Java设计模式二十二:享元模式(Flyweight)
它使用共享物件,用来尽可能减少内存使用量以及分享资讯给尽可能多的相似物件;它适合用于当大量物件只是重复因而导致无法令人接受的使用大量内存。通常物件中的部分状态是可以分享。常见做法是把他们放在外部数据结构,当需要使用时再将它们传递给享元。
原理:
享元对象能做到共享的关键是区分内蕴状态(Internal State)和外蕴状态(External State).
一个内蕴状态是存储在享元对象内部的,并且不会随环境改变而有所不同.因此,一个享元可以具有内蕴状态并可以共享.
一个外蕴状态是随环境改变而改变的,不可以共享状态.享元对象的外蕴状态必须由客户端保存,并在享元对象被创建之后,在需要使用的时候再传到享元对象内部.
外蕴状态不可以影响享元对象的内蕴状态,他们是相互独立的.所有的内蕴状态在对象创建完后就不可再改变.
1) 单纯享元模式
类图:
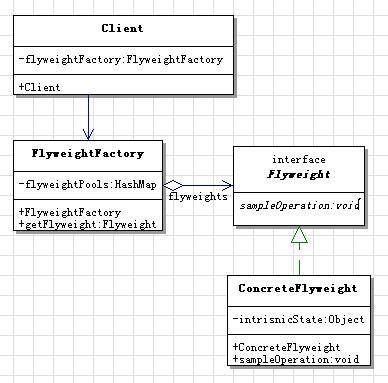
实例:编辑器例程, 编辑器内文字是享元对象中的内蕴状态,文字在文本中的位置和风格是外蕴状态.
public final class Style
{
private String font;
private int locationX;
private int locationY;
public Style(final String font, final int locationX, final int locationY)
{
this.font = font;
this.locationX = locationX;
this.locationY = locationY;
}
public String getFont()
{
return font;
}
public void setFont(final String font)
{
this.font = font;
}
public int getLocationX()
{
return locationX;
}
public void setLocationX(final int locationX)
{
this.locationX = locationX;
}
public int getLocationY()
{
return locationY;
}
public void setLocationY(final int locationY)
{
this.locationY = locationY;
}
}
public interface Flyweight
{
public void sampleOperation(final Style style);
}
public class ConcreteFlyweight implements Flyweight
{
private final String text;
//internal state
public ConcreteFlyweight(final String text)
{
this.text = text;
}
//external state
@Override
public void sampleOperation(final Style style)
{
System.out.println(this.text + ". font is " + style.getFont() + " location x is " + style.getLocationX() + " location y is "
+ style.getLocationY());
}
}
public class FlyweightFactory
{
private final Map<String, Flyweight> textStyle = new HashMap<String, Flyweight>();
public Flyweight factory(final String text)
{
if (textStyle.containsKey(text))
{
return textStyle.get(text);
}
else
{
final Flyweight fly = new ConcreteFlyweight(text);
textStyle.put(text, fly);
return fly;
}
}
}
public class Client
{
public static void main(final String[] args)
{
final FlyweightFactory factory = new FlyweightFactory();
//set internal state
final String text = "this is intrnal state";
final Flyweight fly = factory.factory(text);
//set external state
final Style style = new Style("Sim", 10, 20);
fly.sampleOperation(style);
}
}
结果:
this is intrnal state. font is Sim location x is 10 location y is 20
2) 复合享元模式
类图:
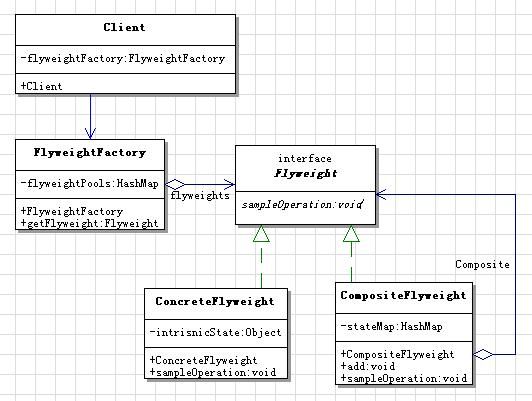
实例:编辑器例程, 编辑器内文字是享元对象中的内蕴状态,文字在文本中的位置和风格是外蕴状态.
Style类,Flyweight接口和ConcreteFlyweight和上面的例子相同
加入下面的类:
public class CompositeFlyweight implements Flyweight
{
private final Map<String, Flyweight> texts = new HashMap<String, Flyweight>();
public void add(final String text, final Flyweight fly)
{
texts.put(text, fly);
}
@Override
public void sampleOperation(final Style style)
{
for (final Iterator it = texts.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();)
{
final Map.Entry textEntry = (Map.Entry) it.next();
final Flyweight fly = (Flyweight) textEntry.getValue();
fly.sampleOperation(style);
}
}
}
public class FlyweightFactory
{
private final Map<String, Flyweight> textStyle = new HashMap<String, Flyweight>();
public Flyweight factory(final String text)
{
if (textStyle.containsKey(text))
{
return textStyle.get(text);
}
else
{
final Flyweight fly = new ConcreteFlyweight(text);
textStyle.put(text, fly);
return fly;
}
}
public CompositeFlyweight factory(final List<String> texts)
{
final CompositeFlyweight compositeFly = new CompositeFlyweight();
for (final String text : texts)
{
compositeFly.add(text, this.factory(text));
}
return compositeFly;
}
}
public class Client
{
public static void main(final String[] args)
{
final FlyweightFactory factory = new FlyweightFactory();
//set internal state
final String text = "this is internal state";
final Flyweight fly = factory.factory(text);
//set external state
final Style style = new Style("Sim", 10, 20);
fly.sampleOperation(style);
//composite
//set internal state
final List<String> texts = new ArrayList<String>();
final String text1 = "this is internal state1";
texts.add(text1);
final String text2 = "this is internal state2";
texts.add(text2);
final String text3 = "this is internal state3";
texts.add(text3);
final Flyweight flyComposite = factory.factory(texts);
//set external state
final Style styleComposite = new Style("Sim", 10, 20);
flyComposite.sampleOperation(styleComposite);
}
}
结果:
this is internal state. font is Sim location x is 10 location y is 20
this is internal state1. font is Sim location x is 10 location y is 20
this is internal state2. font is Sim location x is 10 location y is 20
this is internal state3. font is Sim location x is 10 location y is 20