Flutter布局
在Android中,通过XML编写布局,但在Flutter中,只可以使用widget树来编写布局。排列其他widget的columns、 rows、 grids和其他布局。
Flutter布局
-
- 1.单个子元素的布局widget
-
- 1.1.Container
- 1.2. Align
- 1.3.AspectRatiot
- 1.4. Baseline
- 1.5.ConstrainedBox
- 1.6.Center
- 1.7. Expanded
- 1.8. Padding
- 1.9. FittedBox
- 1.10. FractionallySizedBox
- 1.11. IntrinsicHeight
- 1.12. IntrinsicWidth
- 1.13. LimitedBox
- 1.14. Offstage
- 1.15. OverflowBox
- 1.16. SizedBox
- 1.17. SizedOverflowBox
- 1.18. Transform
- 1.19. CustomSingleChildLayout
- 2.多个子元素的布局widget
-
- 2.1. Row
- 2.2. Column
- 2.3.Stack
- 2.4.IndexedStack
- 2.5.GridView
- 2.6.Flow
- 2.7.Wrap
- 2.8.Table
- 2.9.ListView
- 2.10.ListBody
- 2.11.LayoutBuilder
- 2.12.CustomMultiChildLayout
1.单个子元素的布局widget
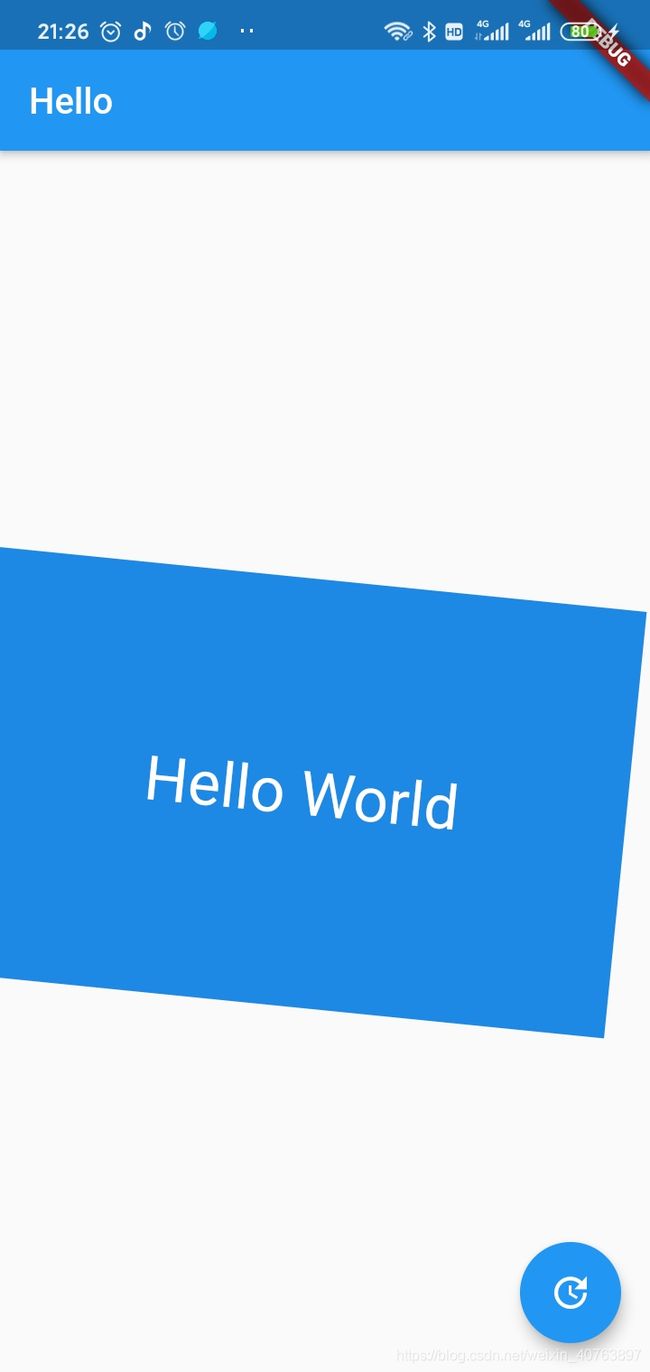
1.1.Container
一个拥有绘制、定位、调整大小的 widget。
Container(
constraints: BoxConstraints.expand(
height: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headline4.fontSize * 1.1 + 200.0,
),
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
color: Colors.blue[600],
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text('Hello World',
style: Theme.of(context)
.textTheme
.headline4
.copyWith(color: Colors.white)),
transform: Matrix4.rotationZ(0.1),
),
1.2. Align
在容器内部对齐元素
Container(// 定义一个容器
height: 220.0,// 容器高
width: 220.0,// 容器宽
color: Colors.blue[50],// 背景颜色
child: Align(// 子元素对齐设置
alignment: Alignment.topRight, // 右上角,也可以指定对齐具体的位置Alignment(0.2, 0.6)
child: FlutterLogo( // 子元素为Flutter的logo图片
size: 60,
),
),
),
1.3.AspectRatiot
可以根据给定的纵横比,显示元素,元素的宽系占满整个容器,元素的高则根据纵横比来计算。
Container(
height: 220.0,
width: 220.0,
color: Colors.blue[50],
child: AspectRatio(aspectRatio: 1.2,child: FlutterLogo(),)
),
),
1.4. Baseline
根据子项的基线对它们的位置进行定位的widget。一般文字排版的时候,可能会用到它。它的作用是根据child的baseline,来调整child的位置。例如两个字号不一样的文字,希望底部在一条水平线上,就可以使用这个控件,是一个非常基础的控件。

new Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: <Widget>[
new Baseline(
baseline: 50.0,
baselineType: TextBaseline.alphabetic,
child: new Text(
'TjTjTj',
style: new TextStyle(
fontSize: 20.0,
textBaseline: TextBaseline.alphabetic,
),
),
),
new Baseline(
baseline: 50.0,
baselineType: TextBaseline.alphabetic,
child: new Container(
width: 30.0,
height: 30.0,
color: Colors.red,
),
),
new Baseline(
baseline: 50.0,
baselineType: TextBaseline.alphabetic,
child: new Text(
'RyRyRy',
style: new TextStyle(
fontSize: 35.0,
textBaseline: TextBaseline.alphabetic,
),
),
),
],
),
Abc
1.5.ConstrainedBox
对其子项施加附加约束的widget。如果你想你的widget有最小的高度,那么就可以用ConstrainedBox widget来约束它。
ConstrainedBox(
constraints: BoxConstraints(minHeight: 50.0),
child: Card(
child: Text("hello Y"),
),
),
1.6.Center
将其子widget居中显示在自身内部的widget
Center(
child:Text("hello world"),
),
1.7. Expanded
扩展Row、Column或Flex的child,这个child会填充满剩下的所有可用空间
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Expanded Column Sample'),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
Container(
color: Colors.blue,
height: 100,
width: 100,
),
Expanded(
child: Container(
color: Colors.amber,
width: 100,
),
),
Container(
color: Colors.blue,
height: 100,
width: 100,
),
],
),
),
);
}
又如:
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Expanded Row Sample'),
),
body: Center(
child: Row(
children: <Widget>[
Expanded(
flex: 2,
child: Container(
color: Colors.amber,
height: 100,
),
),
Container(
color: Colors.blue,
height: 100,
width: 50,
),
Expanded(
flex: 1,
child: Container(
color: Colors.amber,
height: 100,
),
),
],
),
),
);
}
1.8. Padding
一个widget, 会给其子widget添加指定的填充 。
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: const Card(child: const Text('Hello World!')),
),
1.9. FittedBox
按自己的大小调整其子widget的大小和位置。FittedBox组件的作用是对child组件进行缩放和对齐方式的设置。
// fittedBox
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class FittedBoxLearn extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('FittedBox'),
),
body: Center(
child: Container(
width: 300,
height: 400,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
border: Border.all(),
),
// 根据内部child伸缩填充父容器
child: FittedBox(
// 填充方式 比如contain 尽可能大,同时仍然将源完全包含在目标框中。 还有cover、fill、fitWidth、fitHeight等方式
fit: BoxFit.contain,
// 对齐方式
alignment: Alignment(0, 0),
child: Container(
color: Colors.blueAccent,
width: 30,
height: 30,
)
),
),
));
}
}
1.10. FractionallySizedBox
百分比布局。FractionallySizedBox控件会根据现有空间,来调整child的尺寸,所以说child就算设置了具体的尺寸数值,也不起作用。FractionallySizedBox的布局行为主要跟它的宽高因子两个参数有关,当参数为null或者有具体数值的时候,布局表现不一样。当然,还有一个辅助参数alignment,作为对齐方式进行布局。
当设置了具体的宽高因子,具体的宽高则根据现有空间宽高 * 因子,有可能会超出父控件的范围,当宽高因子大于1的时候;
当没有设置宽高因子,则填满可用区域。
/**
* 百分比布局,SizeBox直接通过width,height限制子控件;FractionallySizedBox通过百分比限制
* const FractionallySizedBox({
* Key key,
* this.alignment = Alignment.center,
* this.widthFactor,//宽度因子,乘以宽度就是组件最后的宽
* this.heightFactor,
* Widget child,
* })
*/
Container(
width: 100.0,
height: 100.0,
color: Colors.blue,
child: FractionallySizedBox(
widthFactor: 0.5,
heightFactor: 1.5,
child: Container(
width: 100.0,
height: 100.0,
color: Colors.red,
),
),
),
1.11. IntrinsicHeight
一个widget,它将它的子widget的高度调整其本身实际的高度。IntrinsicHeight的作用是调整child到固定的高度。应用尽量少用,用多会影响效率。
new IntrinsicHeight(
child: new Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: <Widget>[
new Container(color: Colors.blue, width: 100.0),
new Container(color: Colors.red, width: 50.0,height: 50.0,),
new Container(color: Colors.yellow, width: 150.0),
],
),
);
1.12. IntrinsicWidth
一个widget,它将它的子widget的宽度调整其本身实际的宽度。跟IntrinsicHeight类似,一个是调整高度,一个是调整宽度。同样是会存在效率问题,能别使用就尽量别使用。
IntrinsicWidth不同于IntrinsicHeight,它包含了额外的两个参数,stepHeight以及stepWidth。而IntrinsicWidth的布局行为跟这两个参数相关。
当stepWidth不是null的时候,child的宽度将会是stepWidth的倍数,当stepWidth值比child最小宽度小的时候,这个值不起作用;
当stepWidth为null的时候,child的宽度是child的最小宽度;
当stepHeight不为null的时候,效果跟stepWidth相同;
当stepHeight为null的时候,高度取最大高度。
new Container(
color: Colors.green,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
child: new IntrinsicWidth(
stepHeight: 450.0,
stepWidth: 300.0,
child: new Column(
children: <Widget>[
new Container(color: Colors.blue, height: 100.0),
new Container(color: Colors.red, width: 150.0, height: 100.0),
new Container(color: Colors.yellow, height: 150.0,),
],
),
),
)
1.13. LimitedBox
一个当其自身不受约束时才限制其大小的盒子
Row(
children: <Widget>[
Container(
color: Colors.red,
width: 100.0,
),
LimitedBox(
maxWidth: 150.0,
child: Container(
color: Colors.blue,
width: 250.0,
),
),
],
),
1.14. Offstage
一个布局widget,可以控制其子widget的显示和隐藏。
Column(
children: <Widget>[
new Offstage(
offstage: offstage,
child: Container(color: Colors.blue, height: 100.0),
),
],
),
1.15. OverflowBox
对其子项施加不同约束的widget,它可能允许子项溢出父级。
Container(
color: Colors.green,
width: 200.0,
height: 200.0,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
child: OverflowBox(
alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
maxWidth: 300.0,
maxHeight: 500.0,
child: Container(
color: Color(0x33FF00FF),
width: 400.0,
height: 400.0,
),
),
),
1.16. SizedBox
一个特定大小的盒子。这个widget强制它的孩子有一个特定的宽度和高度。如果宽度或高度为NULL,则此widget将调整自身大小以匹配该维度中的孩子的大小。
Container(
color: Colors.green,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
child: SizedBox(
width: 200.0,
height: 200.0,
child: Container(
color: Colors.blue,
width: 100.0,
height: 300.0,
),
),
),
1.17. SizedOverflowBox
一个特定大小的widget,但是会将它的原始约束传递给它的孩子,它可能会溢出。
Container(
color: Colors.green,
alignment: Alignment.topRight,
width: 200.0,
height: 200.0,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
child: SizedOverflowBox(
size: Size(100.0, 200.0),
child: Container(color: Colors.red, width: 200.0, height: 100.0,),
),
),
1.18. Transform
在绘制子widget之前应用转换的widget。
Center(
child: Transform(
transform: Matrix4.rotationZ(0.3),
child: Container(
color: Colors.blue,
width: 100.0,
height: 100.0,
),
),
),
1.19. CustomSingleChildLayout
一个自定义的拥有单个子widget的布局widget。由于SingleChildLayoutDelegate是一个抽象类,我们需要单独写一个继承自它的delegate,来进行相关的布局操作。下面例子中是一个固定尺寸的布局。
Container(
color: Colors.blue,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
child: CustomSingleChildLayout(
delegate: FixedSizeLayoutDelegate(Size(200.0, 200.0)),
child: Container(
color: Colors.red,
width: 100.0,
height: 300.0,
),
),
),
...
class FixedSizeLayoutDelegate extends SingleChildLayoutDelegate {
FixedSizeLayoutDelegate(this.size);
final Size size;
@override
Size getSize(BoxConstraints constraints) => size;
@override
BoxConstraints getConstraintsForChild(BoxConstraints constraints) {
return new BoxConstraints.tight(size);
}
@override
bool shouldRelayout(FixedSizeLayoutDelegate oldDelegate) {
return size != oldDelegate.size;
}
}
2.多个子元素的布局widget
2.1. Row
在水平方向上排列子widget的列表。
Row(
children: <Widget>[
Expanded(
child: Container(
color: Colors.red,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
),
flex: 1,
),
Expanded(
child: Container(
color: Colors.yellow,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
),
flex: 2,
),
Expanded(
child: Container(
color: Colors.blue,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
),
flex: 1,
),
],
),
2.2. Column
在垂直方向上排列子widget的列表。
Column(
children: <Widget>[
Expanded(
child: Container(
color: Colors.red,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
),
flex: 1,
),
Expanded(
child: Container(
color: Colors.yellow,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
),
flex: 2,
),
Expanded(
child: Container(
color: Colors.blue,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
),
flex: 1,
),
],
),
2.3.Stack
可以允许其子widget简单的堆叠在一起。
Stack(
children: <Widget>[
Container(
width: 100,
height: 100,
color: Colors.red,
),
Container(
width: 90,
height: 90,
color: Colors.green,
),
Container(
width: 80,
height: 80,
color: Colors.blue,
),
],
),
Stack(
children: <Widget>[
Container(
width: 250,
height: 250,
color: Colors.white,
),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5.0),
alignment: Alignment.bottomCenter,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
gradient: LinearGradient(
begin: Alignment.topCenter,
end: Alignment.bottomCenter,
colors: <Color>[
Colors.black.withAlpha(0),
Colors.black12,
Colors.black45
],
),
),
child: Text(
"Foreground Text",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 20.0),
),
),
],
),
2.4.IndexedStack
从一个子widget列表中显示单个孩子的Stack。IndexedStack继承自Stack,它的作用是显示第index个child,其他child都是不可见的。所以IndexedStack的尺寸永远是跟最大的子节点尺寸一致。
IndexedStack(
index: 1,
alignment: const Alignment(0.6, 0.6),
children: [
CircleAvatar(
backgroundImage: AssetImage('images/pic.jpg'),
radius: 100.0,
),
Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.black45,
),
child: Text(
'Mia B',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 20.0,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
),
],
),
2.5.GridView
GridView在移动端上非常的常见,就是一个滚动的多列列表。GridView的布局行为不复杂,本身是尽量占满空间区域,布局行为上完全继承自ScrollView。
GridView.count(
//水平子Widget之间间距
crossAxisSpacing: 10.0,
//垂直子Widget之间间距
mainAxisSpacing: 30.0,
//GridView内边距
padding: EdgeInsets.all(10.0),
//一行的Widget数量
crossAxisCount: 2,
//子Widget宽高比例
childAspectRatio: 2.0,
children: List.generate(
100,
(index) {
return Center(
child: Text(
'Item $index',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headline,
),
);
},
),
),
2.6.Flow
一个实现流式布局算法的widget
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(FlowApp());
class FlowApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Flow Example'),
),
body: FlowMenu(),
),
);
}
}
class FlowMenu extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_FlowMenuState createState() => _FlowMenuState();
}
class _FlowMenuState extends State<FlowMenu> with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin {
AnimationController menuAnimation;
IconData lastTapped = Icons.notifications;
final List<IconData> menuItems = <IconData>[
Icons.home,
Icons.new_releases,
Icons.notifications,
Icons.settings,
Icons.menu,
];
void _updateMenu(IconData icon) {
if (icon != Icons.menu)
setState(() => lastTapped = icon);
}
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
menuAnimation = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 250),
vsync: this,
);
}
Widget flowMenuItem(IconData icon) {
final double buttonDiameter = MediaQuery.of(context).size.width / menuItems.length;
return Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 8.0),
child: RawMaterialButton(
fillColor: lastTapped == icon ? Colors.amber[700] : Colors.blue,
splashColor: Colors.amber[100],
shape: CircleBorder(),
constraints: BoxConstraints.tight(Size(buttonDiameter, buttonDiameter)),
onPressed: () {
_updateMenu(icon);
menuAnimation.status == AnimationStatus.completed
? menuAnimation.reverse()
: menuAnimation.forward();
},
child: Icon(
icon,
color: Colors.white,
size: 45.0,
),
),
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
child: Flow(
delegate: FlowMenuDelegate(menuAnimation: menuAnimation),
children: menuItems.map<Widget>((IconData icon) => flowMenuItem(icon)).toList(),
),
);
}
}
class FlowMenuDelegate extends FlowDelegate {
FlowMenuDelegate({
this.menuAnimation}) : super(repaint: menuAnimation);
final Animation<double> menuAnimation;
@override
bool shouldRepaint(FlowMenuDelegate oldDelegate) {
return menuAnimation != oldDelegate.menuAnimation;
}
@override
void paintChildren(FlowPaintingContext context) {
double dx = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < context.childCount; ++i) {
dx = context.getChildSize(i).width * i;
context.paintChild(
i,
transform: Matrix4.translationValues(
dx * menuAnimation.value,
0,
0,
),
);
}
}
}
2.7.Wrap
可以在水平或垂直方向多行显示其子widget。
Wrap(
spacing: 8.0, // gap between adjacent chips
runSpacing: 4.0, // gap between lines
children: <Widget>[
Chip(
avatar: CircleAvatar(backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade900, child: Text('AH')),
label: Text('Hamilton'),
),
Chip(
avatar: CircleAvatar(backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade900, child: Text('ML')),
label: Text('Lafayette'),
),
Chip(
avatar: CircleAvatar(backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade900, child: Text('HM')),
label: Text('Mulligan'),
),
Chip(
avatar: CircleAvatar(backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade900, child: Text('JL')),
label: Text('Laurens'),
),
],
),
2.8.Table
为其子widget使用表格布局算法的widget。
new Table(
border: new TableBorder.all(width: 1.0,color: Colors.purpleAccent),
children: <TableRow>[
new TableRow(
children: <Widget>[
new TableCell(
child: new Center(
child: new Text('设置1'),
),
),
new TableCell(
child: new Center(
child: new Text('设置2'),
),
),
new TableCell(
child: new Center(
child: new Text('设置3'),
),
),
new TableCell(
child: new Center(
child: new Text('设置4'),
),
),
],
),
new TableRow(
children: <Widget>[
new TableCell(
child: new Center(
child: new Text('设置1'),
),
),
new TableCell(
child: new Center(
child: new Text('设置2'),
),
),
new TableCell(
child: new Center(
child: new Text('设置3'),
),
),
new TableCell(
child: new Center(
child: new Text('设置4'),
),
),
],
),
],
),
2.9.ListView
可滚动的列表控件。ListView是最常用的滚动widget,它在滚动方向上一个接一个地显示它的孩子。在纵轴上,孩子们被要求填充ListView。
(1)ListTile
Flutter提供的ListTile很好用了,提供了许多常见的列表 item 样式,如左图标、右图标、标题、副标题等。
const ListTile({
Key key,
this.leading,
this.title,
this.subtitle,
this.trailing,
this.isThreeLine = false,
this.dense,
this.contentPadding,
this.enabled = true,
this.onTap,
this.onLongPress,
this.selected = false,
})
(2)先创建title、icon、subtitle的数据源,以及获取ListTile的方法
Widget buildListData(BuildContext context, String titleItem, Icon iconItem, String subTitleItem) {
return new ListTile(
leading: iconItem,
title: new Text(
titleItem,
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 18),
),
subtitle: new Text(
subTitleItem,
),
trailing: new Icon(Icons.keyboard_arrow_right),
// 创建点击事件
onTap: () {
showDialog(
context: context,
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return new AlertDialog(
title: new Text(
'ListViewAlert',
style: new TextStyle(
color: Colors.black54,
fontSize: 18.0,
),
),
content: new Text('您选择的item内容为:$titleItem'),
);
},
);
},
);
}
List<String> titleItems = <String>[
'keyboard', 'print',
'router', 'pages',
'zoom_out_map', 'zoom_out',
'youtube_searched_for', 'wifi_tethering',
'wifi_lock', 'widgets',
'weekend', 'web',
'图accessible', 'ac_unit',
];
List<Icon> iconItems = <Icon>[
new Icon(Icons.keyboard), new Icon(Icons.print),
new Icon(Icons.router), new Icon(Icons.pages),
new Icon(Icons.zoom_out_map), new Icon(Icons.zoom_out),
new Icon(Icons.youtube_searched_for), new Icon(Icons.wifi_tethering),
new Icon(Icons.wifi_lock), new Icon(Icons.widgets),
new Icon(Icons.weekend), new Icon(Icons.web),
new Icon(Icons.accessible), new Icon(Icons.ac_unit),
];
List<String> subTitleItems = <String>[
'subTitle: keyboard', 'subTitle: print',
'subTitle: router', 'subTitle: pages',
'subTitle: zoom_out_map', 'subTitle: zoom_out',
'subTitle: youtube_searched_for', 'subTitle: wifi_tethering',
'subTitle: wifi_lock', 'subTitle: widgets',
'subTitle: weekend', 'subTitle: web',
'subTitle: accessible', 'subTitle: ac_unit',
];
(3)绑定列表
绑定列表有四种方式,默认方式、ListView.builder、ListView.separated、 ListView.custom。
(I)默认方式
先创建包含ListTile的List数组:
List<Widget> _list = new List();
for (int i = 0; i < titleItems.length; i++) {
_list.add(buildListData(context, titleItems[i], iconItems[i], subTitleItems[i]));
}
若每个item下有分割线,则使用ListTile的divideTiles()方法在每个ListTile之间添加水平间距:
var divideTiles = ListTile.divideTiles(context: context, tiles: _list).toList();
绑定:
body: new Scrollbar(
// 默认写法
child: new ListView(
// 无分割线
children: _list,
// 有分割线
// children: divideTiles,
),
),
(II)ListView.builder
body: new Scrollbar(
// ListView.builder写法
child: new ListView.builder(
// 无分割线
itemBuilder: (context, item) {
return buildListData(context, titleItems[item], iconItems[item], subTitleItems[item]);
}, // 绑定item
// 有分割线
itemBuilder: (context, item) {
return new Container(
child: new Column(
children: <Widget>[
buildListData(context, titleItems[item], iconItems[item], subTitleItems[item]),
new Divider()
],
),
);
},
itemCount: iconItems.length, // 数据长度
),
),
(III)ListView.separated
ListView.separated方法与ListView.builder类似,不过可直接通过separatorBuilder设置分隔符,更加方便。
body: new Scrollbar(
child: new ListView.separated(
itemBuilder: (context, item) {
return buildListData(context, titleItems[item], iconItems[item], subTitleItems[item]);
},
separatorBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) => new Divider(), // 分割线
itemCount: iconItems.length
),
),
(IV)ListView.custom
自定义childrenDelegate 当然我们可以对ListView中的child进行自己需要的操作:
/**
* 继承SliverChildBuilderDelegate 可以对列表的监听
*/
class MyChildrenDelegate extends SliverChildBuilderDelegate {
MyChildrenDelegate(
Widget Function(BuildContext, int) builder, {
int childCount,
bool addAutomaticKeepAlive = true,
bool addRepaintBoundaries = true,
}) : super(builder,
childCount: childCount,
addAutomaticKeepAlives: addAutomaticKeepAlive,
addRepaintBoundaries: addRepaintBoundaries);
///监听 在可见的列表中 显示的第一个位置和最后一个位置
@override
void didFinishLayout(int firstIndex, int lastIndex) {
print('firstIndex: $firstIndex, lastIndex: $lastIndex');
}
///可不重写,重写不能为null 默认是true 添加进来的实例与之前的实例是否相同 相同返回true 反之false
@override
bool shouldRebuild(SliverChildBuilderDelegate oldDelegate) {
// TODO: implement shouldRebuild
print("oldDelegate$oldDelegate");
return super.shouldRebuild(oldDelegate);
}
}
绑定:
///listView custom 构建
Widget listViewLayoutCustom(list) {
return ListView.custom(
itemExtent: 40.0,
childrenDelegate: MyChildrenDelegate(
(BuildContext context, int i) {
return new Container(
child: new Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
new Text(
"${list[i].name}",
style: new TextStyle(fontSize: 18.0, color: Colors.red),
),
new Text(
"${list[i].age}",
style: new TextStyle(fontSize: 18.0, color: Colors.green),
),
new Text(
"${list[i].content}",
style: new TextStyle(fontSize: 18.0, color: Colors.blue),
),
],
));
},
childCount: list.length,
),
cacheExtent: 0.0,
);
}
}
2.10.ListBody
ListBody是一个不常直接使用的控件,一般都会配合ListView或者Column等控件使用。ListBody的作用是按给定的轴方向,按照顺序排列子节点。在主轴上,子节点按照顺序进行布局,在交叉轴上,子节点尺寸会被拉伸,以适应交叉轴的区域。在主轴上,给予子节点的空间必须是不受限制的(unlimited),使得子节点可以全部被容纳,ListBody不会去裁剪或者缩放其子节点。
Flex(
direction: Axis.vertical,
children: <Widget>[
ListBody(
mainAxis: Axis.vertical,
reverse: false,
children: <Widget>[
Container(color: Colors.red, width: 50.0, height: 50.0,),
Container(color: Colors.yellow, width: 50.0, height: 50.0,),
Container(color: Colors.green, width: 50.0, height: 50.0,),
Container(color: Colors.blue, width: 50.0, height: 50.0,),
Container(color: Colors.black, width: 50.0, height: 50.0,),
],
)],
),
2.11.LayoutBuilder
构建一个可以依赖父窗口大小的widget树。
LayoutBuilder(
builder: (context,constraints){
context为父级上下文
constraints.biggest.height; 获取组件在父组件所能设置的最大高度
contraints.maxWidth; 获取父组件宽度,高度同理
return 组件
}
)
示例:
LayoutBuilder(
builder: (context,constraints){
final endHeight=constraints.biggest.height;
return GestureDetector(
onVerticalDragDown: (text){
//当点击时会获取点击坐标
print(endHeight);
print(constraints.maxHeight);
print(constraints.maxWidth);
},
onVerticalDragEnd: (text){
print(text);
},
onVerticalDragCancel: (){
print("取消");
},
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(Icons.search,size: 15,),
GestureDetector(
child:Text('A') ,
onTap: (){
scroll.animateTo(312, duration: Duration(milliseconds: 200), curve: Curves.easeIn);
},
),
GestureDetector(
child:Text('B') ,
onTap: (){
scroll.animateTo(478, duration: Duration(milliseconds: 200), curve: Curves.easeIn);
},
),
GestureDetector(
child:Text('C') ,
onTap: (){
scroll.animateTo(575, duration: Duration(milliseconds: 200), curve: Curves.easeIn);
},
),
GestureDetector(
child:Text('D') ,
onTap: (){
scroll.animateTo(741, duration: Duration(milliseconds: 200), curve: Curves.easeIn);
},
),
Text('E'),
Text('F'),
Text('G'),
Text('H'),
Text('I'),
Text('J'),
Text('K'),
Text('L'),
Text('M'),
Text('N'),
Text('O'),
Text('P'),
Text('Q'),
Text('R'),
Text('S'),
Text('T'),
Text('U'),
Text('V'),
Text('W'),
Text('X'),
Text("Y"),
Text("#")
],
),
);
},
),
2.12.CustomMultiChildLayout
之前单节点布局控件中介绍过一个类似的控件——CustomSingleChildLayout,都是通过delegate去实现自定义布局,只不过这次是多节点的自定义布局的控件,通过提供的delegate,可以实现控制节点的位置以及尺寸。
CustomMultiChildLayout提供的delegate可以控制子节点的布局,具体在如下几点:
可以决定每个子节点的布局约束条件;
可以决定每个子节点的位置;
可以决定自身的尺寸,但是自身的自身必须不能依赖子节点的尺寸。
可以看到,跟CustomSingleChildLayout的delegate提供的作用类似,只不过CustomMultiChildLayout的稍微会复杂点。
class MyMultiLayoutDelegate extends MultiChildLayoutDelegate {
MyMultiLayoutDelegate();
static const String title = 'title';
static const String description = 'description';
@override
void performLayout(Size size) {
final BoxConstraints constraints = new BoxConstraints(maxWidth: size.width);
final Size titleSize = layoutChild(title, constraints);
positionChild(title, new Offset(0.0, 0.0));
final double descriptionY = titleSize.height;
layoutChild(description, constraints);
positionChild(description, new Offset(0.0, descriptionY));
}
@override
bool shouldRelayout(MyMultiLayoutDelegate oldDelegate) => false;
}
Container(
width: 200.0,
height: 100.0,
color: Colors.yellow,
child: CustomMultiChildLayout(
delegate: MyMultiLayoutDelegate(),
children: <Widget>[
LayoutId(
id: MyMultiLayoutDelegate.title,
child: new Text("This is title",
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 20.0, color: Colors.black)),
),
LayoutId(
id: MyMultiLayoutDelegate.description,
child: new Text("This is description",
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 14.0, color: Colors.red)),
),
],
),
),