SpringBoot使用Redis
SpringBoot使用Redis
【原文链接】
1、SpringBoot链接Redis
使用redisTemplate该类可以存放任意类型的数据,但是该类型的数据必须实现序列,获取redis中对应的数据时,会进行反序列化。 如果使用RedisTemplate建议大家指定key,value,以及hashkey的序列化方式。
锁都是多线程的,所以普通方式是不能测试出来的,此时需要用软件【点这里】,使用压力测试,测试多线程。
1、1 配置application.properties文件
#Redis服务器IP地址
spring.redis.host=192.168.31.33
#Redis服务器端口号
spring.redis.port=6379
#Redis服务器最大活跃数
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=20
#Redis服务器最大空闲数
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=8
#Redis服务器最小空闲数
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=0
#Redis服务器链接最大超时20000
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=20000
# 哨兵模式开启下面的
# spring.redis.sentinel.master=mymaster
# spring.redis.sentinel.nodes=192.168.213.188:26379
# 去中心化集群
# spring.redis.cluster.nodes=192.168.213.188:8001,192.168.213.188:8002,192.168.213.188:8003,192.168.213.188:8004,192.168.213.188:8005,192.168.213.188:8006
1、2创建RedisConfig文件
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.*;
import java.time.Duration;
@EnableCaching
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
//比如验证码
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value hashmap序列化
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 配置序列化(解决乱码的问题),过期时间600秒
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(600)) //缓存过期10分钟 ---- 业务需求。
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))//设置key的序列化方式
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer)) //设置value的序列化
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}
使用单元测试:
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootRedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "张三");
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("k3","v3");
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name"));
redisTemplate.expire("k3", 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(redisTemplate.getExpire("k3"));
//获取所有的key
Set<String> keys = redisTemplate.keys("*");
System.out.println(keys);
}
@Test
void testString() {
ValueOperations<String, String> forValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();//操作字符串类型
forValue.set("k1","v1");
System.out.println(forValue.get("k1"));
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("k9","v9");
map.put("k10","v10");
forValue.multiSet(map);
}
}
2、redis使用场景
2、1作为缓存
-
为什么使用缓存?
减少数据库的访问频率。 提高数据的访问率。 -
什么样的数据适合放入缓存?
1.热点数据。 2. 修改频率比较低。3.安全系数低的。
2、1、1如何使用缓存?
1、搭建springboot+mbaitsplus工程
2、引入相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
</dependency>
3、配置application.properties文件
server.port=8888
spring.datasource.druid.url=jdbc:mysql:///lianxi?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
spring.datasource.druid.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.druid.username=root
spring.datasource.druid.password=root
spring.redis.cluster.nodes=192.168.213.188:8001,192.168.213.188:8002,192.168.213.188:8003,192.168.213.188:8004,192.168.213.188:8005,192.168.213.188:8006
开启缓存注解:
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.dao")
@EnableCaching //开启缓存的注解
public class SpringbootRedis02Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootRedis02Application.class, args);
}
}
忽略基本配置,创建service代码:
@Service
public class DeptService {
@Resource
private DeptDao deptDao;
//该注解作用:会先查询缓存,如果缓存存在,则不会执行代码块。 如果缓存中不存在则执行该方法,并把该方法的返回值存放到redis中
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "findById",key = "#deptid") //缓存的key值 为findById
public Dept findById(Integer deptId){
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
Dept dept = deptDao.selectById(deptId);
return dept;
}
//数据库和缓存同步问题!
// beforeInvocation:是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,
// 如果指定为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存。缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存。
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "findById",key = "#deptId")
public int delete(Integer deptId){
int i = deptDao.deleteById(deptId);
return i;
}
//这个注解是必须执行方法体,而且会把方法体执行的结果放入到缓存中。 如果发生异常则不操作缓存。
@CachePut(cacheNames = "findById",key = "#dept.deptId")
public Dept update(Dept dept){
int i = deptDao.updateById(dept);
return dept;
}
}
2、2 作为分布式锁
2、2、1 redis分布式锁简介
提到分布式锁之前,首先要提到与分布式锁相对应的是线程锁、进程锁。
-
线程锁:主要用来给方法、代码块加锁。当某个方法或代码使用锁,在同一时刻仅有一个线程执行该方法或该代码段。线程锁只在同一JVM中有效果,因为线程锁的实现在根本上是依靠线程之间共享内存实现的,比如synchronized是共享对象头,显示锁Lock是共享某个变量(state)。
-
进程锁:为了控制同一操作系统中多个进程访问某个共享资源,因为进程具有独立性,各个进程无法访问其他进程的资源,因此无法通过synchronized等线程锁实现进程锁。
-
分布式锁:当多个进程不在同一个系统中,用分布式锁控制多个进程对资源的访问。
2、2、2 redis分布式锁的使用场景
线程间并发问题和进程间并发问题都是可以通过分布式锁解决的,但是强烈不建议这样做!因为采用分布式锁解决这些小问题是非常消耗资源的!分布式锁应该用来解决分布式情况下的多进程并发问题才是最合适的。
有这样一个情境,线程A和线程B都共享某个变量Y。
如果是单机情况下(单JVM),线程之间共享内存,只要使用线程锁就可以解决并发问题。
如果是分布式情况下(多JVM),线程A和线程B很可能不是在同一JVM中,这样线程锁就无法起到作用了,这时候就要用到分布式锁来解决。
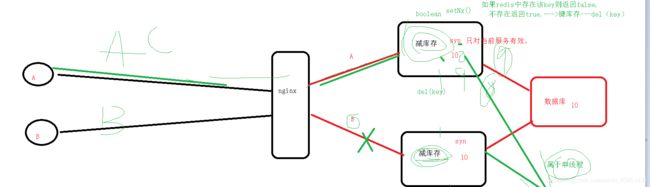
图实在潦草,将就一下看吧,哈哈!
2、2、3 正常状态下:
@Service
public class StockService02 {
@Resource
private StockDao stockDao;
public String decrStock(Integer productId) {
//synchronized () 同步方法 同步代码块
//查询对应的id的库存
synchronized (this) {
Stock stock = stockDao.selectById(productId);
if (stock.getNum() > 0) {
//根据id修改库存
stock.setNum(stock.getNum() - 1);
stockDao.updateById(stock);
System.out.println("库存剩余:" + (stock.getNum()));
return "库存减少成功";
} else {
return "库存不足";
}
}
}
}

经过测试,发现开始有冲突了,此时就需要redis来解决分布式锁的问题。
2、2、3 redis分布式锁:
@Service
public class StockService {
@Resource
private StockDao stockDao;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public String decrStock(Integer productId) {
//synchronized () 同步方法 同步代码块
Boolean flag = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("product::" + productId, "yth",30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//查询对应的id的库存
if(flag) {
//获取锁了
try {
Stock stock = stockDao.selectById(productId);
if (stock.getNum() > 0) {
//根据id修改库存
stock.setNum(stock.getNum() - 1);
stockDao.updateById(stock); //异常发生
// int c=10/0;
System.out.println("库存剩余:" + (stock.getNum()));
return "库存减少成功";
} else {
return "库存不足";
}
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
finally {
redisTemplate.delete("product::" + productId);//释放锁资源 一定再finally
}
}else{
System.out.println("服务器正忙请稍后再试..........");
return "服务器正忙请稍后再试..........";
}
}
}
到这里基本上已经差不多了,但是依然还是有问题,某一个线程超过30秒了,导致释放锁是另外一个线程的,此时使用第三方组件redisson-----专门用于解决分布式问题
2、2、4 redission:
简介:
在一些高并发的场景中,比如秒杀,抢票,抢购这些场景,都存在对核心资源,商品库存的争夺,控制不好,库存数量可能被减少到负数,出现超卖的情况,或者 产生唯一的一个递增ID,由于web应用部署在多个机器上,简单的同步加锁是无法实现的,给数据库加锁的话,对于高并发,1000/s的并发,数据库可能由行锁变成表锁,性能下降会厉害。那相对而言,redis的分布式锁,相对而言,是个很好的选择,redis官方推荐使用的Redisson就提供了分布式锁和相关服务。
- 引入jar包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.13.4</version>
</dependency>
- 主启动类加入bean
@Bean
public RedissonClient getRedisson(){
Config config=new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.213.188:6379");
RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create(config);
return redissonClient;
}
- 创建新的service
@Service
public class StockService {
@Resource
private StockDao stockDao;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redisson;
public String decrStock(Integer productId) {
//synchronized () 同步方法 同步代码块
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("product::" + productId);//获取锁对象
try {
lock.tryLock(60,20,TimeUnit.SECONDS); //自己别设置时间。
Stock stock = stockDao.selectById(productId);
if (stock.getNum() > 0) {
//根据id修改库存
stock.setNum(stock.getNum() - 1);
stockDao.updateById(stock); //异常发生
// int c=10/0;
// Thread.sleep(35000);
System.out.println("库存剩余:" + (stock.getNum()));
return "库存减少成功";
} else {
return "库存不足";
}
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
这里不能指定lock.lock,如果业务超过指定时间,redis会自动解锁,当前业务执行完后又要解锁,可能会解锁到另一个线程加的锁,所以自己指定的解锁时间一定大于业务执行的时间。
这里提一下看门狗吧!
-
如果我们指定了锁的超时时间,就发送给redis执行脚本,进行占锁,默认超时就是我们制定的时间,不会自动续期;
-
如果我们未指定锁的超时时间,就使用 lockWatchdogTimeout = 30 * 1000 【看门狗默认时间】
-
只要占锁成功,就会启动一个定时任务【重新给锁设置过期时间,新的过期时间就是看门狗的默认时间】,每隔10秒都会自动再续成30秒;
-
自动续期时间:internalLockLeaseTime 【看门狗时间 30s】 / 3, 10s
2、3 作为点赞量videaId,0 incr(videaId),排行榜,转发量
此处只作为简介:
- 什么是计数器,如电商网站商品的浏览量、视频网站视频的播放数等。为了保证数据实时效,每次浏览都得给+1,并发量高时如果每次都请求数据库操作无疑是种挑战和压力。Redis提供的incr命令来实现计数器功能,内存操作,性能非常好,非常适用于这些计数场景 。
- 关系型数据库在排行榜方面查询速度普遍偏慢,所以可以借助redis的SortedSet进行热点数据的排序。 在奶茶活动中,我们需要展示各个部门的点赞排行榜, 所以我针对每个部门做了一个SortedSet,然后以用户的openid作为上面的username,以用户的点赞数作为上面的score, 然后针对每个用户做一个hash, 通过zrangebyscore就可以按照点赞数获取排行榜,然后再根据username获取用户的hash信息,这个当时在实际运用中性能体验也蛮不错的。
2、4 限时业务的运用
此处只作为简介:
- redis中可以使用expire命令设置一个键的生存时间,到时间后redis会删除它。利用这一特性可以运用在限时的优惠活动信息、手机验证码等业务场景。

