Android ANR机制的原理以及问题分析(二)
文章目录
-
-
-
- 一、前言
- 二、Service Timeout
- 三、 Service 设置定时器
- 四、Service 重置定时器
- 五、Service触发ANR
- 六、总结
-
-
一、前言
ANR⼤致划分为Service、Broadcast、InputDispatch、Provider四中类型,下⾯⼀
⼀解释他们各⾃的监测原理。本篇我们将集合源码,对四种Service类型的触发机制做详尽的介绍。
二、Service Timeout
Service Timeout是位于”ActivityManager”线程中的ActivityManagerService.MainHandler收到 SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG 或 者 SERVICE_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT_MSG 消息时触发。
⾸先,AMS初始化时,启动了⼀个THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND优先级
的ServiceThread,mHandler运⾏在这个线程:
public ActivityManagerService(Context systemContext) {
...
//ServiceThread 是⼀个HandlerThread
mHandlerThread = new ServiceThread(TAG,
THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND, false /*allowIo*/);
mHandlerThread.start();
mHandler = new MainHandler(mHandlerThread.getLooper());
..
}
三、 Service 设置定时器
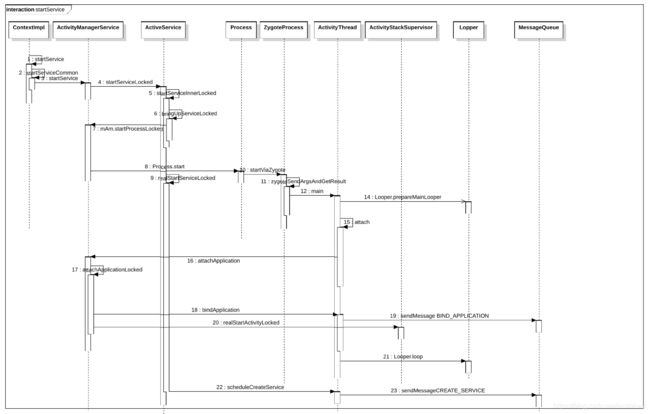
service 启动时就⼀句话, startService 或者 binderService() ,关于Service的启
动流程,这⾥不做详细分析,简单介绍⼀下。
startService最终调⽤到AMS,
- AMS通过Socket通信⽅式向Zygote进程请求⽣成(fork)⽤于承载服务的进程,并
且初始化ActivityThread对象。ActivityThread是应⽤程序的主线程; - Zygote通过fork的⽅法,将zygote进程复制⽣成新的进程,并将ActivityThread
相关的资源加载到新进程; - ActivityManagerService向新⽣成的ActivityThread进程,通过Binder⽅式发送
⽣成服务的请求; - ActivityThread通过反射的⽅式创建RemoteService

在service启动的流程中,会在Service进程attach到system_server进程的过程最终会
调⽤ realStartServiceLocked() ,发送延迟消息,设置 定时器 ,
realStartServiceLocked 主要有如下两件事情:
【1】post 延迟消息
【2】调⽤service的onCreate⽅法
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
//...省略...
//【1】post 延迟消息
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "create");
boolean created = false;
try {
//【2】调⽤service的onCreate⽅法
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.application
Info),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Application dead when creating service
" + r);
mAm.appDiedLocked(app);
throw e;
} finally {
if (!created) {
//...
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying,
inDestroying);
//..
}
}
//...省略...
}
接下来看bumpServiceExecutingLocked ⽅法,调⽤
scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked 发送延迟消息,并且根据service前后台的属性,来决
定TIMEOUT的时间.
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
private final void bumpServiceExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r,
boolean fg, String why) {
//...
scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(r.app);
//...
}
void scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(ProcessRecord proc) {
if (proc.executingServices.size() == 0 || proc.thread == null) {
return;
}
Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = proc;
//当超时后仍没有remove该SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG消息,则执⾏Service Timeout流程
mAm.mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg,
proc.execServicesFg ? SERVICE_TIMEOUT :
SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT);
}
【1】其中发送的延迟消息分为前台和后台两种,定义如下:
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveS
ervices.java
// How long we wait for a service to finish executing.
static final int SERVICE_TIMEOUT = 20*1000;
// How long we wait for a service to finish executing.
static final int SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT = SERVICE_TIMEOUT * 10;
- 对于前台服务,则超时为SERVICE_TIMEOUT = 20s;
- 对于后台服务,则超时为SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT = 200s
【2】mHandler是AMS的MainHandler
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java$MainHandler
final class MainHandler extends Handler {
case SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG: {
//【1】 执⾏ActiveService中的SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG
mServices.serviceTimeout((ProcessRecord)msg.obj);
}
break;
case SERVICE_FOREGROUND_TIMEOUT_MSG: {
//【2】这个是前台服务启动的timeout,这⾥不做详细分析.
mServices.serviceForegroundTimeout((ServiceRecord)msg.obj);
}
break;
}
MainHandler 中会根据SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG 来执⾏serviceTimeout.其中我们
看到这个Timeout在10s,后台服务更是达到了200s,所以⼀般情况下都不会触发,那么
我们抛给Handler的消息肯定就有地⽅需要移除,下⾯就是情况定时器的地⽅
四、Service 重置定时器
回到 一、Service 设置定时器 章节中, 第⼆步【2】调⽤service的onCreate⽅法
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws
RemoteException {
//【2】调⽤service的onCreate⽅法 thread 指的是ActivityThread中的ApplicationThread binder对象
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.application
Info),
app.repProcState);
}
scheduleCreateService 的实现如下,最终会发送⼀个Message给到H handler.⽽这
个是创建在⽬标进程中执⾏的.
//frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int
processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
//⽬标进程的handleCreateService,
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl =
packageInfo.getClassLoader();
//通过可⾃定义的getAppFactory,反射初始化service实例.
service = packageInfo.getAppFactory()
.instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent);
} catch (Exception e) {
//...省略
}
try {
//context 创建service context
ContextImpl context =
ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
//创建application对象
Application app =
packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
//执⾏service的默认attach⽅法.
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService());
//调⽤service的onCreate()⽅法
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
//【*】重点serviceDoneExecuting
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
//...省略
}
} catch (Exception e) {
//...省略
}
}
在这个过程会创建⽬标应⽤的Service对象,以及执⾏客户端中的onCreate()⽅法, 然 后Binder通信调⽤回到system_server来执⾏serviceDoneExecuting
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
private void serviceDoneExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r,
boolean inDestroying, boolean finishing) {
r.executeNesting--;
if (r.executeNesting <= 0) {
if (r.app != null) {
if (r.app.executingServices.size() == 0) {
//【*】当前服务所在进程中没有正在执⾏的service,清 空TIMEOUT MSG
mAm.mHandler.removeMessages(ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIM
EOUT_MSG, r.app);
} else if (r.executeFg) {
// Need to re-evaluate whether the app still needs to be in the foreground.
for (int i=r.app.executingServices.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
if (r.app.executingServices.valueAt(i).executeFg) {
r.app.execServicesFg = true;
break;
}
}
}
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(r.app, true);
}
//...省略
}
}
ActiveServices 中serviceDoneExecutingLocked核⼼功能是当前服务所在进程中没
有正在执⾏的service,清空TIMEOUT MSG
五、Service触发ANR
前⾯介绍了设置TIMEOUT和移除TIMEOUT的过程, 如果在TIMEOUT结束之前成
功移除,那么就不会触发ANR, 但是世事难料,如果应⽤写的不好,或者系统负载⽐较
⾼,CPU/IO等因素会导致规定的时间内⽆法执⾏结束,其结果就是ANR.
在system_server进程中有⼀个Handler线程, 名叫”ActivityManager”.当倒计时结束
便会向该Handler线程发送 ⼀条信息 SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG ,如 一、Service 设置
定时器 中描述的.
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveS
ervices.java
void serviceTimeout(ProcessRecord proc) {
String anrMessage = null;
synchronized(mAm) {
if (proc.executingServices.size() == 0 || proc.thread == null) {
return;
}
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final long maxTime = now - (proc.execServicesFg ? SERVICE_TIMEOUT :
SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT);
ServiceRecord timeout = null;
long nextTime = 0;
for (int i=proc.executingServices.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ServiceRecord sr = proc.executingServices.valueAt(i);
if (sr.executingStart < maxTime) {
timeout = sr;
break;
}
if (sr.executingStart > nextTime) {
nextTime = sr.executingStart;
}
}
if (timeout != null && mAm.mLruProcesses.contains(proc)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Timeout executing service: " + timeout);
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
PrintWriter pw = new FastPrintWriter(sw, false, 1024);
pw.println(timeout);
timeout.dump(pw, " ");
pw.close();
mLastAnrDump = sw.toString();
mAm.mHandler.removeCallbacks(mLastAnrDumpClearer);
mAm.mHandler.postDelayed(mLastAnrDumpClearer, LAST_ANR_LIFETIME_DURATION_MSECS);
anrMessage = "executing service " + timeout.shortName;
} else {
Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = proc;
mAm.mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, proc.execServicesFg
? (nextTime+SERVICE_TIMEOUT) :
(nextTime + SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT));
}
}
if (anrMessage != null) {
//弹出对话框,就是远近闻名的ANR对话框,anrMessage 就是前⾯的“executing service”
mAm.mAppErrors.appNotResponding(proc, null, null, false, anrMessage);
}
}