作者:李佶澳 转载请保留:原文地址 发布时间:2018-09-30 16:07:13 +0800
说明
先说组成
控制平面与数据平面
CustomResourceDefinitions
开始部署
使用演示
参考
说明
这是API网关Kong的系列教程中的一篇,使用过程中遇到的问题和解决方法记录在API网关Kong的使用过程中遇到的问题以及解决方法。
经过前面的学习(Nginx、OpenResty和Kong的基本概念与使用方法),对Api网关是什么,以及Kong能够做什么已经有了足够的了解。现在Kubernetes一统计算资源与应用发布编排的趋势已经形成,我们更关心Kong能否和Kubernetes结合。
Kong是一个Api网关,也是一个特性更丰富的反向代理。既然它有代理流量的功能,那么能不能直接成为Kubernetes的流量入口?使Kubernetes上托管的服务都通过Kong发布。
Kong实现了一个Kubernetes Ingress Controller(后面用kong-ingress-controller指代这个项目)来做这件事。另外把整个Kong部署在Kubernetes中也是可行的,见Kong CE or EE on Kubernetes。
先说组成
Kubernetes Ingress Controller for Kong中介绍了在kubernetes中的部署方法,总共有三部分。
第一部分是数据库。kong不支持mysql,使用的数据库只能是9.4及以上版本的postgres,或者Cassandra 3.x.x。
第二部分是ingress-controller.yaml,是一个Deployment,Pod中有三个容器:
第一个容器是InitContainer,负责初始化数据库;
第二个容器是kong-proxy,只开放了admin接口,负责提供Kong的管理API;
第三个容器是kong-ingress-controller,负责Kubernetes资源与Kong的衔接,监测Kubernetes资源的变动,及时调用Kong的管理API,更新Kong的配置。
第三部分是kong.yaml,可以是Deployment,也可以是Daemonset,pod中只有一个kong-proxy容器,禁用了admin接口,只提供代理服务。
控制平面与数据平面
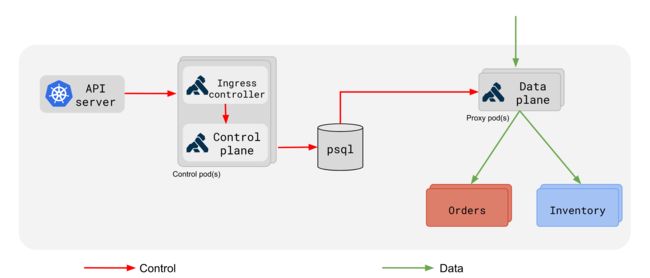
ingress-controller.yaml是控制平面,提供管理接口、下发规则;kong.yaml是数据平面,反向代理对API的请求。
下面是kong-ingress-controller中给出的示意图,红色箭头表示控制信息的流动,绿色箭头表示API请求的流动,dataplane就是属于kong.yaml的多个Pod:
CustomResourceDefinitions
Kubernetes支持自定义资源Extend the Kubernetes API with CustomResourceDefinitions,kong-ingress-controller充分利用了这个简称为CRD的特性。
Cluster-types.yml中定义了KongPlugin、KongConsumer、KongCredential和KongIngress四种CRD资源(@2018-09-30 17:19:38)。
Kong ingress controller: custom types对这四种CRD资源做了说明:
KongConsumer: kong的用户
KongPlugin: kong的插件的配置项
KongCredential: kong用户的认证凭证
KongIngress: 对用户创建的ingress的补充配置
KongConsumer定义了kong的用户:
apiVersion: configuration.konghq.com/v1
kind: KongConsumer
metadata:
name:
namespace:
username:
custom_id:
例如:
apiVersion: configuration.konghq.com/v1
kind: KongConsumer
metadata:
name: consumer-team-x
username: team-X
custom_id: my_team_x # optional and not recommended, please use `username`
KongCredential是用户的认证凭证,它的type与kong支持的认证方式一一对应:
apiVersion: configuration.konghq.com/v1
kind: KongCredential
metadata:
name: credential-team-x
consumerRef: consumer-team-x
type: key-auth
config:
key: 62eb165c070a41d5c1b58d9d3d725ca1
KongPlugin是可以具体到用户的插件配置,注意它可是全局配置,也可以是针对某个用户的配置(consumerRef关联到特定用户):
apiVersion: configuration.konghq.com/v1
kind: KongPlugin
metadata:
name:
namespace:
labels:
global: "true" # optional, please note the quotes around true
consumerRef:
disabled:
config:
key: value
plugin:
例如:
apiVersion: configuration.konghq.com/v1
kind: KongPlugin
metadata:
name: http-svc-consumer-ratelimiting
consumerRef: consumer-team-x
config:
hour: 1000
limit_by: ip
second: 100
plugin: rate-limiting
KongIngress是对已经存在的ingress的补充。Kong-ingress-controller会主动监测kuernetes集群中所有的ingress,为每个配置了host的ingress在kong中创建一个router,为每个被ingress使用的backend在kong中创建一个service。Ingress是kubernetes定义的(Kubernetes Ingress定义),对于那些与kong相关但是Ingress不支持的配置项,需要在KongIngress中配置。
下面是一个完成的KongIngress定义,包含upstream、proxy和route三部分:
apiVersion: configuration.konghq.com/v1
kind: KongIngress
metadata:
name: configuration-demo
upstream:
hash_on: none
hash_fallback: none
healthchecks:
active:
concurrency: 10
healthy:
http_statuses:
- 200
- 302
interval: 0
successes: 0
http_path: "/"
timeout: 1
unhealthy:
http_failures: 0
http_statuses:
- 429
interval: 0
tcp_failures: 0
timeouts: 0
passive:
healthy:
http_statuses:
- 200
successes: 0
unhealthy:
http_failures: 0
http_statuses:
- 429
- 503
tcp_failures: 0
timeouts: 0
slots: 10
proxy:
protocol: http
path: /
connect_timeout: 10000
retries: 10
read_timeout: 10000
write_timeout: 10000
route:
methods:
- POST
- GET
regex_priority: 0
strip_path: false
preserve_host: true
protocols:
- http
- https
它们的用法在后面章节演示。
开始部署
这里主要是学习,直接使用了Master分支中提供的yaml文件(commit: 34e9b4165ab64318d00028f42b797e77dac65e24),不是正式的Release版本。
创建custerm-types:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kong/kubernetes-ingress-controller/master/deploy/manifests/custom-types.yaml
kubectl create -f custom-types.yaml
创建名为kong的namespace,后面yaml描述的任务部署在这个namespace中:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kong/kubernetes-ingress-controller/master/deploy/manifests/namespace.yaml
kubectl create -f namespace.yaml
设置RBAC,为kong namespace中的serivceaccount绑定角色,并赋予权限:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kong/kubernetes-ingress-controller/master/deploy/manifests/rbac.yaml
kubectl create -f rbac.yaml
部署postgre,这里为了方便直接在Kubernetes部署了,在操作系统上的部署方法参考:PostgresSQL数据库的基本使用。
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kong/kubernetes-ingress-controller/master/deploy/manifests/postgres.yaml
kubectl create -f postgres.yaml
注意postgres.yaml是一个statfulset,并且要为每个Pod绑定PV,如果你的集群不支持,且纯粹试用可以注释掉(这样postgre的pod重建时,数据会丢失):
...
volumes:
- name: datadir
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: datadir
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: datadir
spec:
accessModes:
- "ReadWriteOnce"
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
部署kube-ingress-controller:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kong/kubernetes-ingress-controller/master/deploy/manifests/ingress-controller.yaml
kubectl create -f ingress-controller.yaml
部署kong:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kong/kubernetes-ingress-controller/master/deploy/manifests/kong.yaml
kubectl create -f kong.yaml
kong.yaml中少了一个service(commit: 34e9b4165ab64318d00028f42b797e77dac65e24),需要加上:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kong-proxy
namespace: kong
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: kong-proxy
port: 80
targetPort: 8000
protocol: TCP
- name: kong-proxy-ssl
port: 443
targetPort: 8443
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: kong
确保所有的Pod正常运行:
$ kubectl -n kong get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
kong-54875c6bd7-8ttgf 1/1 Running 0 15s 192.168.78.8 10.10.173.203
kong-ingress-controller-cfc7dc7d-vnp64 2/2 Running 7 15m 192.168.78.6 10.10.173.203
postgres-0 1/1 Running 0 17m 192.168.78.5 10.10.173.203
相关Service的状态:
$ kubectl -n kong get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kong-ingress-controller NodePort 10.254.147.53
kong-proxy NodePort 10.254.237.61
postgres ClusterIP 10.254.77.113
然后可以部署一个第三方提供的Dashboard:PGBI/kong-dashboard:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kong-dashboard
namespace: kong
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: kong-dashboard
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: dashboard
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: dashboard
namespace: kong
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: dashboard
app: dashboard
spec:
containers:
- name: kong-dashboard
args:
- start
- --kong-url http://kong-ingress-controller:8001
- --basic-auth admin=admin
image: pgbi/kong-dashboard:latest
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
使用演示
在另一个namespaces中创建一个完整应用:webshell-all-in-one.yaml。
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/introclass/kubernetes-yamls/master/all-in-one/webshell-all-in-one.yaml
namespace "demo-webshell" created
ingress "webshell-ingress" created
service "webshell" created
deployment "webshell" created
上面的yaml文件,在demo-webshellnamespaces中,创建了deployment、serivce和ingress。
创建成功之后,在kong的dashboard中,可以看到自动创建了为demo-webshell.webshell.80 的Route:
Service Methods Protocols Hosts Paths Priority
demo-webshell.webshell.80 (none) http webshell.com / 0
和一个同名的service:
Name Protocol Host Port PATH
demo-webshell.webshell.80 http demo-webshell.webshell.80 80 /
之后可以通过kong-proxy服务访问webshell:
// kong-proxy的采用NodePort方式,端口是32057
kong-proxy NodePort 10.254.237.61
访问效果如下,10.10.173.203是kubernetes一个node的IP:
$ curl -v -H "Host: webshell.com" 10.10.173.203:32057* About to connect() to 10.10.173.203 port 32057 (#0)* Trying 10.10.173.203...* Connected to 10.10.173.203 (10.10.173.203) port 32057 (#0)> GET / HTTP/1.1> User-Agent: curl/7.29.0> Accept: */*> Host: webshell.com>webshell-cc785f4f8-2vp6c