在Java中通常实现锁有两种方式,一种是synchronized关键字,另一种是Lock。二者其实并没有什么必然联系,但是各有各的特点,在使用中可以进行取舍的使用。首先我们先对比下两者。
实现:#####
首先最大的不同:synchronized是基于JVM层面实现的,而Lock是基于JDK层面实现的。曾经反复的找过synchronized的实现,可惜最终无果。但Lock却是基于JDK实现的,我们可以通过阅读JDK的源码来理解Lock的实现。
使用:#####
对于使用者的直观体验上Lock是比较复杂的,需要lock和realse,如果忘记释放锁就会产生死锁的问题,所以,通常需要在finally中进行锁的释放。但是synchronized的使用十分简单,只需要对自己的方法或者关注的同步对象或类使用synchronized关键字即可。但是对于锁的粒度控制比较粗,同时对于实现一些锁的状态的转移比较困难。例如:
特点:#####
| tips | synchronized | Lock |
|---|---|---|
| 锁获取超时 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 获取锁响应中断 | 不支持 | 支持 |
优化:#####
在JDK1.5之后synchronized引入了偏向锁,轻量级锁和重量级锁,从而大大的提高了synchronized的性能,同时对于synchronized的优化也在继续进行。期待有一天能更简单的使用java的锁。
在以前不了解Lock的时候,感觉Lock使用实在是太复杂,但是了解了它的实现之后就被深深吸引了。
Lock的实现主要有ReentrantLock、ReadLock和WriteLock,后两者接触的不多,所以简单分析一下ReentrantLock的实现和运行机制。
ReentrantLock类在java.util.concurrent.locks包中,它的上一级的包java.util.concurrent主要是常用的并发控制类.
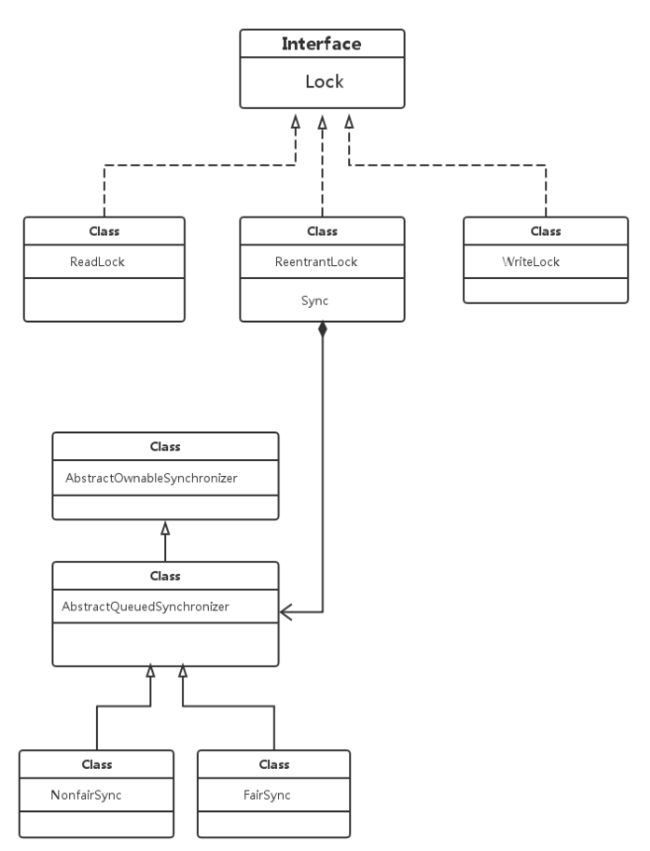
下面是ReentrantLock的UML图,从图中可以看出,ReentrantLock实现Lock接口,在ReentrantLock中引用了AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的子类,所有的同步操作都是依靠AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(队列同步器)实现。
研究一个类,需要从一个类的静态域,静态类,静态方法和成员变量开始。
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984872572414699L;
/** Synchronizer providing all implementation mechanics */
private final Sync sync;
/**
* Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed
* into fair and nonfair versions below. Uses AQS state to
* represent the number of holds on the lock.
*/
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L;
/**
* Performs {@link Lock#lock}. The main reason for subclassing
* is to allow fast path for nonfair version.
*/
abstract void lock();
/**
* Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is
* implemented in subclasses, but both need nonfair
* try for trylock method.
*/
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {
// While we must in general read state before owner,
// we don't need to do so to check if current thread is owner
return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();
}
final ConditionObject newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
// Methods relayed from outer class
final Thread getOwner() {
return getState() == 0 ? null : getExclusiveOwnerThread();
}
final int getHoldCount() {
return isHeldExclusively() ? getState() : 0;
}
final boolean isLocked() {
return getState() != 0;
}
/**
* Reconstitutes this lock instance from a stream.
* @param s the stream
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
setState(0); // reset to unlocked state
}
}
从上面的代码可以看出来首先ReentrantLock是可序列化的,其次是ReentrantLock里有一个对AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的引用。
看完了成员变量和静态域,我们需要了解下构造方法:
/**
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}.
* This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}.
*/
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
/**
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the
* given fairness policy.
*
* @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy
*/
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
从上面代码可以看出,ReentrantLock支持两种锁模式,公平锁和非公平锁。默认的实现是非公平的。公平和非公平锁的实现如下:
/**
* Sync object for non-fair locks
*/
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
/**
* Sync object for fair locks
*/
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
/**
* Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless
* recursive call or no waiters or is first.
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 是一个抽象类,所以在使用这个同步器的时候,需要通过自己实现预期的逻辑,Sync、FairSync和NonfairSync都是ReentrantLock为了实现自己的需求而实现的内部类,之所以做成内部类,我认为是只在ReentrantLock使用上述几个类,在外部没有使用到。
我们着重关注默认的非公平锁的实现:
在ReentrantLock调用lock()的时候,调用的是下面的代码:
/**
* Acquires the lock.
*
* Acquires the lock if it is not held by another thread and returns
* immediately, setting the lock hold count to one.
*
*
If the current thread already holds the lock then the hold
* count is incremented by one and the method returns immediately.
*
*
If the lock is held by another thread then the
* current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling
* purposes and lies dormant until the lock has been acquired,
* at which time the lock hold count is set to one.
*/
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
sync的实现是NonfairSync,所以调用的是NonfairSync的lock方法:
/**
* Sync object for non-fair locks
* tips:调用Lock的时候,尝试获取锁,这里采用的CAS去尝试获取锁,如果获取锁成功
* 那么,当前线程获取到锁,如果失败,调用acquire处理。
*
*/
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
接下来看看compareAndSetState方法是怎么进行锁的获取操作的:
/**
* Atomically sets synchronization state to the given updated
* value if the current state value equals the expected value.
* This operation has memory semantics of a volatile read
* and write.
*
* @param expect the expected value
* @param update the new value
* @return true if successful. False return indicates that the actual
* value was not equal to the expected value.
*
* tips: 1.compareAndSetState的实现主要是通过Unsafe类实现的。
* 2.之所以命名为Unsafe,是因为这个类对于JVM来说是不安全的,我们平时也是使用不了这个类的。
* 3.Unsafe类内封装了一些可以直接操作指定内存位置的接口,是不是感觉和C有点像了?
* 4.Unsafe类封装了CAS操作,来达到乐观的锁的争抢的效果
*/
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
// See below for intrinsics setup to support this
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
主要的说明都在方法的注释中,接下来简单的看一下compareAndSwapInt的实现:
/**
* Atomically update Java variable to x if it is currently
* holding expected.
* @return true if successful
*/
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object o, long offset,
int expected,
int x);
一个native方法,沮丧.....但是从注释看意思是,以CAS的方式将制定字段设置为指定的值。同时我们也明白了这个方法可能是用java实现不了,只能依赖JVm底层的C代码实现。下面看看操作的stateOffset:
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private static final long stateOffset;
private static final long headOffset;
private static final long tailOffset;
private static final long waitStatusOffset;
private static final long nextOffset;
static {
try {
//这个方法很有意思,主要的意思是获取AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的state成员的偏移量
//通过这个偏移量来更新state成员,另外state是volatile的来保证可见性。
stateOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("state"));
headOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("head"));
tailOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("tail"));
waitStatusOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(Node.class.getDeclaredField("waitStatus"));
nextOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(Node.class.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
stateOffset 是AbstractQueuedSynchronizer内部定义的一个状态量,AbstractQueuedSynchronizer是线程的竞态条件,所以只要某一个线程CAS改变状态成功,同时在没有释放的情况下,其他线程必然失败(对于Unsafe类还不是很熟悉,后面还需要系统的学习)。
对于竞争成功的线程会调用setExclusiveOwnerThread方法:
/**
* The current owner of exclusive mode synchronization.
*/
private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread;
/**
* Sets the thread that currently owns exclusive access. A
* null argument indicates that no thread owns access.
* This method does not otherwise impose any synchronization or
* volatile field accesses.
*/
protected final void setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread t) {
exclusiveOwnerThread = t;
}
这个实现是比较简单的,只是获取当前线程的引用,令AbstractOwnableSynchronizer中的exclusiveOwnerThread引用到当前线程。
对于竞争失败的线程,会调用acquire方法,这个方法也是ReentrantLock设计的精华之处:
/**
* Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented
* by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire},
* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly
* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link
* #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used
* to implement method {@link Lock#lock}.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and
* can represent anything you like.
* tips:此处主要是处理没有获取到锁的线程
* tryAcquire:重新进行一次锁获取和进行锁重入的处理。
* addWaiter:将线程添加到等待队列中。
* acquireQueued:自旋获取锁。
* selfInterrupt:中断线程。
* 三个条件的关系为and,如果 acquireQueued返回true,那么线程被中断selfInterrupt会中断线程
*/
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer为抽象方法,调用tryAcquire时,调用的为NonfairSync的tryAcquire。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
/**
* Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is
* implemented in subclasses, but both need nonfair
* try for trylock method.
*/
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
nonfairTryAcquire方法主要是做重入锁的实现,synchronized本身支持锁的重入,而ReentrantLock则是通过此处实现。在锁状态为0时,重新尝试获取锁。如果已经被占用,那么做一次是否当前线程为占用锁的线程的判断,如果是一样的那么进行计数,当然在锁的relase过程中会进行递减,保证锁的正常释放。
如果没有重新获取到锁或者锁的占用线程和当前线程是一个线程,方法返回false。那么把线程添加到等待队列中,调用addWaiter:
/**
* Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.
*
* @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared
* @return the new node
*/
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
/**
* Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above.
* @param node the node to insert
* @return node's predecessor
*/
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
这里主要是用当前线程构建一个Node的等待队列双向链表,这里addWaiter中和enq中的部分逻辑是重复的,个人感觉可能是如果能一次成功就避免了enq中的死循环。因为tail节点是volatile的同时node也是不会发生竞争的所以node.prev = pred;是安全的。但是tail的next是不断竞争的,所以利用compareAndSetTail保证操作的串行化。接下来调用acquireQueued方法:
/**
* Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in
* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.
*
* @param node the node
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting
*/
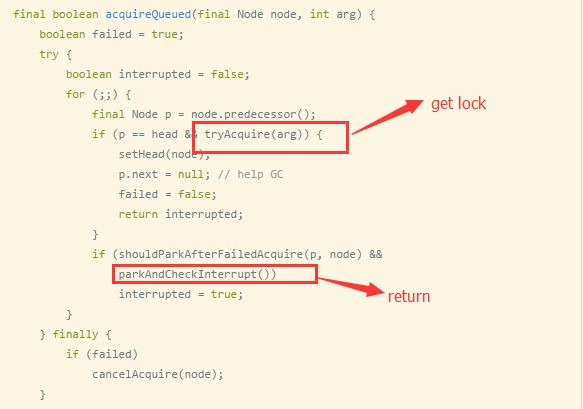
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
此处是做Node节点线程的自旋过程,自旋过程主要检查当前节点是不是head节点的next节点,如果是,则尝试获取锁,如果获取成功,那么释放当前节点,同时返回。至此一个非公平锁的锁获取过程结束。
如果这里一直不断的循环检查,其实是很耗费性能的,JDK的实现肯定不会这么“弱智”,所以有了shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire和parkAndCheckInterrupt,这两个方法就实现了线程的等待从而避免无限的轮询:
/**
* Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire.
* Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal
* control in all acquire loops. Requires that pred == node.prev
*
* @param pred node's predecessor holding status
* @param node the node
* @return {@code true} if thread should block
*/
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
首先,检查一下当前Node的前置节点pred是否是SIGNAL,如果是SIGNAL,那么证明前置Node的线程已经Park了,如果waitStatus>0,那么当前节点已经Concel或者中断。那么不断调整当前节点的前置节点,将已经Concel的和已经中断的线程移除队列。如果waitStatus<0,那么设置waitStatus为SIGNAL,因为调用shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire的方法为死循环调用,所以终将返回true。接下来看parkAndCheckInterrupt方法,当shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire返回True的时候执行parkAndCheckInterrupt方法:
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
此方法比较简单,其实就是使当前的线程park,即暂停了线程的轮询。当Unlock时会做后续节点的Unpark唤醒线程继续争抢锁。
接下来看一下锁的释放过程,锁释放主要是通过unlock方法实现:
/**
* Attempts to release this lock.
*
* If the current thread is the holder of this lock then the hold
* count is decremented. If the hold count is now zero then the lock
* is released. If the current thread is not the holder of this
* lock then {@link IllegalMonitorStateException} is thrown.
*
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread does not
* hold this lock
*/
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
主要是调用AbstractQueuedSynchronizer同步器的release方法:
/**
* Releases in exclusive mode. Implemented by unblocking one or
* more threads if {@link #tryRelease} returns true.
* This method can be used to implement method {@link Lock#unlock}.
*
* @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryRelease} but is otherwise uninterpreted and
* can represent anything you like.
* @return the value returned from {@link #tryRelease}
*/
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
tryRelease方法为ReentrantLock中的Sync的tryRelease方法:
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
tryRelease方法主要是做了一个释放锁的过程,将同步状态state -1,直到减到0为止,这主要是兼容重入锁设计的,同时setExclusiveOwnerThread(null)清除当前占用的线程。这些head节点后的线程和新进的线程就可以开始争抢。这里需要注意的是对于同步队列中的线程来说在setState(c),且c为0的时候,同步队列中的线程是没有竞争锁的,因为线程被park了还没有唤醒。但是此时对于新进入的线程是有机会获取到锁的。
下面代码是进行线程的唤醒:
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
因为在setState(c)释放了锁之后,是没有线程竞争的,所以head是当前的head节点,先检查当前的Node是否合法,如果合法则unpark it。开始锁的获取。就回到了上面的for循环执行获取锁逻辑:
至此锁的释放就结束了,可以看到ReentrantLock是一个不断的循环的状态模型,里面有很多东西值得我们学习和思考。
ReentrantLock具有公平和非公平两种模式,也各有优缺点:
公平锁是严格的以FIFO的方式进行锁的竞争,但是非公平锁是无序的锁竞争,刚释放锁的线程很大程度上能比较快的获取到锁,队列中的线程只能等待,所以非公平锁可能会有“饥饿”的问题。但是重复的锁获取能减小线程之间的切换,而公平锁则是严格的线程切换,这样对操作系统的影响是比较大的,所以非公平锁的吞吐量是大于公平锁的,这也是为什么JDK将非公平锁作为默认的实现。
最后:#####
关于并发和Lock还有很多的点还是比较模糊,我也会继续学习,继续总结,如果文章中有什么问题,还请各位看客及时指出,共同学习。