"<
29 blockqueue *bq=new blockqueue(5);
30 pthread_t t1,t2;
31 pthread_create(&t1,NULL,run,(void*)bq);
32 pthread_create(&t2,NULL,run1,(void*)bq);
33 pthread_join(t1,NULL);
34 pthread_join(t2,NULL);
35 }
~
- 线程一执行数据分配任务,线程二执行数据相加任务。