【学习打卡】Java高级(十)
学习目标:
Java 高级编程 学习打卡 第十天
学习内容:
1、一个IP对应着哪个类的一个对象?实例化这个类的两种方式是?两个常用的方法是?
InetAddress
InetAddress.getByName(String host);
InetAddress.getLocalHost();//获取本地ip
getHostName();
getHostAddress();
2、传输层的TCP协议和UDP协议的主要区别是?
TCP:可靠的数据传输(三次握手);进行大数据量的传输;效率低
UDP:不可靠;以数据报形式发送,数据报限定为64k;效率高
3、什么是URL,你能写一个URL吗?
URL:统一资源定位符
URL url = new URL(“http://192.168.14.100:8080/examples/hello.txt?username=Tom”);
4、谈谈你对对象序列化机制的理解
序列化过程和反序列化过程
5、对象要想实现序列化,需要满足哪几个条件
1. 实现接口:Serializable 标识接口
2. 对象所在的类提供常量:序列版本号
3. 要求对象的属性也必须是可序列化的。(基本数据类型、String:本身就已经是可序列化的。)
学习时间:
2021年5月04日
学习产出:
【学习打卡】Java高级 第一天
【学习打卡】Java高级 第二天
【学习打卡】Java高级 第三天
【学习打卡】Java高级 第四天
【学习打卡】Java高级 第五天
【学习打卡】Java高级 第六天
【学习打卡】Java高级 第七天
【学习打卡】Java高级 第八天
【学习打卡】Java高级 第九天
【学习打卡】Java高级 第十天
学习总结:
Path、Paths、Files的使用
1、NIO的使用说明
Java NIO (New IO,Non-Blocking IO)是从Java 1.4版本开始引入的一套新的IO API,可以替代标准的Java IO API。
NIO与原来的IO有同样的作用和目的,但是使用的方式完全不同,NIO支持面向缓冲区的(IO是面向流的)、基于通道的IO操作。
NIO将以更加高效的方式进行文件的读写操作。
Java API中提供了两套NIO,一套是针对标准输入输出NIO,另一套就是网络编程NIO。
随着 JDK 7 的发布,Java对NIO进行了极大的扩展,增强了对文件处理和文件系统特性的支持,以至于我们称他们为 NIO.2。
2、Path的使用——jdk7提供
1、Path的说明:
Path替换原有的File类
2、如何实例化:
3、Files工具类——jdk提供
1、作用:
操作文件或文件目录的工具类
2、常用方法:
InetAddress类的使用
实现网络通信需要解决的两个问题
1、如何准确地定位网络上一台或多台主机;定位主机上的特定的应用
2、找到主机后如何可靠高效地进行数据传输
网络通信的两个要素:
1、对应问题一:IP和端口号
2、对应问题二:提供网络通信协议:TCP/IP参考模型(应用层、传输层、网络层、物理+数据链路层)
通信要素一:IP和端口号
1、IP的理解
(1)IP:唯一的标识 Internet 上的计算机(通信实体)
(2)在Java中使用InetAddress类代表IP
(3)IP分类:IPv4 和 IPv6 ; 万维网 和 局域网
(4)域名: www.baidu.com www.mi.com www.sina.com www.jd.com
域名解析:域名容易记忆,当在连接网络时输入一个主机的域名后,域名服务器(DNS)负责将域名转化成IP地址,这样才能和主机建立连接。 -------域名解析
(5)本地回路地址:127.0.0.1 对应着:localhost
2、InetAddress类:此类的一个对象就代表着一个具体的IP地址
(1)实例化
getByName(String host) 、 getLocalHost()
(2)常用方法
getHostName() / getHostAddress()
(3)端口号:正在计算机上运行的进程。
要求:不同的进程不同的端口号
范围:被规定为一个 16 位的整数 0~65535。
端口号与IP地址的组合得出一个网络套接字:Socket
通信要素二:网络通信协议
1、分型模型
2、TCP和UDP的区别
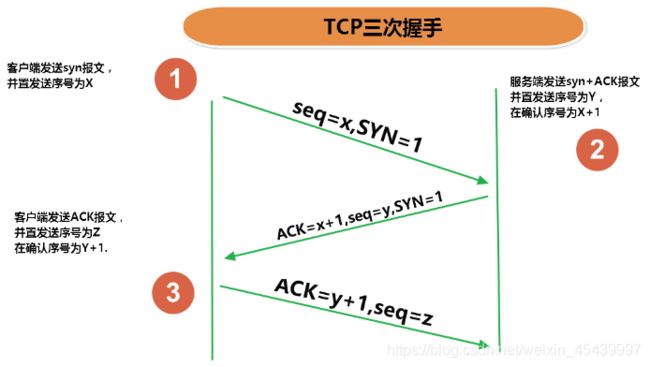
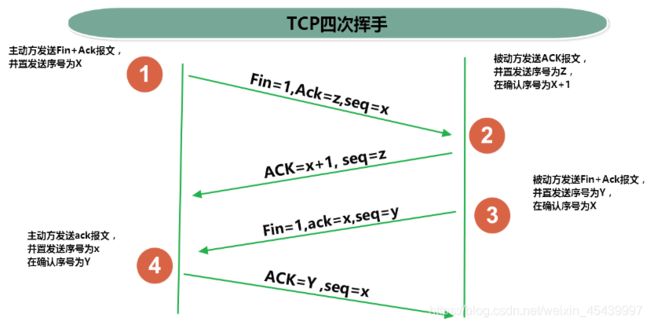
3、TCP三次握手和四次挥手
TCP网络编程
代码示例1:客户端发送信息给服务端,服务端将数据显示在控制台上
//客户端
@Test
public void client() {
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
//1.创建Socket对象,指明服务器端的ip和端口号
InetAddress inet = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.14.100");
socket = new Socket(inet,8899);
//2.获取一个输出流,用于输出数据
os = socket.getOutputStream();
//3.写出数据的操作
os.write("你好,我是客户端mm".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.资源的关闭
if(os != null){
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket != null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//服务端
@Test
public void server() {
ServerSocket ss = null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
try {
//1.创建服务器端的ServerSocket,指明自己的端口号
ss = new ServerSocket(8899);
//2.调用accept()表示接收来自于客户端的socket
socket = ss.accept();
//3.获取输入流
is = socket.getInputStream();
//不建议这样写,可能会乱码
// byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
// int len;
// while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
// String str = new String(buffer,0,len);
// System.out.print(str);
// }
//4.读取输入流中的数据
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[5];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
System.out.println("收到了来自于:" + socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress() + "的数据");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(baos != null){
//5.关闭资源
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is != null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket != null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(ss != null){
try {
ss.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
代码示例2:客户端发送文件给服务端,服务端将文件保存在本地。
/*
这里涉及到的异常,应该使用try-catch-finally处理
*/
@Test
public void client() throws IOException {
//1.
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),9090);
//2.
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
//3.
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("beauty.jpg"));
//4.
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//5.
fis.close();
os.close();
socket.close();
}
/*
这里涉及到的异常,应该使用try-catch-finally处理
*/
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
//1.
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9090);
//2.
Socket socket = ss.accept();
//3.
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
//4.
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("beauty1.jpg"));
//5.
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//6.
fos.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
代码示例3:从客户端发送文件给服务端,服务端保存到本地。并返回“发送成功”给客户端。并关闭相应的连接。
/*
这里涉及到的异常,应该使用try-catch-finally处理
*/
@Test
public void client() throws IOException {
//1.
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),9090);
//2.
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
//3.
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("beauty.jpg"));
//4.
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//关闭数据的输出
socket.shutdownOutput();
//5.接收来自于服务器端的数据,并显示到控制台上
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] bufferr = new byte[20];
int len1;
while((len1 = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len1);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
//6.
fis.close();
os.close();
socket.close();
baos.close();
}
/*
这里涉及到的异常,应该使用try-catch-finally处理
*/
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
//1.
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9090);
//2.
Socket socket = ss.accept();
//3.
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
//4.
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("beauty2.jpg"));
//5.
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("图片传输完成");
//6.服务器端给予客户端反馈
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好,美女,照片我已收到,非常漂亮!".getBytes());
//7.
fos.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
os.close();
}
UDP网络编程
代码示例:
//发送端
@Test
public void sender() throws IOException {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();
String str = "我是UDP方式发送的导弹";
byte[] data = str.getBytes();
InetAddress inet = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data,0,data.length,inet,9090);
socket.send(packet);
socket.close();
}
//接收端
@Test
public void receiver() throws IOException {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(9090);
byte[] buffer = new byte[100];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer,0,buffer.length);
socket.receive(packet);
System.out.println(new String(packet.getData(),0,packet.getLength()));
socket.close();
}
URL编程
1、URL(Uniform Resource Locator)的理解:
统一资源定位符,对应着互联网的某一资源地址
2、URL的5个基本结构:
http://localhost:8080/examples/beauty.jpg?username=Tom
协议 主机名 端口号 资源地址 参数列表
3、如何实例化:
URL url = new URL(“http://localhost:8080/examples/beauty.jpg?username=Tom”);
4、常用方法:
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/examples/myTest.txt");
System.out.println("getProtocol() :"+url.getProtocol());
System.out.println("getHost() :"+url.getHost());
System.out.println("getPort() :"+url.getPort());
System.out.println("getPath() :"+url.getPath());
System.out.println("getFile() :"+url.getFile());
System.out.println("getQuery() :"+url.getQuery());
5.可以读取、下载对应的url资源:
public static void main(String[] args) {
HttpURLConnection urlConnection = null;
InputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/examples/beauty.jpg");
urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
urlConnection.connect();
is = urlConnection.getInputStream();
fos = new FileOutputStream("day10\\beauty3.jpg");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("下载完成");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
if(is != null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos != null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(urlConnection != null){
urlConnection.disconnect();
}
}
}