本文是对前几天的打脸
打脸之处就在于发现了muscle的R包,从此不用再为序列比对东奔西跑——
Step 1. 从基因名拿到序列
sub1 <- c("HDAC1","HDAC2","HDAC3","HDAC8")
sub2 <- c("HDAC4","HDAC5","HDAC6","HDAC7","HDAC9","HDAC10")
sub3 <- paste0("SIRT",1:7)
sub4 <- "HDAC11"
allsymb <- c(sub1,sub2,sub3,sub4)
这一步用到的包:biomaRt ,选择用symbol获取蛋白质序列。
library(biomaRt)
mart <- useMart("ensembl","hsapiens_gene_ensembl")
all_ppseqs <- getSequence(id = allsymb,
type="hgnc_symbol",
seqType="peptide",
mart = mart)
检查一下,发现少了SIRT6.
table(all_ppseqs$hgnc_symbol)
#
# HDAC1 HDAC10 HDAC11 HDAC2 HDAC3 HDAC4 HDAC5 HDAC6 HDAC7 HDAC8 HDAC9 SIRT1 SIRT2
# 3 6 16 12 4 8 8 18 23 45 18 4 14
# SIRT3 SIRT4 SIRT5 SIRT7
# 12 3 7 4
会出现部分基因名匹配不到序列的情况,一般用 ENTREZ ID 可以避免这种情况。于是现在需要补上SIRT6的序列。
library(org.Hs.eg.db)
sirt6entrez <- AnnotationDbi::select(org.Hs.eg.db,"SIRT6","ENTREZID","SYMBOL")
sirt6entrez
# SYMBOL ENTREZID
# 1 SIRT6 51548
sirt6_ppseqs <- getSequence(id = "51548",
type="entrezgene_id",
seqType="peptide",
mart = mart)
再和其他序列合并成一个数据框,去除unavailable序列。
colnames(sirt6_ppseqs)[2] <- "hgnc_symbol"
sirt6_ppseqs[,2] <- "SIRT6"
allppseqs <- rbind(all_ppseqs,sirt6_ppseqs)
allppseqs <- allppseqs[allppseqs$peptide!="Sequence unavailable",]
allppseqs <- allppseqs[order(allppseqs$hgnc_symbol),]
给重复的基因名重命名:
index <- duplicated(allppseqs$hgnc_symbol)
i <- 1
for(j in 1:nrow(allppseqs)){
if(index[j]==FALSE){
i = 1
allppseqs[j,2] <- paste0(allppseqs[j,2], ".",i)
}
else {
i = i+1
allppseqs[j,2] <- paste0(allppseqs[j,2], ".",i)
}
}
输出为FASTA文件:
exportFASTA(allppseqs,"allppseqs.fasta")
Step 2. 多序列比对及绘制进化树
用到的包:Biostrings muscle ape
library(Biostrings)
library(muscle)
library(ape)
MUSCLE 算法的特点之一就是快,采用了k-mer的全局/成对比对方法,最后得出计分矩阵。
MUSCLE 在EBI的网页版工具传送门 https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/muscle/
MUSCLE 软件版传送门 http://www.drive5.com/muscle/downloads.htm
The MUSCLE algorithm is a progressive alignment method that works with DNA, RNA, and amino acidsequences producing high-accuracy alignments with very fast computational times (Edgar, 2004,a). The algorithm is iterative, with later iterations refining the earlier alignments. In each iteration, pairwise alignment scores are computed for all sequence pairs (based on k-mer counting or global pairwise alignments) and the values are entered into a triangular distance matrix.
读入FASTA文件:
myseq <- readAAStringSet("allppseqs.fasta", format="fasta",
nrec=-1L, skip=0L, seek.first.rec=FALSE, use.names=TRUE)
muscle多序列比对:
aln <- muscle::muscle(myseq)
这一步一般比较费时。
当然 muscle() 有很多参数可以设置,提速或设定空位罚分等等:
-
diags = TRUE速度提高自然意味着准确度下降Enhanced speed. To enhance the speed of the algorithm, the diags = TRUE flag will optimize the speed with a potential loss of accuracy.
-
gapopen = -30空位罚分Gap penalties. Default gap penalties can be modified to produce altered alignments. The gap penalty must be negative, with larger negative values indicating more stringent penalties.
-
maxhours = 24.0比对运行的最大时限Maximum number of hours. If an alignment is expected to take a long time, a maximum total numberof hours can be specified, which, if reached, will lead to the algorithm stopping at this point and returningthe current alignment.
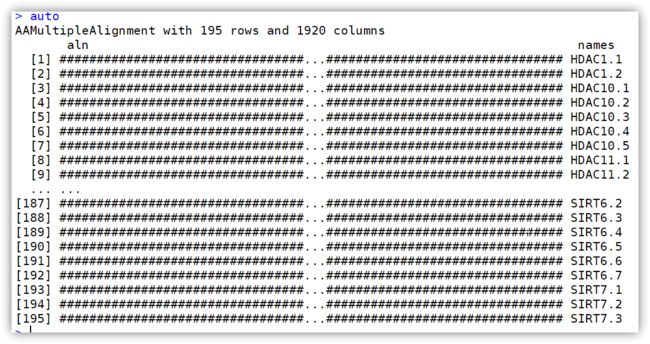
aln
detail(aln)
修剪序列:
auto <- maskGaps(aln, min.fraction=0.5, min.block.width=4)
auto
除此之外还可以用 rowmask() colmask() 手动设置masking区域。
画树!
sdist <- stringDist(as(aotu,"AAStringSet"), method="hamming")
clust <- hclust(sdist, method = "single")
plot(as.phylo(clust),type="fan",cex = 0.8)
References
- A guide to using muscle https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/vignettes/muscle/inst/doc/muscle-vignette.pdf
- plot单独画出pheatmap返回的聚类结果(聚类树)http://www.omicsclass.com/article/510
最后,向大家隆重推荐生信技能树的一系列干货!
- 生信技能树全球公益巡讲:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/E9ykuIbc-2Ja9HOY0bn_6g
- B站公益74小时生信工程师教学视频合辑:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/IyFK7l_WBAiUgqQi8O7Hxw
- 招学徒:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/KgbilzXnFjbKKunuw7NVfw