习题 27: 记住逻辑关系
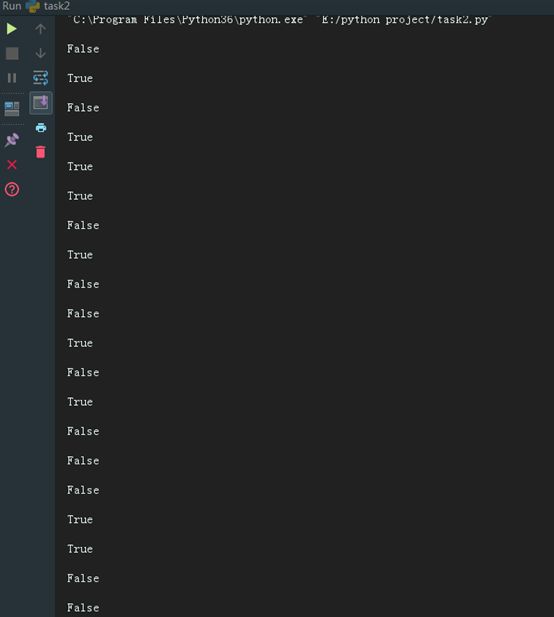
本科时数学课上学过这部分内容,所以逻辑运算符并不陌生,这些真值表也能够在看一遍的基础上理解和记忆,难度系数一颗星。
习题 28: 布尔表达式练习
">" :大于
">=" :大于等于
"<" :小于
"<=" :小于等于
"==" :等于
"!=" :不等于
习题 29: 如果(if)
people = 20
cats = 30
dogs = 15
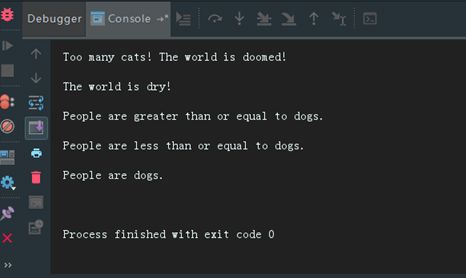
if people < cats:
print('Too many cats! The world is doomed!')
if people > cats:
print("Not many cats! The world is saved!")
if people < dogs:
print("The world is drooled on!")
if people > dogs:
print("The world is dry!")
dogs += 5
if people >= dogs:
print ("People are greater than or equal to dogs.")
if people <= dogs:
print ("People are less than or equal to dogs.")
if people == dogs:
print ("People are dogs.")
(1) 进行逻辑判断
(2) 4个空格,是作为同一段语句的判断
(3) 不缩进就会报错,IndentationError: expected an indented block意思就是缩进错误
(4) 可以实现
(5) 会报错, SyntaxError: invalid syntax意思是变量赋值不完整。
习题 30: Else 和 If
people = 30
cars = 40
buses = 15
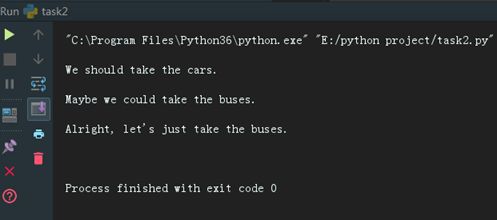
if cars > people:
print ("We should take the cars.")
elif cars < people:
print ("We should not take the cars.")
else:
print ("We can't decide.")
if buses > cars:
print ("That's too many buses.")
elif buses < cars:
print ("Maybe we could take the buses.")
else:
print ("We still can't decide.")
if people > buses:
print ("Alright, let's just take the buses.")
else:
print ("Fine, let's stay home then.")
(1) elif 等于 else if,但elif和else都是if的子块,不能单独存在,If和elif的对应关系是一对多。
(2) 修改变量的大小,都可能对输入结果产生影响,具体要看变量之间的大小关系而定。
习题 32: 循环和列表
the_count = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
fruits = ['apples', 'oranges', 'pears', 'apricots']
change = [1, 'pennies', 2, 'dimes', 3, 'quarters']
this first kind of for-loop goes through a list
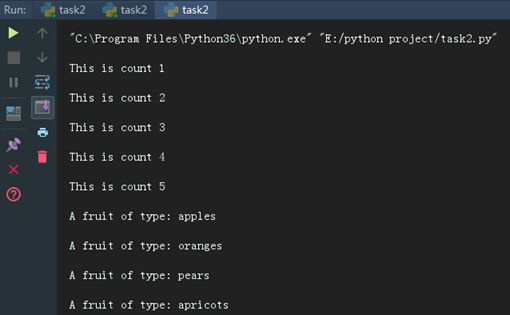
for number in the_count:
print ("This is count %d" % number)
same as above
for fruit in fruits:
print ("A fruit of type: %s" % fruit)
also we can go through mixed lists too
notice we have to use %r since we don't know what's in it
for i in change:
print ("I got %r" % i)
we can also build lists, first start with an empty one
elements = []
then use the range function to do 0 to 5 counts
for i in range(0, 6):
print ("Adding %d to the list." % i)
append is a function that lists understand
elements.append(i)
now we can print them out too
for i in elements:
print ("Element was: %d" % i)
(1) range函数里可以传入三个值,第一个是起始值,第二个是结束值(开区间),第三个值是步长
(2) 如果不使用for循环遍历的话,那么输出elements的结果还是列表形式的。
(3) 列表操作包含以下函数:
1、cmp(list1, list2):比较两个列表的元素
2、len(list):列表元素个数
3、max(list):返回列表元素最大值
4、min(list):返回列表元素最小值
5、list(seq):将元组转换为列表
列表操作包含以下方法:
1、list.append(obj):在列表末尾添加新的对象
2、list.count(obj):统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数
3、list.extend(seq):在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值(用新列表扩展原来的列表)
4、list.index(obj):从列表中找出某个值第一个匹配项的索引位置
5、list.insert(index, obj):将对象插入列表
6、list.pop(obj=list[-1]):移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值
7、list.remove(obj):移除列表中某个值的第一个匹配项
8、list.reverse():反向列表中元素
9、list.sort([func]):对原列表进行排序
习题 33: While 循环
i = 0
numbers = []
while i < 6:
print ("At the top i is %d" % i)
numbers.append(i)
i = i + 1
print ("Numbers now: ", numbers)
print ("At the bottom i is %d" % i)
print ("The numbers: ")
for num in numbers:
print(num)
结果:
At the top i is 0
Numbers now: [0]
At the bottom i is 1
At the top i is 1
Numbers now: [0, 1]
At the bottom i is 2
At the top i is 2
Numbers now: [0, 1, 2]
At the bottom i is 3
At the top i is 3
Numbers now: [0, 1, 2, 3]
At the bottom i is 4
At the top i is 4
Numbers now: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
At the bottom i is 5
At the top i is 5
Numbers now: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
At the bottom i is 6
The numbers:
0
1
2
3
4
5
(1)
def fx(a):
numbers = []
i = 0
while i < a :
print ("At the top i is %d" % i)
numbers.append(i)
i = i + 1
print ("Numbers now: ", numbers)
print ("At the bottom i is %d" % i)
return (numbers)
print ("The numbers: ")
for num in fx(6) :
print (num)
(3)
def fx(a,b):
numbers = []
i = 0
while i < a :
print ("At the top i is %d" % i)
numbers.append(i)
i = i + b
print ("Numbers now: ", numbers)
print ("At the bottom i is %d" % i)
return (numbers)
print ("The numbers: ")
for num in fx(6,1) :
print (num)
习题 34: 访问列表的元素
color = ["red", "yellow", "green", "blue", "pink", "black", "white"]
print ("1.The color at 1 is 2rd and he is", color[1])
print ("2.The 3rd color is at 2 and he is", color[2])
print ("3.The 1st color is at 0 and he is", color[0])
print ("4.The color at 3 is 2rd and he is", color[3])
print ("5.The 5th color is 4 and he is", color[4])
print ("6.The color at 2 is 3rd and he is", color[2])
print ("7.The 6th color is 5 and He is", color[5])
print ("8.The color at 4 is 5th and he is", color[4])
结果:1.The color at 1 is 2rd and he is yellow
2.The 3rd color is at 2 and he is green
3.The 1st color is at 0 and he is red
4.The color at 3 is 2rd and he is blue
5.The 5th color is 4 and he is pink
6.The color at 2 is 3rd and he is green
7.The 6th color is 5 and He is black
8.The color at 4 is 5th and he is pink