Tendermint 共识分析
概述
Tendermint的共识算法可以看成是POS+BFT,Tendermint在进行BFT共识算法确认区块前 ,首先使用POS算法从Validators中选举出Proposer。然后由Proposer进行提案,最后使用BFT算法生成区块。Tendermint 的共识协议使用的gossip协议。
其中使节点成为Validator有两种方法,具体可参考:https://docs.tendermint.com/master/nodes/validators.html
round-robin
从Validators中选举出proposer需要使用round-robin协议,这篇文章很好的解释了round-robin协议:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/84962067
round-based
在同一高度确认一个区块需要使用round-based协议,包括以下五个步骤:NewHeight, Propose, Prevote, Precommit 和 Commit
其中Propose、Prevote、Precommit又被称为round,在同一高度确认一个区块可能需要多个round。以下情况就会需要多个round:
- 指定的proposer节点不在线
- 由proposer提交的区块时无效的
- 被提案的区块没有及时的广播
- proposal block有效,但是没有足够多的节点在Precommit 阶段及时收到对应的 +2/3 的prevotes
- proposal block有效,也有足够多的节点接收到了+2/3 的prevotes,但是没有足够多的节点收到+2/3 的 precommits
round-based过程如下:
+-------------------------------------+
v |(Wait til `CommmitTime+timeoutCommit`)
+-----------+ +-----+-----+
+----------> | Propose +--------------+ | NewHeight |
| +-----------+ | +-----------+
| | ^
|(Else, after timeoutPrecommit) v |
+-----+-----+ +-----------+ |
| Precommit | <------------------------+ Prevote | |
+-----+-----+ +-----------+ |
|(When +2/3 Precommits for block found) |
v |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Commit |
| |
| * Set CommitTime = now; |
| * Wait for block, then stage/save/commit block; |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------+
Tendermint的共识算法大体流程就是这些,具体的细节将在分析源码的时候进行探讨。
这个文章对共识进行详细描述,并且也解释了重要的锁机制:https://www.odaily.com/post/5134145
源码分析
Tendermint的共识功能主要在tendermint/consensus/state.go文件里进行实现
NewState
func NewState(
config *cfg.ConsensusConfig,
state sm.State,
blockExec *sm.BlockExecutor,
blockStore sm.BlockStore,
txNotifier txNotifier,
evpool evidencePool,
options ...StateOption,
) *State {
cs := &State{
config: config,
blockExec: blockExec,
blockStore: blockStore,
txNotifier: txNotifier,
peerMsgQueue: make(chan msgInfo, msgQueueSize),
internalMsgQueue: make(chan msgInfo, msgQueueSize),
timeoutTicker: NewTimeoutTicker(),
statsMsgQueue: make(chan msgInfo, msgQueueSize),
done: make(chan struct{
}),
doWALCatchup: true,
wal: nilWAL{
},
evpool: evpool,
evsw: tmevents.NewEventSwitch(),
metrics: NopMetrics(),
}
// 设置一些默认函数,在reactor没有启动前可以被重写
cs.decideProposal = cs.defaultDecideProposal
cs.doPrevote = cs.defaultDoPrevote
cs.setProposal = cs.defaultSetProposal
// We have no votes, so reconstruct LastCommit from SeenCommit.
if state.LastBlockHeight > 0 {
cs.reconstructLastCommit(state)
}
cs.updateToState(state)
// NOTE: we do not call scheduleRound0 yet, we do that upon Start()
cs.BaseService = *service.NewBaseService(nil, "State", cs)
for _, option := range options {
option(cs)
}
return cs
}
OnStart
Onstart通过WAL加载最新的state,并开启超时和接收消息协程
func (cs *State) OnStart() error {
...
...
...
// Double Signing Risk Reduction
if err := cs.checkDoubleSigningRisk(cs.Height); err != nil {
return err
}
// 开启接收信息的协程
go cs.receiveRoutine(0)
// schedule the first round!
// use GetRoundState so we don't race the receiveRoutine for access
cs.scheduleRound0(cs.GetRoundState())
return nil
}
receiveRoutine
这个函数就比较重要了,它处理了可能导致状态转换的消息。其中超时消息、完成一个提案和超过2/3的投票都会导致状态转换。
func (cs *State) receiveRoutine(maxSteps int) {
onExit := func(cs *State) {
// NOTE: the internalMsgQueue may have signed messages from our
// priv_val that haven't hit the WAL, but its ok because
// priv_val tracks LastSig
// close wal now that we're done writing to it
if err := cs.wal.Stop(); err != nil {
cs.Logger.Error("failed trying to stop WAL", "error", err)
}
cs.wal.Wait()
close(cs.done)
}
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
cs.Logger.Error("CONSENSUS FAILURE!!!", "err", r, "stack", string(debug.Stack()))
// stop gracefully
//
// NOTE: We most probably shouldn't be running any further when there is
// some unexpected panic. Some unknown error happened, and so we don't
// know if that will result in the validator signing an invalid thing. It
// might be worthwhile to explore a mechanism for manual resuming via
// some console or secure RPC system, but for now, halting the chain upon
// unexpected consensus bugs sounds like the better option.
onExit(cs)
}
}()
for {
if maxSteps > 0 {
if cs.nSteps >= maxSteps {
cs.Logger.Debug("reached max steps; exiting receive routine")
cs.nSteps = 0
return
}
}
rs := cs.RoundState
var mi msgInfo
select {
// 把有效交易添加到交易池的时候会设置TxAvailable
case <-cs.txNotifier.TxsAvailable():
cs.handleTxsAvailable()
// peer消息通道
case mi = <-cs.peerMsgQueue:
if err := cs.wal.Write(mi); err != nil {
cs.Logger.Error("failed writing to WAL", "err", err)
}
// 处理 proposal、block parts、votes的消息
cs.handleMsg(mi)
// 处理内部消息
case mi = <-cs.internalMsgQueue:
err := cs.wal.WriteSync(mi) // NOTE: fsync
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf(
"failed to write %v msg to consensus WAL due to %v; check your file system and restart the node",
mi, err,
))
}
if _, ok := mi.Msg.(*VoteMessage); ok {
// we actually want to simulate failing during
// the previous WriteSync, but this isn't easy to do.
// Equivalent would be to fail here and manually remove
// some bytes from the end of the wal.
fail.Fail() // XXX
}
// handles proposals, block parts, votes
cs.handleMsg(mi)
// 处理超时消息
case ti := <-cs.timeoutTicker.Chan(): // tockChan:
if err := cs.wal.Write(ti); err != nil {
cs.Logger.Error("failed writing to WAL", "err", err)
}
// if the timeout is relevant to the rs
// go to the next step
cs.handleTimeout(ti, rs)
case <-cs.Quit():
onExit(cs)
return
}
}
}
上面的函数运行完毕后,就可以等待进入状态跃迁的函数,进行共识了。
官方的共识流程图表示如下:
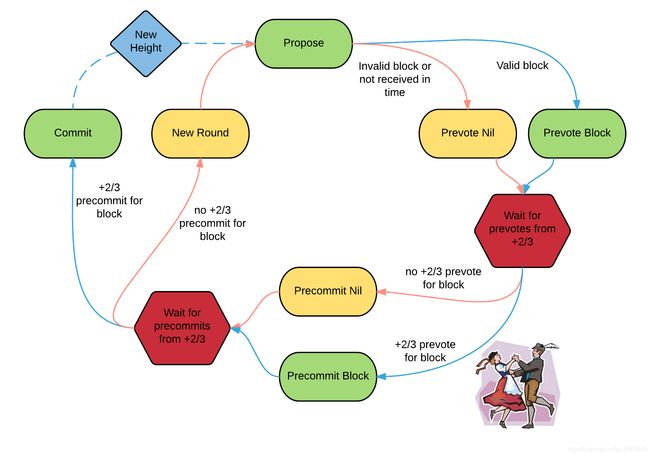 单节点共识完整流程的代码流程为:
单节点共识完整流程的代码流程为:
- 首先进入enterNewRound
- 之后从enterNewRound进入enterPropose
- 进入enterPropose后,判断自己是不是validator.只有一个节点自己就是,进入defaultDecideProposal
- 进入defaultDecideProposal,把proposal和blockPartMsg发送到internalMsgQueue
- 收到internalMsgQueue的消息,然后进入handleMsg,通过handleMsg进入addProposalBlockPart
- 通过addProposalBlockPart 最后进入到enterPrevote
- 通过enterPrevote进入到defaultDoPrevote,对proposal进行签名,并发送到internalMsgQueue
- handleMsg对收到的消息进行处理,进入到tryAddVote
- tryAddVote判断vote正确,并且满足超过三分之二的情况,进入enterPrevoteWait
- 计时器超时,从enterPrevoteWait进入到enterPrecommit
- 通过enterPrevote对proposal进行再次签名,并发送到internalMsgQueue
- handleMsg对收到的消息进行处理,进入到tryAddVote
- tryAddVote判断vote正确,进入enterCommit,这里涉及情况比较多(在多个节点的条件下).
- enterCommit落地区块,将区块发送给abci,收到返回后,此次共识结束.
由于代码较多,会把相对不太重要的代码给省略掉。这里主要列举对共识流程重要的代码。
enterNewRound
func (cs *State) enterNewRound(height int64, round int32) {
logger := cs.Logger.With("height", height, "round", round)
// 进行状态校验
if cs.Height != height || round < cs.Round || (cs.Round == round && cs.Step != cstypes.RoundStepNewHeight) {
logger.Debug(
"entering new round with invalid args",
"current", fmt.Sprintf("%v/%v/%v", cs.Height, cs.Round, cs.Step),
)
return
}
// 开启定时器
if now := tmtime.Now(); cs.StartTime.After(now) {
logger.Debug("need to set a buffer and log message here for sanity", "start_time", cs.StartTime, "now", now)
}
logger.Debug("entering new round", "current", fmt.Sprintf("%v/%v/%v", cs.Height, cs.Round, cs.Step))
// 如果有新的Validator就添加
validators := cs.Validators
if cs.Round < round {
validators = validators.Copy()
validators.IncrementProposerPriority(tmmath.SafeSubInt32(round, cs.Round))
}
// 开始一轮新的round
cs.updateRoundStep(round, cstypes.RoundStepNewRound)
cs.Validators = validators
if round == 0 {
// We've already reset these upon new height,
// and meanwhile we might have received a proposal
// for round 0.
} else {
logger.Debug("resetting proposal info")
cs.Proposal = nil
cs.ProposalBlock = nil
cs.ProposalBlockParts = nil
}
cs.Votes.SetRound(tmmath.SafeAddInt32(round, 1)) // also track next round (round+1) to allow round-skipping
cs.TriggeredTimeoutPrecommit = false
if err := cs.eventBus.PublishEventNewRound(cs.NewRoundEvent()); err != nil {
cs.Logger.Error("failed publishing new round", "err", err)
}
cs.metrics.Rounds.Set(float64(round))
// 在我们进入round 0 之前要等待交易在mempool中设置为available,
// 如果最后一个区块改变了app hash我们需要一个空的proof区块,并且立即进入enterProposer函数
waitForTxs := cs.config.WaitForTxs() && round == 0 && !cs.needProofBlock(height)
if waitForTxs {
if cs.config.CreateEmptyBlocksInterval > 0 {
cs.scheduleTimeout(cs.config.CreateEmptyBlocksInterval, height, round,
cstypes.RoundStepNewRound)
}
} else {
// 进入enterPropose
cs.enterPropose(height, round)
}
}
enterPropose
func (cs *State) enterPropose(height int64, round int32) {
...
...
// 节点验证
if cs.privValidatorPubKey == nil {
// If this node is a validator & proposer in the current round, it will
// miss the opportunity to create a block.
logger.Error("propose step; empty priv validator public key", "err", errPubKeyIsNotSet)
return
}
address := cs.privValidatorPubKey.Address()
// if not a validator, we're done
if !cs.Validators.HasAddress(address) {
logger.Debug("node is not a validator", "addr", address, "vals", cs.Validators)
return
}
// 判断当前节点是否为proposer,如果是的话就开始准备提案
if cs.isProposer(address) {
logger.Debug(
"propose step; our turn to propose",
"proposer", address,
)
cs.decideProposal(height, round)
} else {
logger.Debug(
"propose step; not our turn to propose",
"proposer", cs.Validators.GetProposer().Address,
)
}
}
decideProposal
func (cs *State) defaultDecideProposal(height int64, round int32) {
...
...
// 创建proposal
propBlockID := types.BlockID{
Hash: block.Hash(), PartSetHeader: blockParts.Header()}
proposal := types.NewProposal(height, round, cs.ValidRound, propBlockID)
p := proposal.ToProto()
// 等待最大数量的proposal
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.TODO(), cs.config.TimeoutPropose)
defer cancel()
// 对proposal进行签名
if err := cs.privValidator.SignProposal(ctx, cs.state.ChainID, p); err == nil {
proposal.Signature = p.Signature
// 把数据发送到 sendInternalMessage channel中
// 这个channel在receiveRoutine函数启动、等待消息的传入
cs.sendInternalMessage(msgInfo{
&ProposalMessage{
proposal}, ""})
for i := 0; i < int(blockParts.Total()); i++ {
part := blockParts.GetPart(i)
cs.sendInternalMessage(msgInfo{
&BlockPartMessage{
cs.Height, cs.Round, part}, ""})
}
cs.Logger.Debug("signed proposal", "height", height, "round", round, "proposal", proposal)
} else if !cs.replayMode {
cs.Logger.Error("propose step; failed signing proposal", "height", height, "round", round, "err", err)
}
}
addProposalBlockPart
func (cs *State) addProposalBlockPart(msg *BlockPartMessage, peerID p2p.NodeID) (added bool, err error) {
...
...
if cs.Step <= cstypes.RoundStepPropose && cs.isProposalComplete() {
// Move onto the next step
cs.enterPrevote(height, cs.Round)
if hasTwoThirds {
// this is optimisation as this will be triggered when prevote is added
cs.enterPrecommit(height, cs.Round)
}
} else if cs.Step == cstypes.RoundStepCommit {
// If we're waiting on the proposal block...
cs.tryFinalizeCommit(height)
}
return added, nil
}
return added, nil
}
signAddVote
addProposalBlockPart 会进入到enterPrevote,再然后进入到doPrevote,doPrevote的默认函数为doPrevoteproposal,doPrevoteproposal通过调用signAddVote对进行Proposal签名,并发送到internalMsgQueue。
func (cs *State) signAddVote(msgType tmproto.SignedMsgType, hash []byte, header types.PartSetHeader) *types.Vote {
...
...
// TODO: pass pubKey to signVote
vote, err := cs.signVote(msgType, hash, header)
if err == nil {
cs.sendInternalMessage(msgInfo{
&VoteMessage{
vote}, ""})
cs.Logger.Debug("signed and pushed vote", "height", cs.Height, "round", cs.Round, "vote", vote)
return vote
}
...
...
}
addVote
从internalMsgQueue进入到tryAddVote后,会调用addVote进行投票。其投票的条件为vote字段正确、满足2/3的情况。
...
...
switch vote.Type {
case tmproto.PrevoteType:
prevotes := cs.Votes.Prevotes(vote.Round)
cs.Logger.Debug("added vote to prevote", "vote", vote, "prevotes", prevotes.StringShort())
// If +2/3 prevotes for a block or nil for *any* round:
if blockID, ok := prevotes.TwoThirdsMajority(); ok {
// There was a polka!
// If we're locked but this is a recent polka, unlock.
// If it matches our ProposalBlock, update the ValidBlock
// Unlock if `cs.LockedRound < vote.Round <= cs.Round`
// NOTE: If vote.Round > cs.Round, we'll deal with it when we get to vote.Round
if (cs.LockedBlock != nil) &&
(cs.LockedRound < vote.Round) &&
(vote.Round <= cs.Round) &&
!cs.LockedBlock.HashesTo(blockID.Hash) {
cs.Logger.Debug("unlocking because of POL", "locked_round", cs.LockedRound, "pol_round", vote.Round)
cs.LockedRound = -1
cs.LockedBlock = nil
cs.LockedBlockParts = nil
if err := cs.eventBus.PublishEventUnlock(cs.RoundStateEvent()); err != nil {
return added, err
}
}
// Update Valid* if we can.
// NOTE: our proposal block may be nil or not what received a polka..
if len(blockID.Hash) != 0 && (cs.ValidRound < vote.Round) && (vote.Round == cs.Round) {
if cs.ProposalBlock.HashesTo(blockID.Hash) {
cs.Logger.Debug("updating valid block because of POL", "valid_round", cs.ValidRound, "pol_round", vote.Round)
cs.ValidRound = vote.Round
cs.ValidBlock = cs.ProposalBlock
cs.ValidBlockParts = cs.ProposalBlockParts
} else {
cs.Logger.Debug(
"valid block we do not know about; set ProposalBlock=nil",
"proposal", cs.ProposalBlock.Hash(),
"block_id", blockID.Hash,
)
// we're getting the wrong block
cs.ProposalBlock = nil
}
if !cs.ProposalBlockParts.HasHeader(blockID.PartSetHeader) {
cs.ProposalBlockParts = types.NewPartSetFromHeader(blockID.PartSetHeader)
}
cs.evsw.FireEvent(types.EventValidBlock, &cs.RoundState)
if err := cs.eventBus.PublishEventValidBlock(cs.RoundStateEvent()); err != nil {
return added, err
}
}
}
// If +2/3 prevotes for *anything* for future round:
switch {
case cs.Round < vote.Round && prevotes.HasTwoThirdsAny():
//如果有别的投票数大于这个投票数,就跳过这一轮
cs.enterNewRound(height, vote.Round)
// 当前round
case cs.Round == vote.Round && cstypes.RoundStepPrevote <= cs.Step: // current round
// 判断是否有大于2/3的投票
blockID, ok := prevotes.TwoThirdsMajority()
// 提案完成并且有大于2/3的prevotes
if ok && (cs.isProposalComplete() || len(blockID.Hash) == 0) {
cs.enterPrecommit(height, vote.Round)
} else if prevotes.HasTwoThirdsAny() {
cs.enterPrevoteWait(height, vote.Round)
}
case cs.Proposal != nil && 0 <= cs.Proposal.POLRound && cs.Proposal.POLRound == vote.Round:
// If the proposal is now complete, enter prevote of cs.Round.
if cs.isProposalComplete() {
cs.enterPrevote(height, cs.Round)
}
}
...
...
enterPrevoteWait
func (cs *State) enterPrevoteWait(height int64, round int32) {
logger := cs.Logger.With("height", height, "round", round)
if cs.Height != height || round < cs.Round || (cs.Round == round && cstypes.RoundStepPrevoteWait <= cs.Step) {
logger.Debug(
"entering prevote wait step with invalid args",
"current", fmt.Sprintf("%v/%v/%v", cs.Height, cs.Round, cs.Step),
)
return
}
// 开始投票
if !cs.Votes.Prevotes(round).HasTwoThirdsAny() {
panic(fmt.Sprintf(
"entering prevote wait step (%v/%v), but prevotes does not have any +2/3 votes",
height, round,
))
}
logger.Debug("entering prevote wait step", "current", fmt.Sprintf("%v/%v/%v", cs.Height, cs.Round, cs.Step))
defer func() {
// Done enterPrevoteWait:
cs.updateRoundStep(round, cstypes.RoundStepPrevoteWait)
cs.newStep()
}()
// 等待最多的prevote,然后进入到enterPrecommit;
cs.scheduleTimeout(cs.config.Prevote(round), height, round, cstypes.RoundStepPrevoteWait)
}
finalizeCommit
进入到enterprecommit后,经过一系列判断最后会进入到finalizeCommit,具体可以参考源代码,这里就不再重复了。进入到finalizeCommit后,会把区块发送给ABCI APP并收到ABCI的返回值,然后结束共识。
func (cs *State) finalizeCommit(height int64) {
...
...
// 保存区块
if cs.blockStore.Height() < block.Height {
// NOTE: the seenCommit is local justification to commit this block,
// but may differ from the LastCommit included in the next block
precommits := cs.Votes.Precommits(cs.CommitRound)
seenCommit := precommits.MakeCommit()
cs.blockStore.SaveBlock(block, blockParts, seenCommit)
} else {
// Happens during replay if we already saved the block but didn't commit
logger.Debug("calling finalizeCommit on already stored block", "height", block.Height)
}
fail.Fail() // XXX
// Write EndHeightMessage{} for this height, implying that the blockstore
// has saved the block.
//
// If we crash before writing this EndHeightMessage{}, we will recover by
// running ApplyBlock during the ABCI handshake when we restart. If we
// didn't save the block to the blockstore before writing
// EndHeightMessage{}, we'd have to change WAL replay -- currently it
// complains about replaying for heights where an #ENDHEIGHT entry already
// exists.
//
// Either way, the State should not be resumed until we
// successfully call ApplyBlock (ie. later here, or in Handshake after
// restart).
endMsg := EndHeightMessage{
height}
if err := cs.wal.WriteSync(endMsg); err != nil {
// NOTE: fsync
panic(fmt.Sprintf(
"failed to write %v msg to consensus WAL due to %v; check your file system and restart the node",
endMsg, err,
))
}
fail.Fail() // XXX
// Create a copy of the state for staging and an event cache for txs.
stateCopy := cs.state.Copy()
// Execute and commit the block, update and save the state, and update the mempool.
// NOTE The block.AppHash wont reflect these txs until the next block.
var (
err error
retainHeight int64
)
// 与ABCI APP交互, 返回区块的状态副本,当前高度
stateCopy, retainHeight, err = cs.blockExec.ApplyBlock(
stateCopy,
types.BlockID{
Hash: block.Hash(),
PartSetHeader: blockParts.Header(),
},
block,
)
if err != nil {
logger.Error("failed to apply block", "err", err)
return
}
fail.Fail() // XXX
// Prune old heights, if requested by ABCI app.
if retainHeight > 0 {
pruned, err := cs.pruneBlocks(retainHeight)
if err != nil {
logger.Error("failed to prune blocks", "retain_height", retainHeight, "err", err)
} else {
logger.Debug("pruned blocks", "pruned", pruned, "retain_height", retainHeight)
}
}
// must be called before we update state
cs.recordMetrics(height, block)
// 更新state
cs.updateToState(stateCopy)
fail.Fail() // XXX
...
...
补充
Tendermint 为什么不会分叉
如果小于1/3节点是拜占庭节点(如果大于等于1/3,那么共识就没法达成了)。当validator commit了区块B,那么表示有大于2/3的节点在R轮投了precommit,这表示至少有大于1/3节点(大于1/3节点哪儿来的呢,就是大于2/3减去小于1/3,为什么是这么算呢,有人说不是有大于2/3的节点投了precommit那么这些人不都是诚实节点吗,当然不是了,拜占庭节点的意思它工作随性,有时候正确有时候失败,假设这个时候所有的拜占庭节点正确的工作了,所以都算在在+2/3节点内,所以这么算了)被lock在了R‘>R。如果这个时候有针对同一区块高度的投票,那么由于这+1/3节点被lock在了R’轮,所以不会有+2/3的节点投prevote,也就不会在同一高度达成一个新的共识区块,所以就不会分叉。参考的文章地址:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/84962224
Tendermint 的不足之处
Tendermint 是使用一种确定的循环协议方案来选出提议者的;该协议不具备随机性。提议者是根据投票权和验证者被选次数的堆排序算法选出的。攻击者只能通过添加或删除权益来干预协议,但这种干预不能立即生效,因为验证者在系统中移除或者添加权益所需的时间很长。尽管如此,攻击者就可以有更长的时间提前计划好如何操纵提议者的选择。
我们上边还提到,Tendermint 允许 Validator 可以被跳过(就是轮到一个 Validator 出块的时候但是此 Validator 没出块)。Validator 在移到下一轮投票之前等待一小段时间来接收提议者(此轮出块的验证者)提出的整个区块。这种对超时的依赖让 Tendermint 成为一个弱同步协议,而不是一个异步协议。在系统效率上虽然较 PoW 共识机制有很大的提高,但仍有待改善。同时,Tendermint 虽然依靠额外协议管理方法来与寡头垄断验证者进行对抗。但还是无法有效阻止「卡尔特形式」的发生。参考文章的地址:https://www.528btc.com/college/51031.html
最后
至此,Tendermint consensus源码就分析完了。博主也在学习阶段,如果有错误之处,希望路过的大佬能够指点指点。最后推荐一位大佬的公众号,欢迎关注哦:区块链技术栈
另外这个GitHub上还有很多区块链学习资料:https://github.com/mindcarver/blockchain_guide
参考文章:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/130b054b5552
https://www.odaily.com/post/5134145
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/84962224